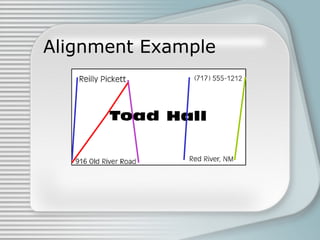
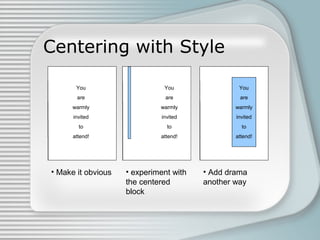
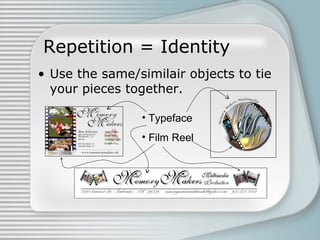
This document discusses four basic principles of graphic and publication design: contrast, repetition, alignment, and proximity. It defines each principle and provides examples to illustrate proper and improper uses. Contrast involves using differences in visual properties like color, size, and shape to distinguish objects. Repetition means repeating design elements throughout a piece to tie it together and guide the reader's eyes. Alignment positions elements purposefully, not just centered, using things like lines. Proximity groups related items close together and separates unrelated items.