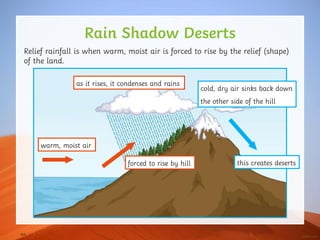
Trade wind deserts are formed by the Hadley cell circulation pattern. Warm air rises at the equator, causing low pressure. As the air moves away and cools, it sinks over the tropics, creating high pressure that prevents rain formation. No rain leads to desert conditions in these areas. Rain shadow deserts occur when moist air is forced to rise over hills or mountains, condensing and raining on one side while dry air sinks on the lee side, creating a desert.