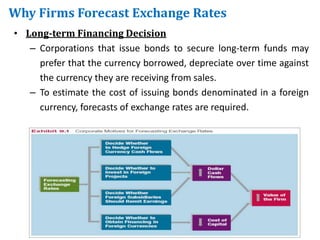
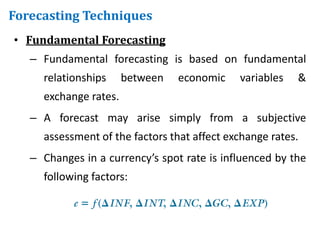
This document discusses why MNCs forecast exchange rates and different techniques for doing so. MNCs need to forecast exchange rates for hedging decisions, short-term financing, investments, capital budgeting, earnings assessments, and long-term financing. Exchange rate forecasts help MNCs determine things like whether to hedge currency risk, which currency to borrow in, and whether to remit foreign subsidiary earnings. There are four main categories of forecasting techniques: technical analysis of historical exchange rate data, fundamental analysis of economic factors affecting exchange rates, market-based analysis using current spot or forward rates, and subjective assessments.