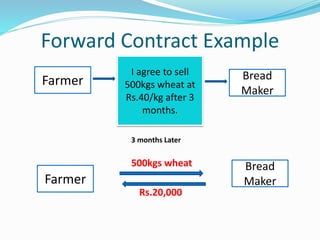
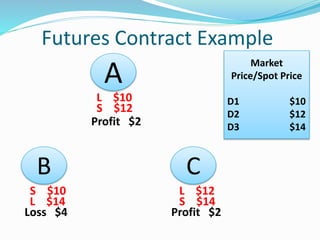
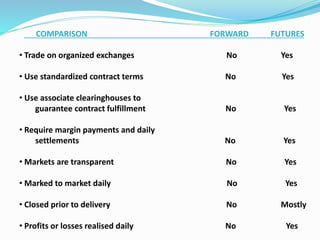
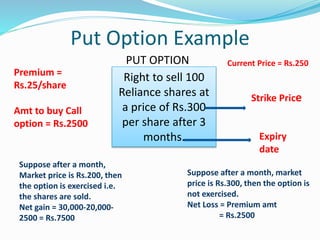
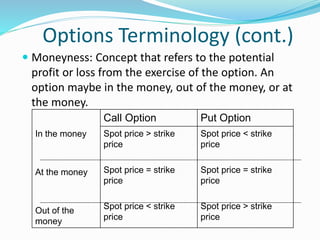
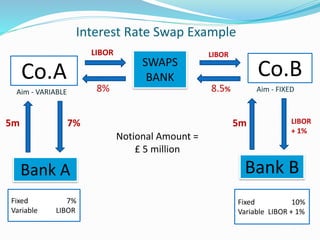
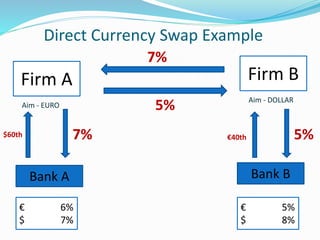
Derivatives are financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset. The three main types of traders in derivatives markets are hedgers who use derivatives to reduce risk, speculators who trade for profits, and arbitrageurs who exploit price discrepancies across markets. Derivatives can be traded over-the-counter (OTC) through privately negotiated contracts or on exchanges through standardized contracts. Common types of derivatives include forwards, futures, options, and swaps. Forwards and futures are binding agreements to buy or sell an asset in the future at an agreed upon price, while options provide the right but not obligation to buy or sell. Swaps involve exchanging cash flows of one asset for another.