Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

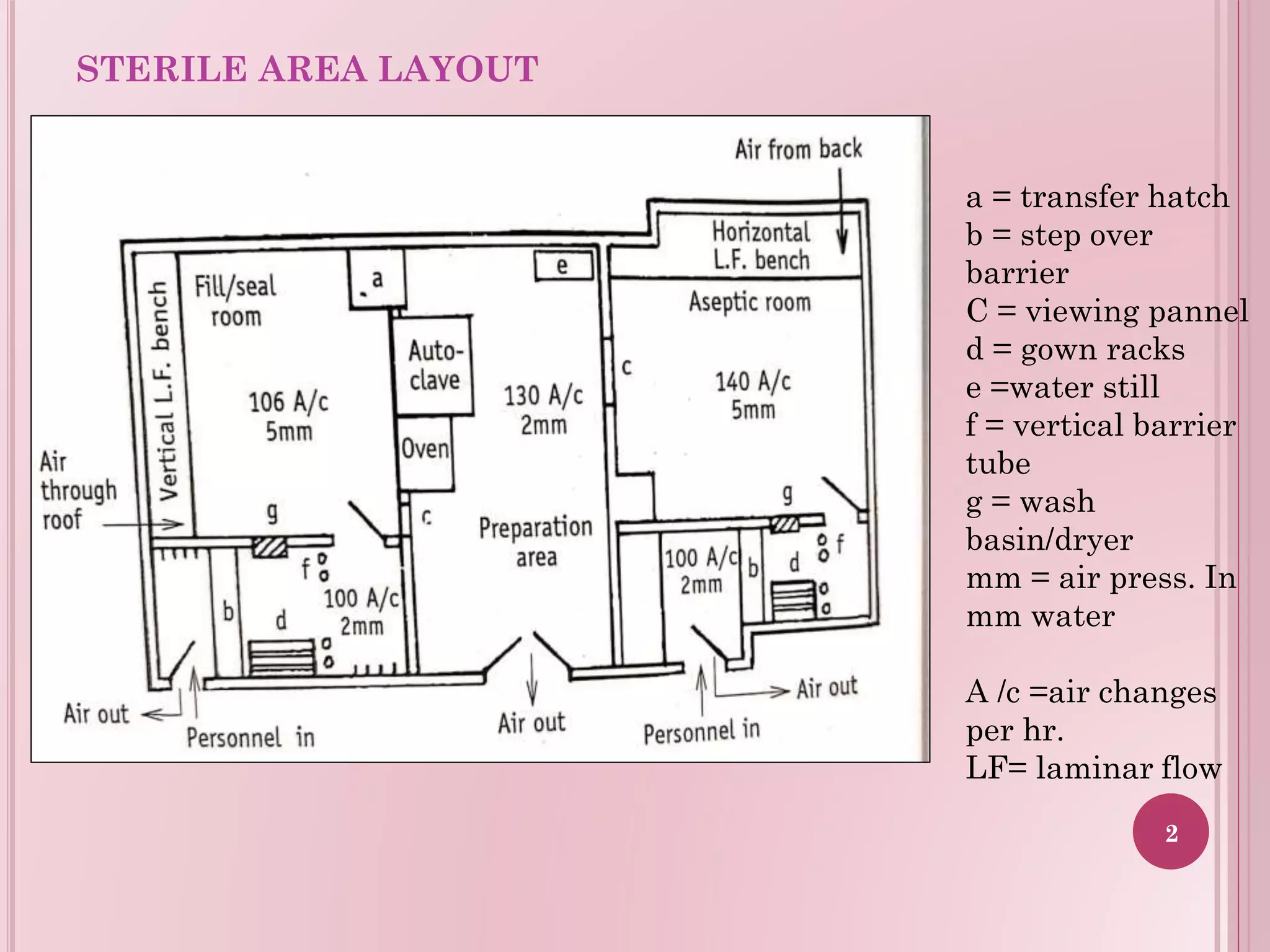

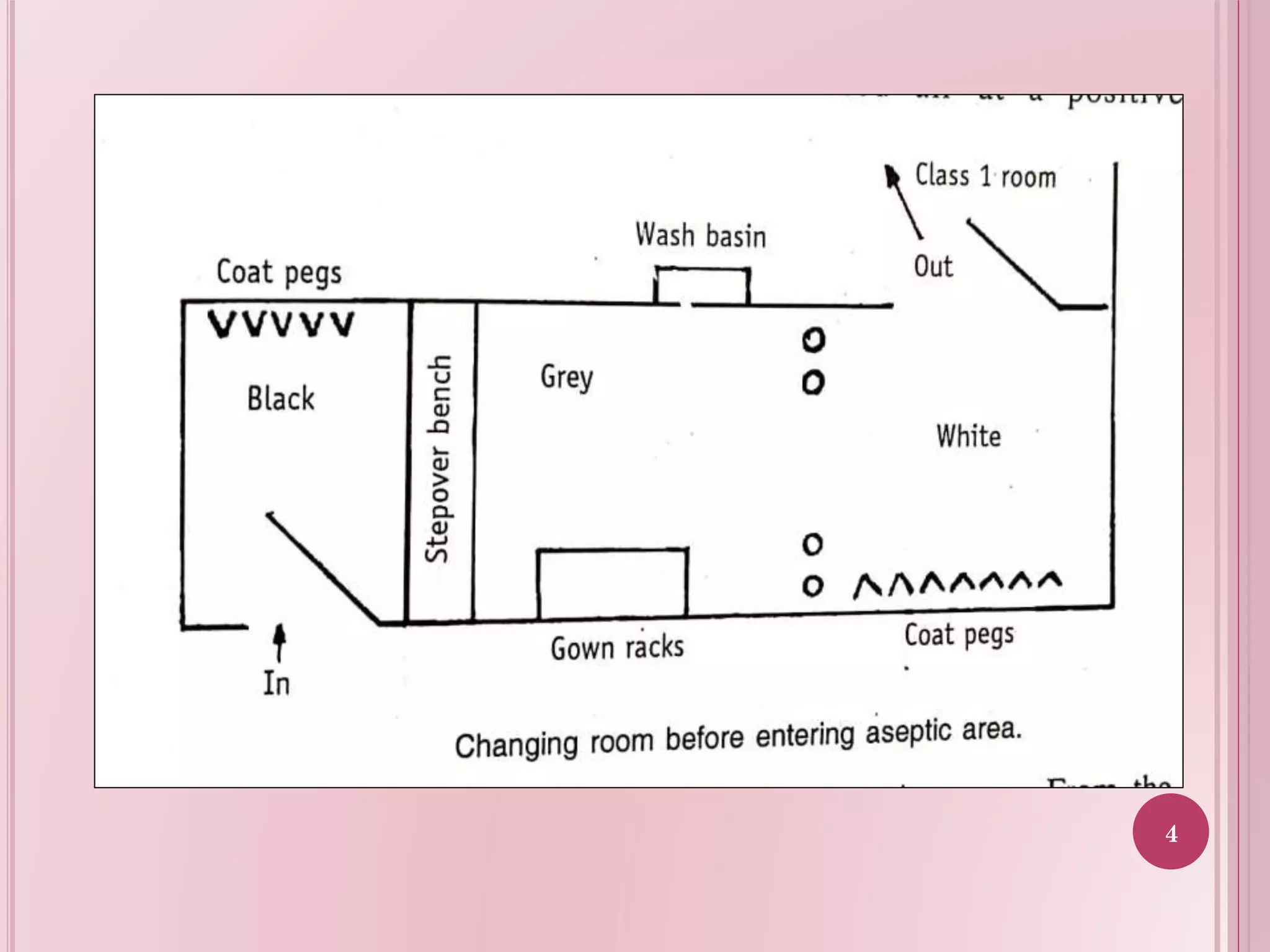


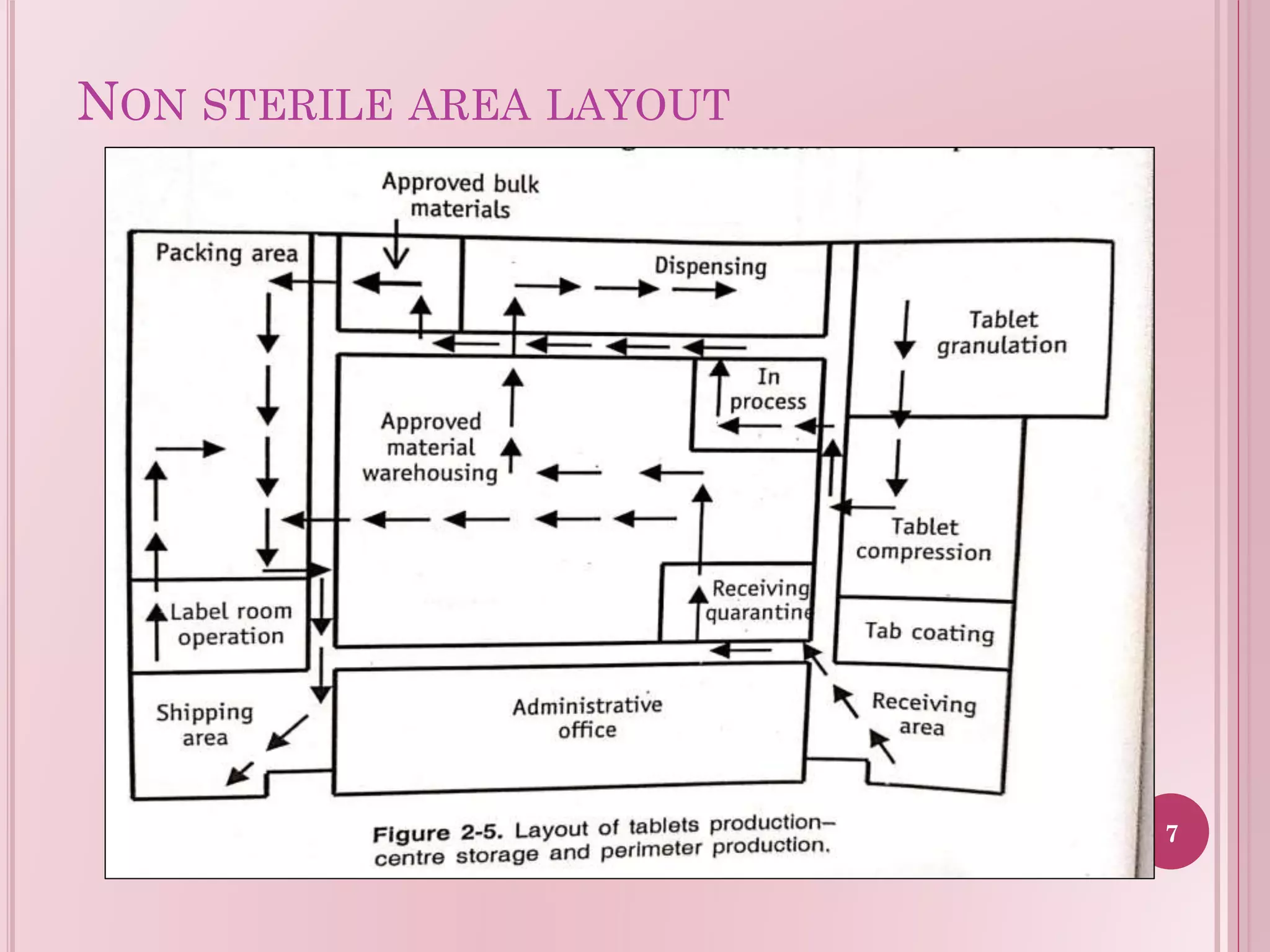

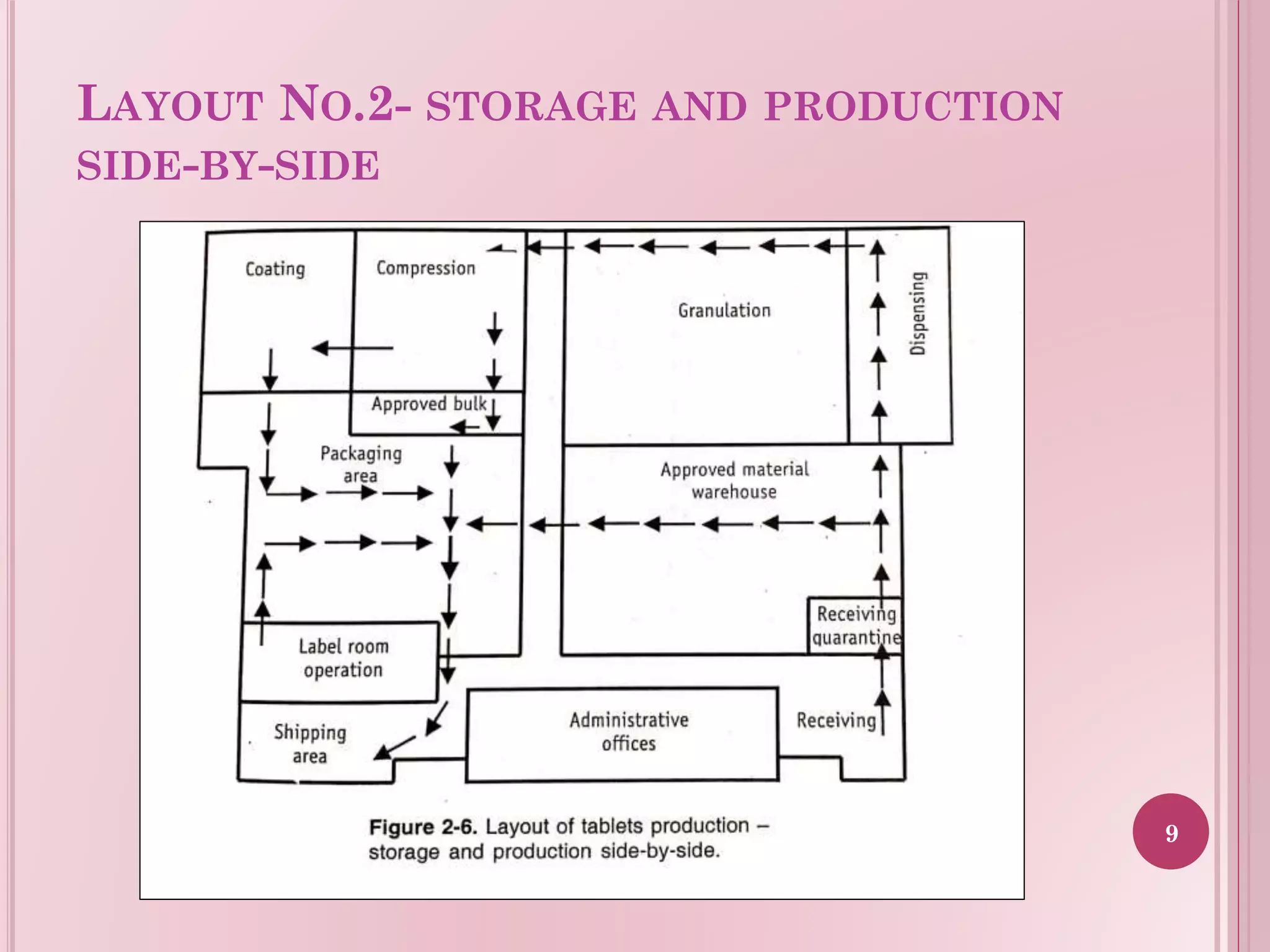

This document provides guidelines for the layout of sterile and non-sterile areas in a plant. For sterile areas, it outlines airflow patterns with air entering at positive pressure above atmospheric pressure. It describes personnel movement through airlocks and changing rooms to maintain cleaner conditions moving from potential contamination to less. Material passes through hatches and airlocks. For non-sterile areas, it presents three layout options: a central storage warehouse with perimeter production, side-by-side storage and production, and a straight-line layout. The layouts aim to optimize space, traffic flow, and separation of functions.










Introduction to sterile and non-sterile plant layout concepts by the Quality Assurance Department.
Illustration of components like transfer hatch, gown racks, and air changes in sterile area layout.
Description of air flow mechanisms and pressure levels for maintaining sterile environments.
Access control and movement protocols for personnel in sterile zones, ensuring air cleanliness.
Use of hatchways and airlocks for secure materials transport into sterile areas, enhancing safety.
Introduction to the layout design for non-sterile areas in a plant facility.
Description of a layout focusing on center storage for efficiency but risking traffic crossover.
Introduction to a layout design option that places storage and production adjacent to each other.
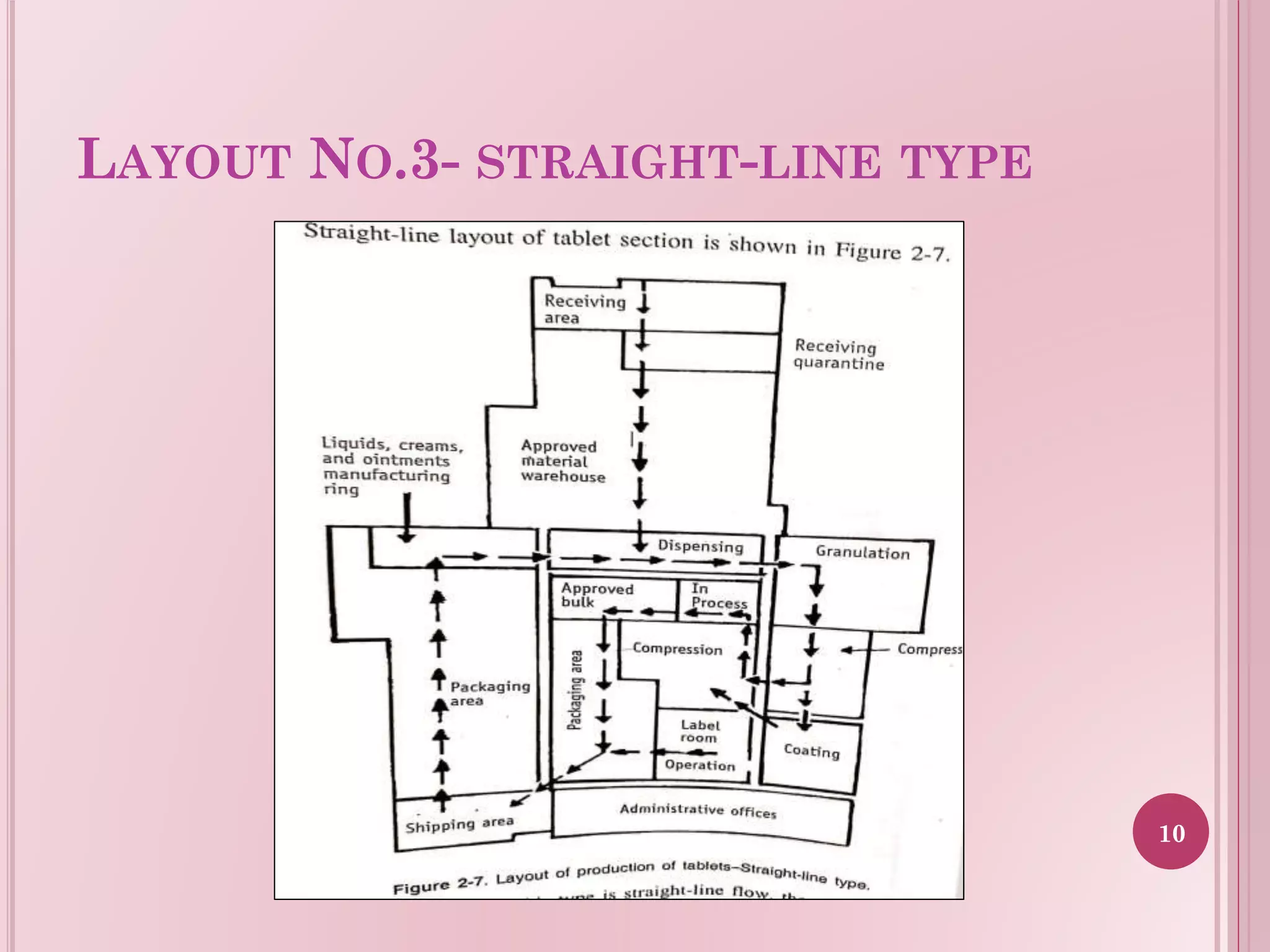
Overview of the straight-line layout design for production processes optimizing flow.