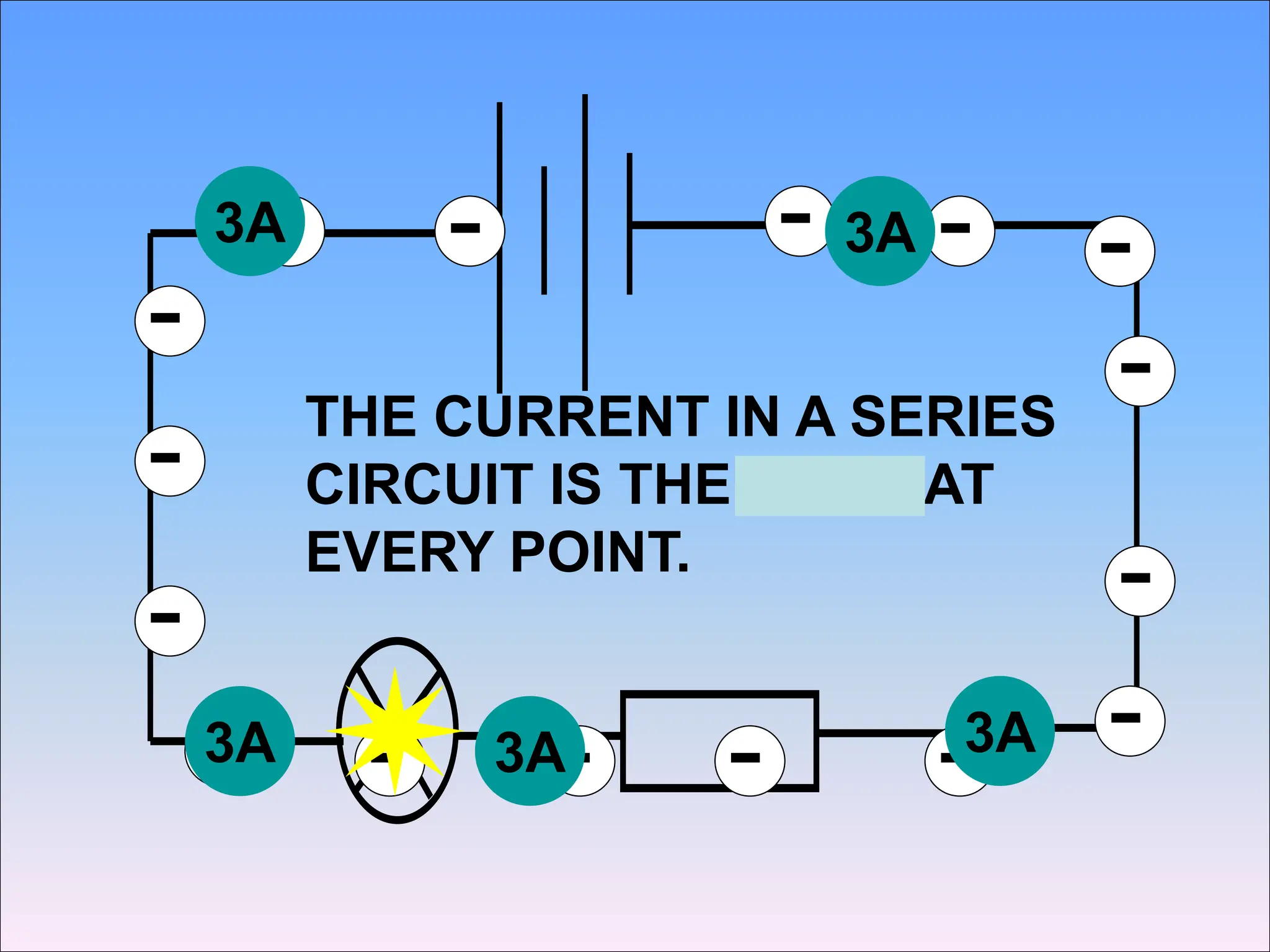
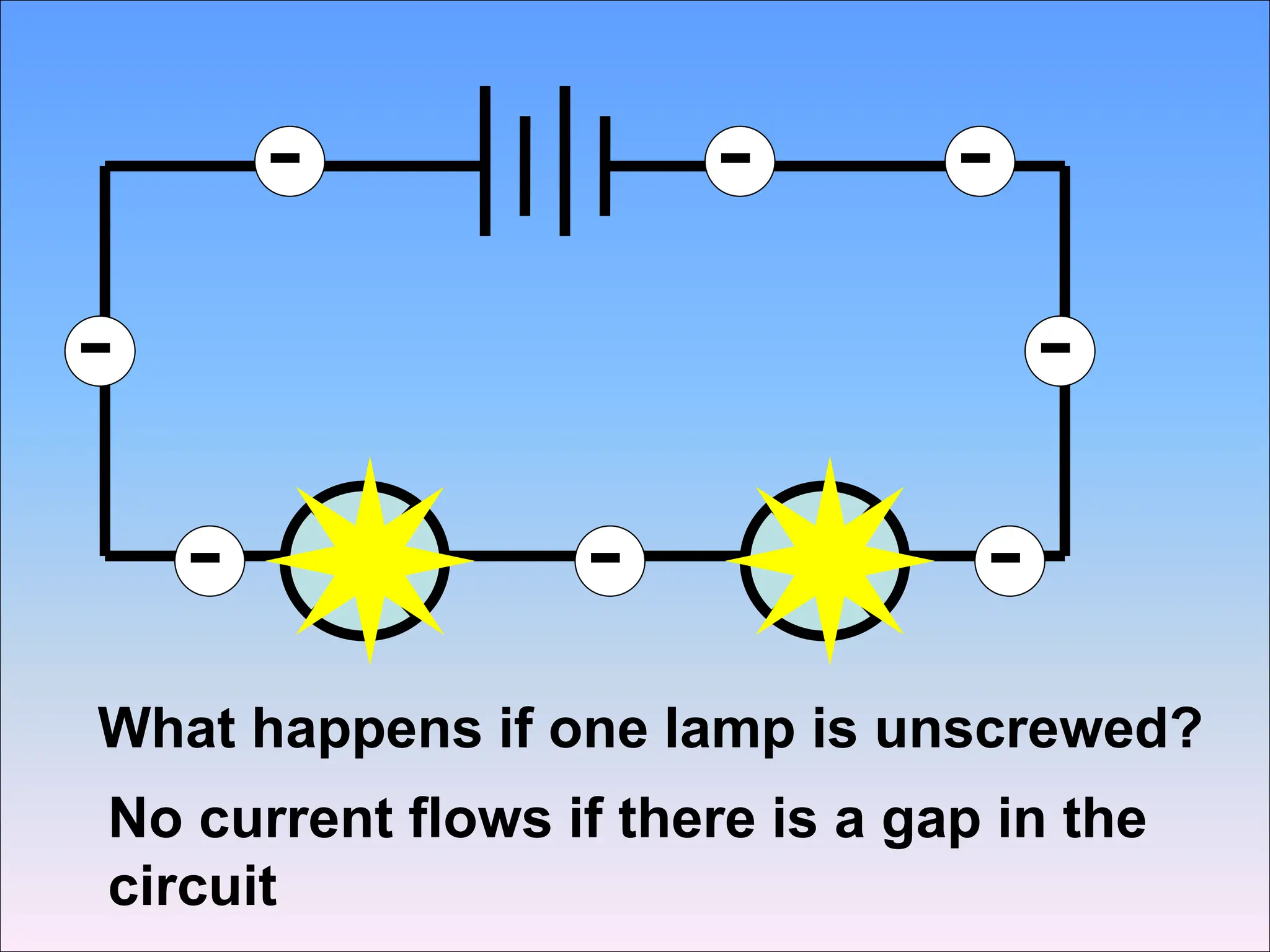
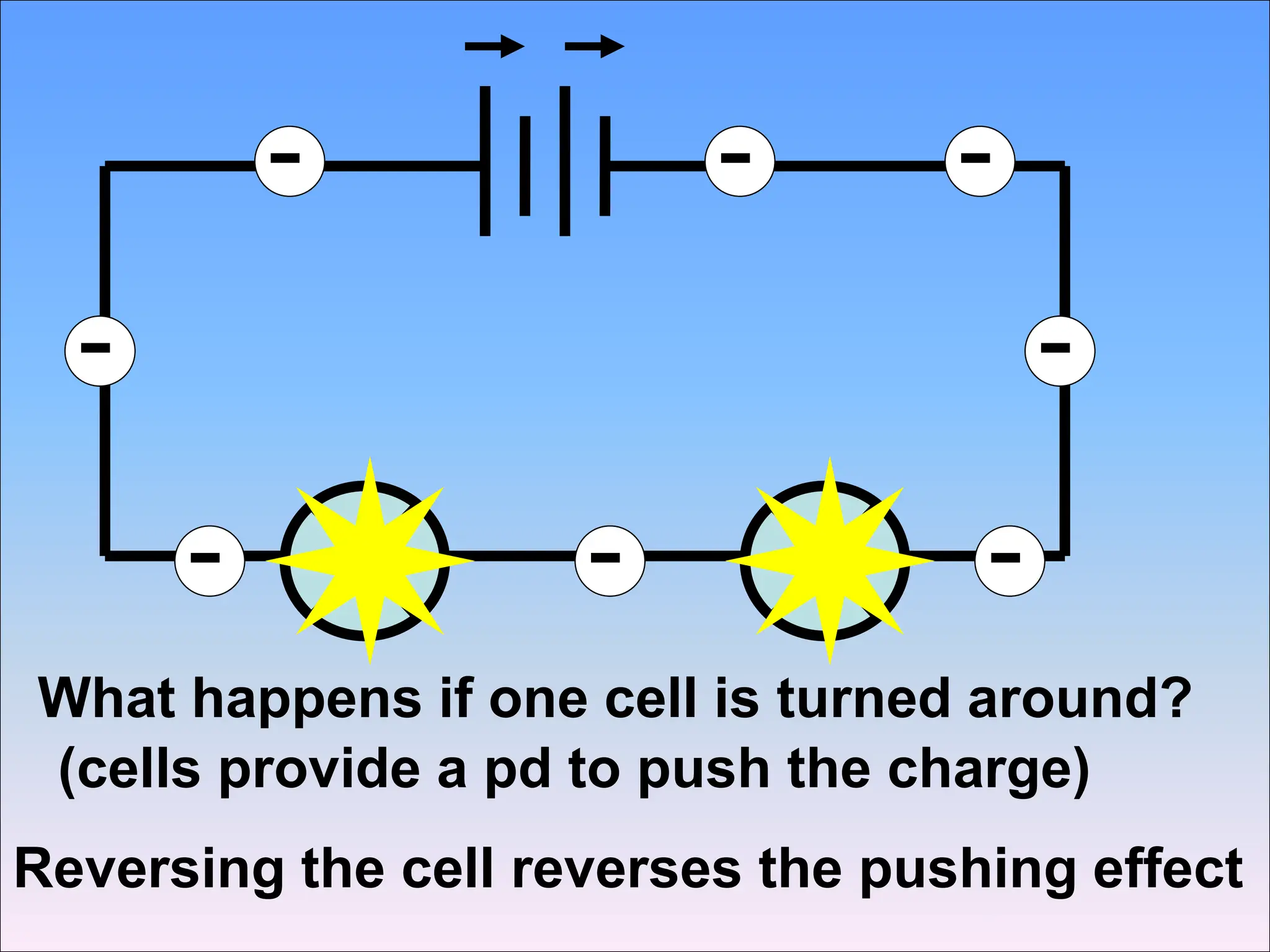
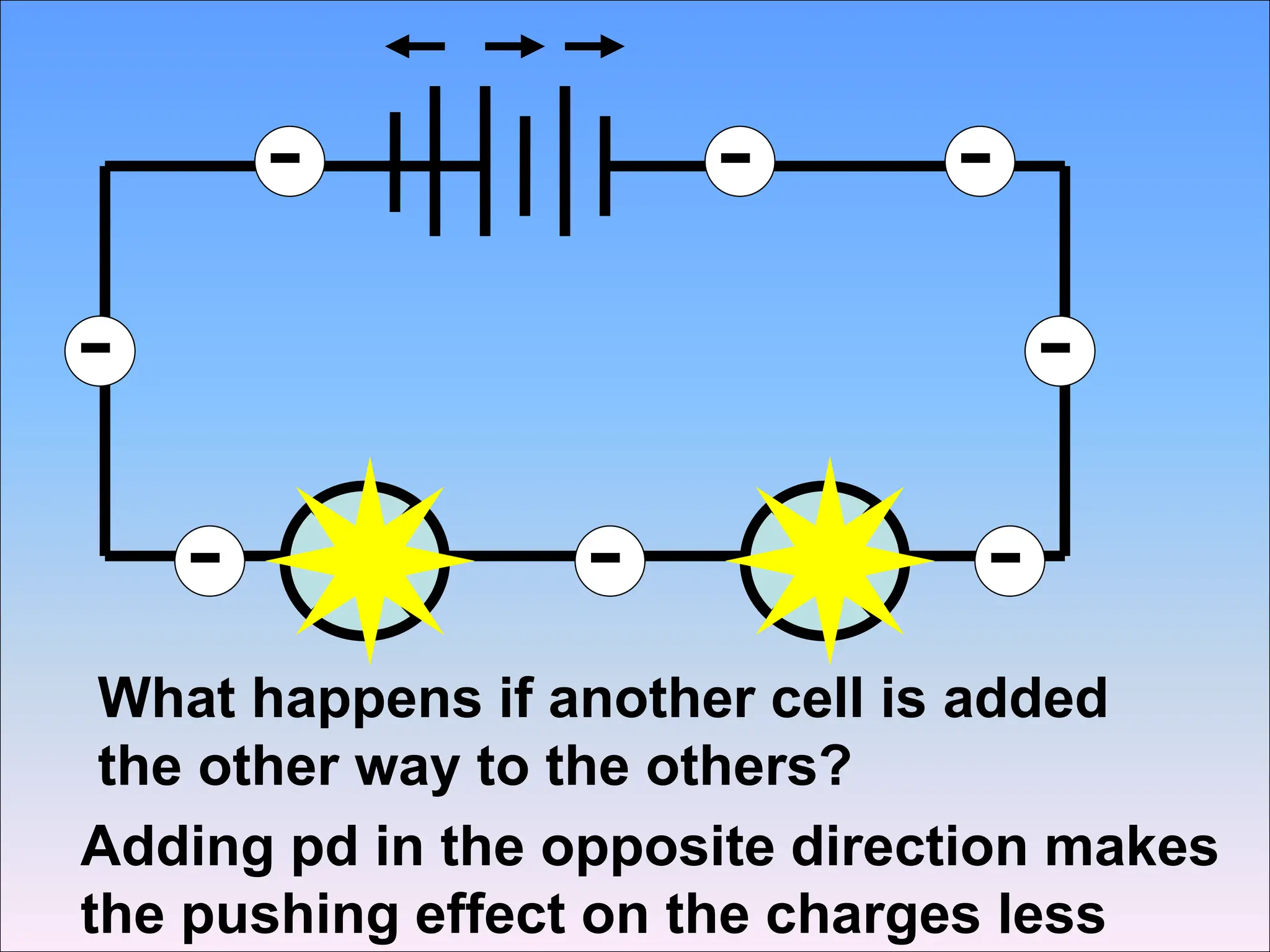
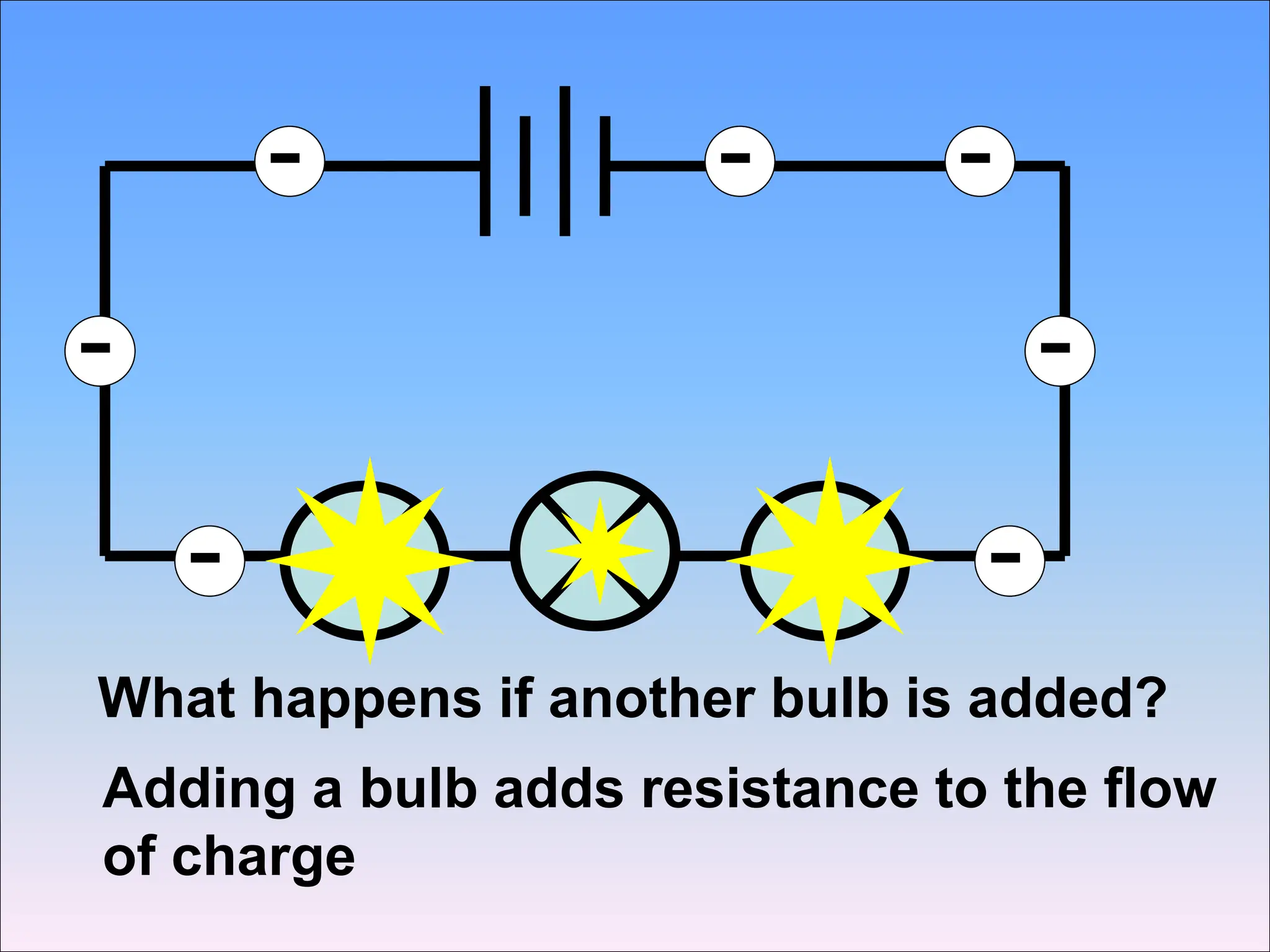
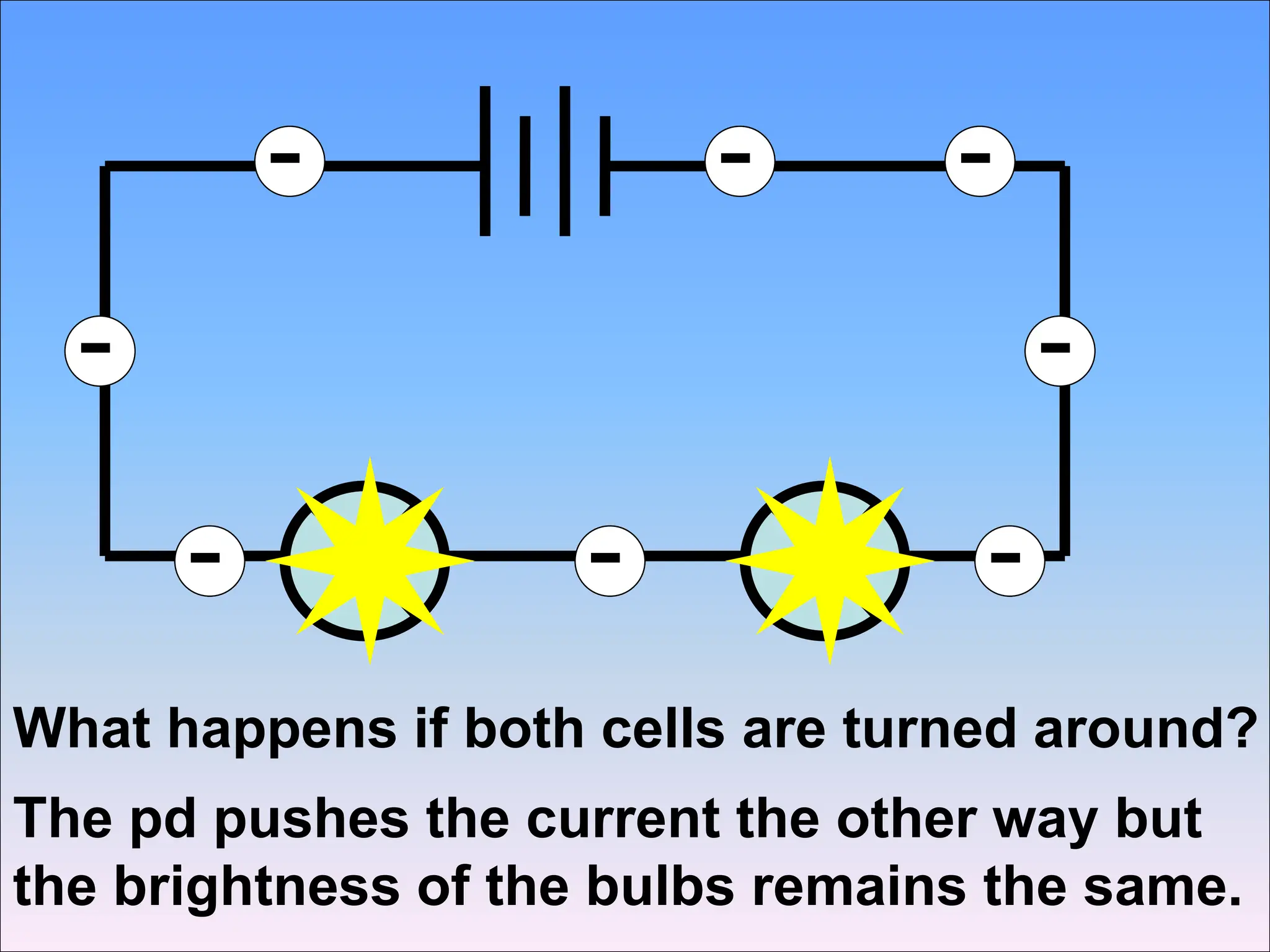
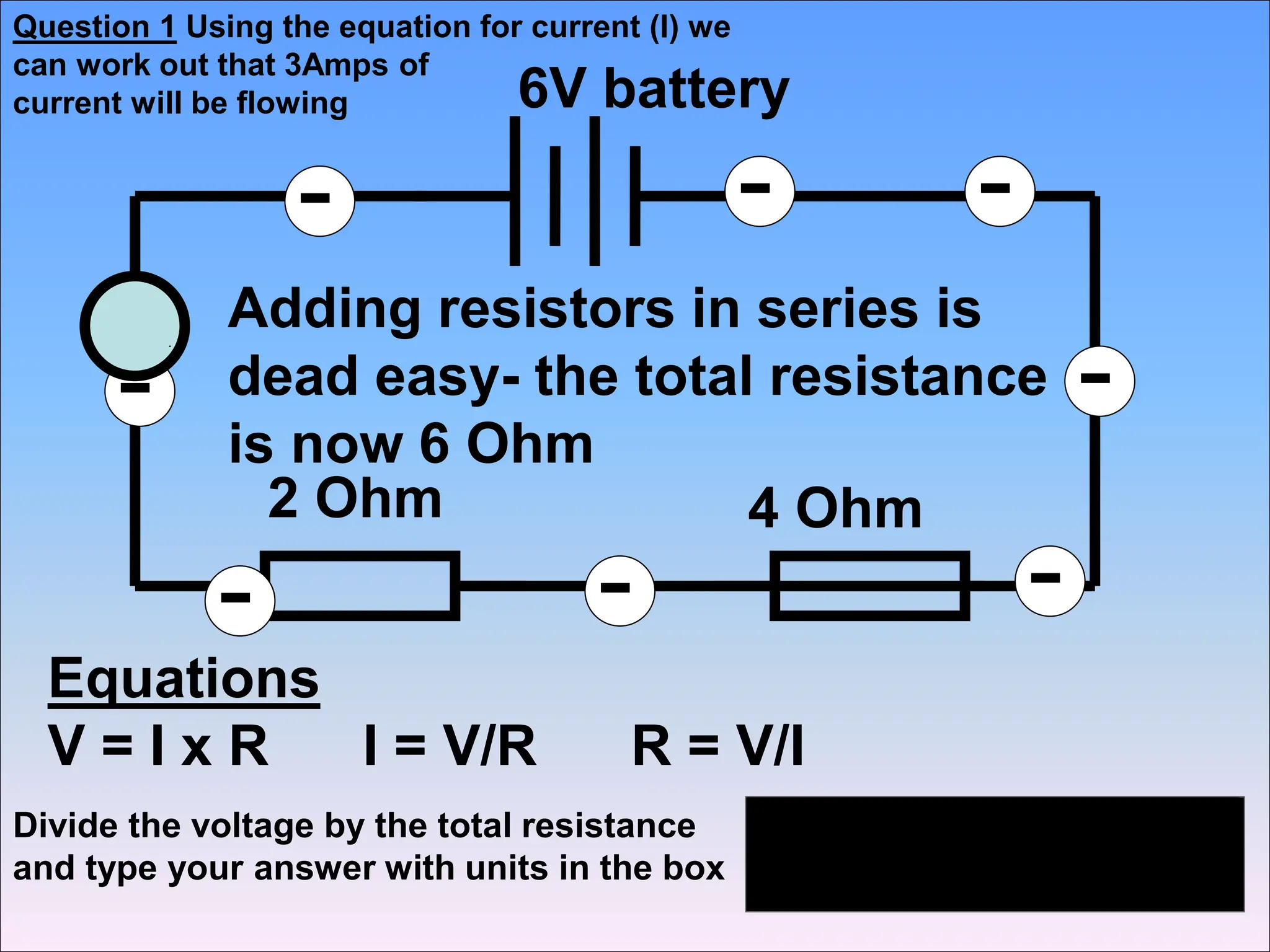
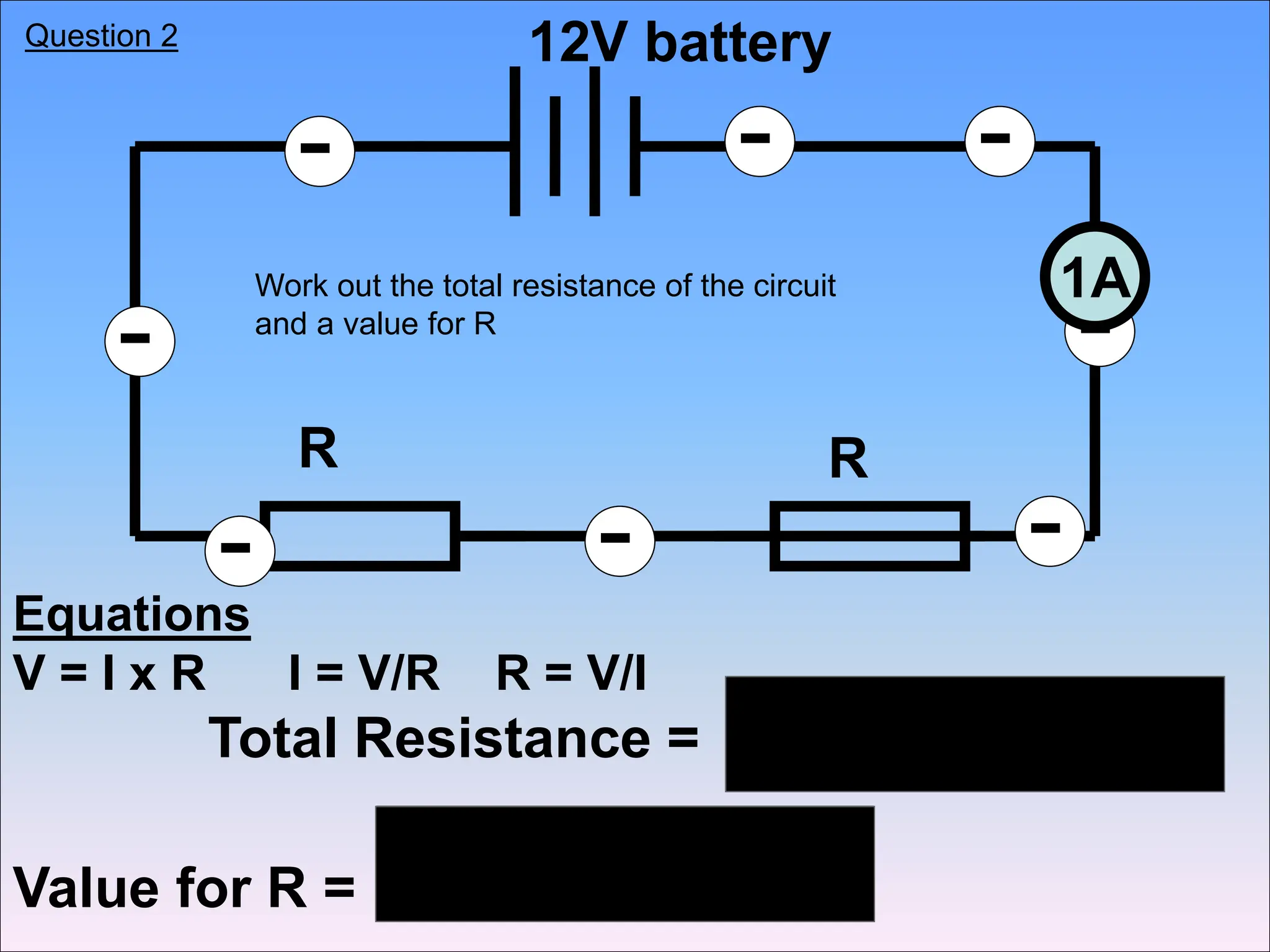
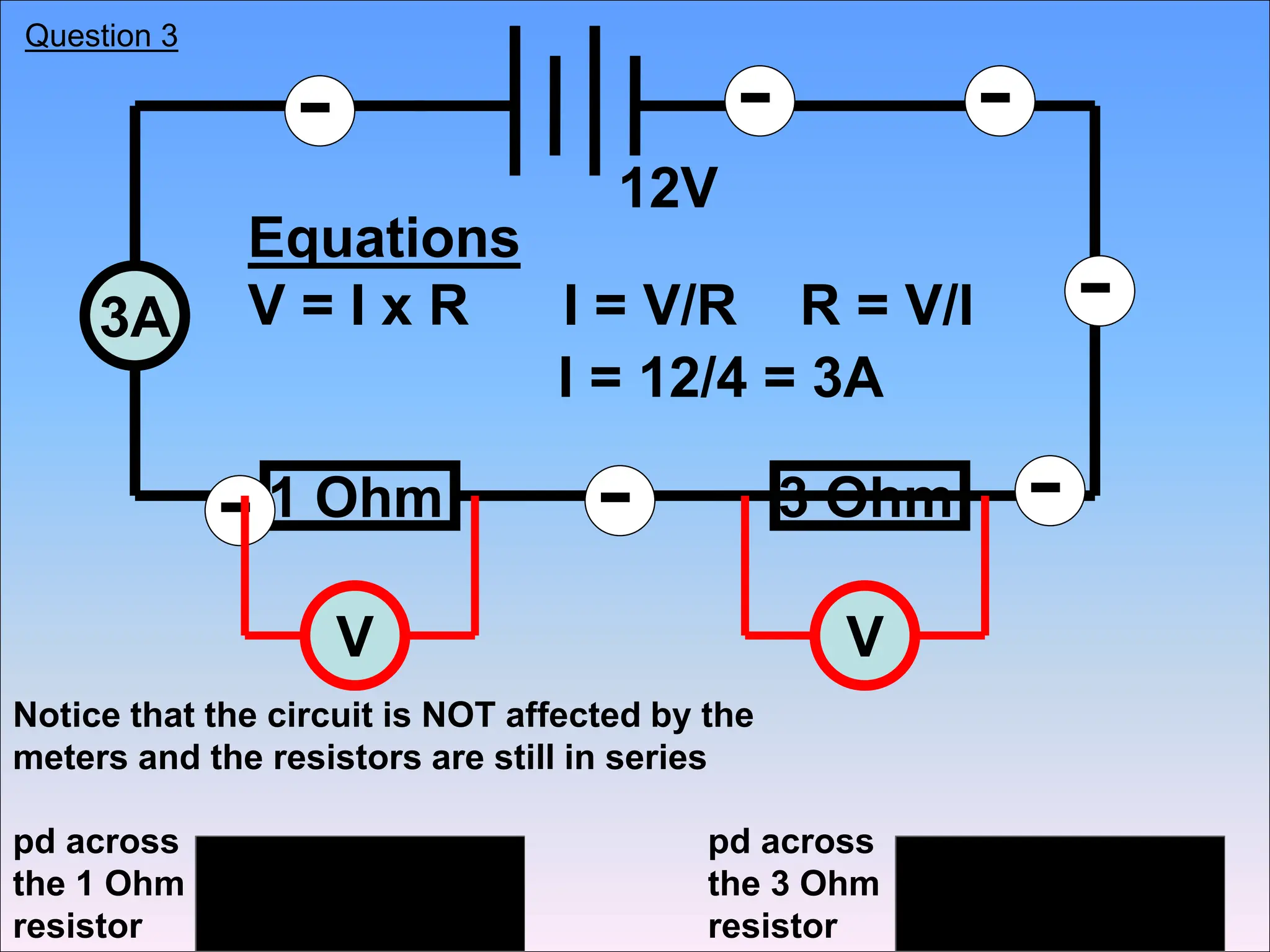
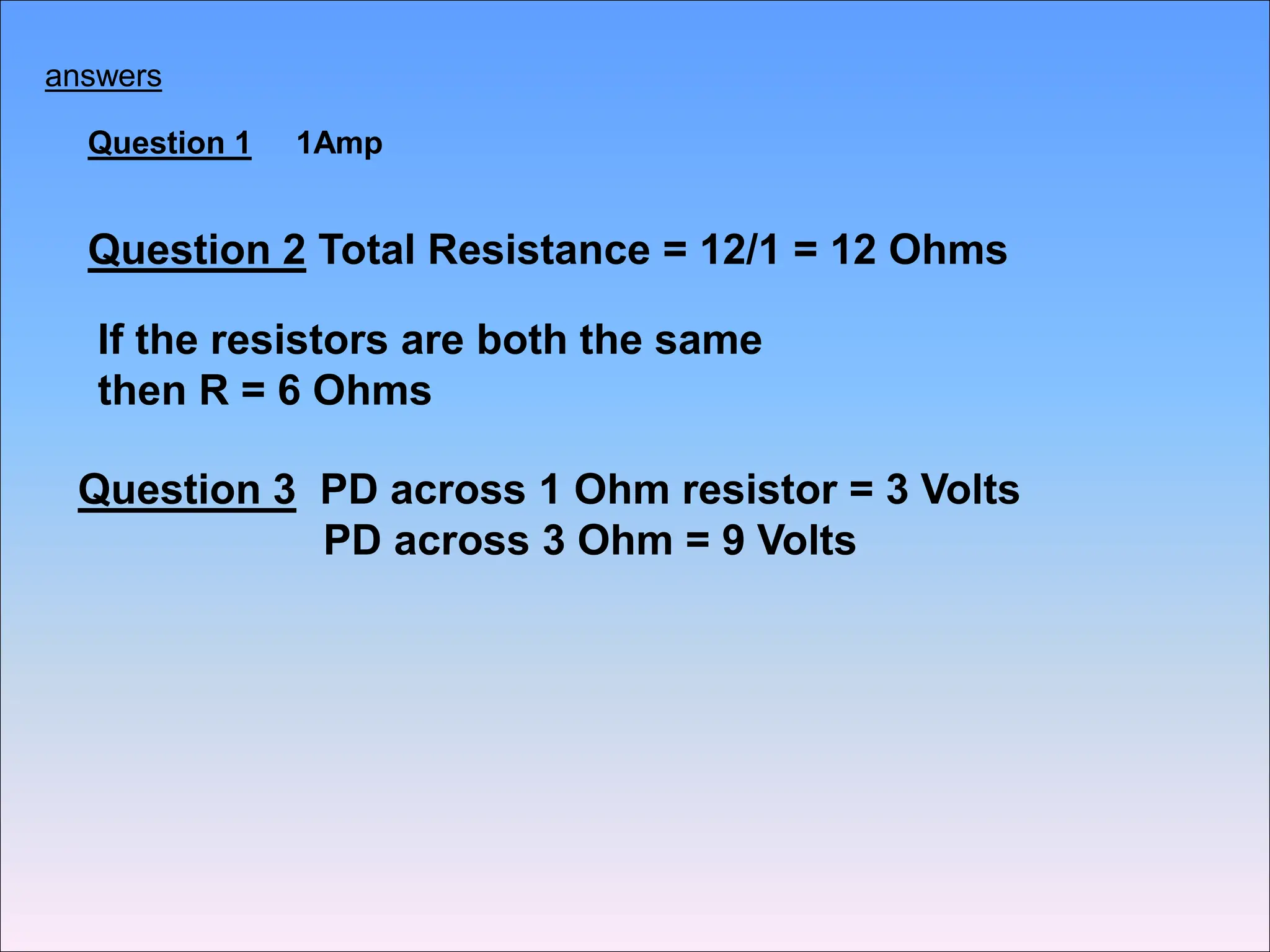
This document discusses series circuits and the rules that govern their behavior. It explains that in a series circuit, the current is the same through all components and the voltage is shared across the components. It also notes that the total resistance of components in series is calculated by adding the individual resistances together. Several examples are provided to demonstrate how changing components in a series circuit impacts the current, voltage, and resistance. Key equations for calculating current, voltage and resistance in series circuits are also shown.