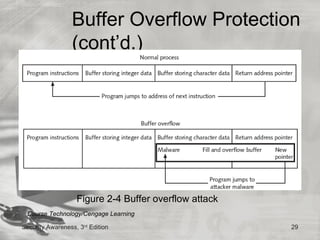
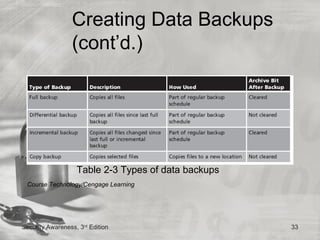
This document discusses desktop security and attacks. It describes two categories of attacks: malicious software attacks and hardware attacks. Malicious software, or malware, includes viruses, worms, Trojan horses, rootkits, and logic bombs that can damage systems covertly. Defenses include managing software patches, using antivirus software, enabling buffer overflow protection, protecting against physical theft, regularly backing up data, and following steps to recover from attacks by disinfecting and reinstalling systems.