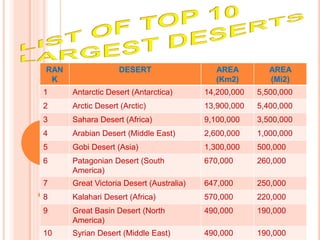
This document describes five main types of deserts: midlatitude deserts, rain shadow deserts, coastal deserts, monsoon deserts, and polar deserts. It provides details on the locations and characteristics of each type. Midlatitude deserts occur between 30-50 degrees north and south, and the Sonoran Desert is given as an example. Rain shadow deserts form on the leeward side of mountain ranges where moisture is blocked. Coastal deserts are near the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn and affected by cold ocean currents. Monsoon deserts like the Thar and Rajasthan develop due to seasonal temperature variations between land and sea. The document also includes images of plants and animals commonly found