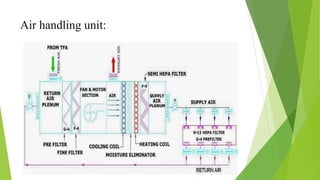
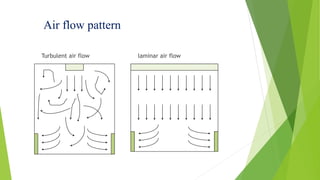
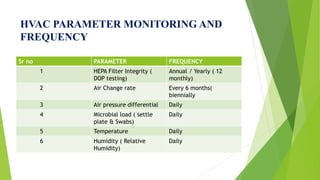
This document discusses air circulation maintenance in sterile and non-sterile pharmaceutical areas. It covers the importance of HVAC systems in maintaining air quality, including components like ducting, filters, and airflow patterns. Different classification systems are used for sterile versus non-sterile areas. HVAC systems can use either full fresh air or air recirculation with HEPA filters. Key parameters to monitor include filter integrity, air changes, pressure, microbial loads, temperature, and humidity. Proper air handling is crucial for pharmaceutical manufacturing to control contamination.