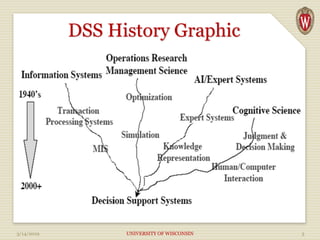
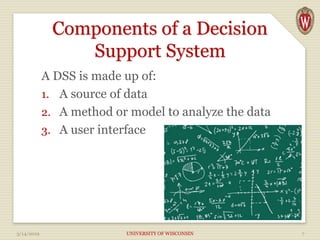
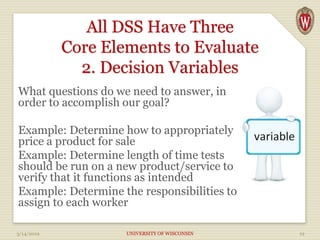
The document discusses Decision Support Systems (DSS), which help senior executives manage vast amounts of disparate data to improve decision-making across various sectors. It outlines the components, processes, and types of DSS, emphasizing the importance of technology and data analysis in complex decision-making scenarios. Additionally, it details various types of decision-making challenges and the advantages of modern DSS, including enhanced decision quality, cost reduction, and improved productivity.