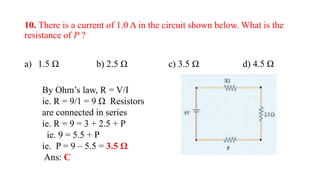
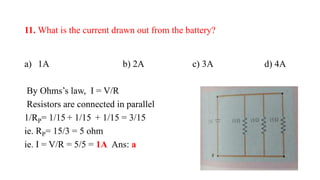
The document contains a series of multiple-choice questions and explanations related to current electricity aimed at Class XII students. It covers topics such as resistance, power calculations, the color code for resistors, and the behavior of conductors and semiconductors under temperature changes. Each example includes a question followed by a calculated answer and a brief explanation of the underlying principles.








![Contd…
Now we have,
1/RP= 1/R + 1/R = 2/R ie RP = R/2
Power dissipation
P2 = V2/ R/2 ----- 2 Dividing equation 2 by equation 1 we get
P2 / P1 = [V2/ (R/2)] x (2R/V2 ) = (2V2 / R) x (2R/V2 ) = 4
ie. P2 / P1 = 4 Ans: d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currentelectricitymcqclassxii-240712093304-6b5039b7/85/Current-Electricity-MCQ-Class-XII-Physics-pptx-9-320.jpg)


![12. The temperature coefficient of resistance of a wire is 0.00125 per °C. At
20°C, its resistance is 1 Ω. The resistance of the wire will be 2 Ω at
a) 800 °C b) 700 °C c) 850 °C d) 820 °C
R2 = R1[1+ α (T2 - T1)]
R1 = Resistance at temperature T1(20 °C) = 1 Ω
R2 = Resistance at temperature T2 = 2 Ω
α – Temperature coefficient of resistance = 0.00125 per °C
2 = 1[1+ 0.00125 (T2 - T1)]
ie. 2 = 1+ 0.00125 (T2 - T1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currentelectricitymcqclassxii-240712093304-6b5039b7/85/Current-Electricity-MCQ-Class-XII-Physics-pptx-14-320.jpg)




