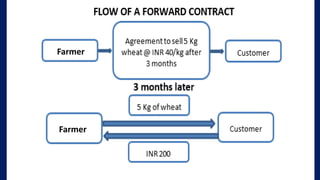
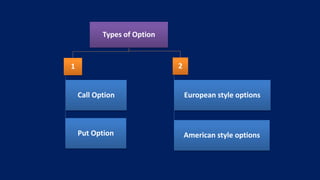
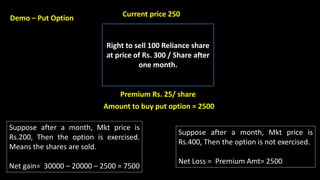
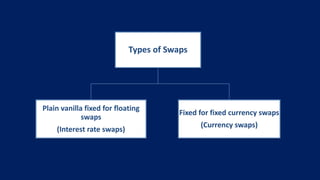
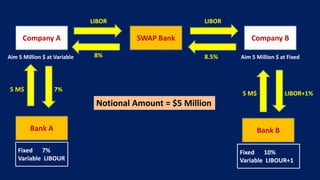
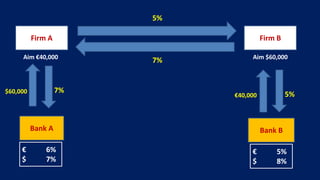
This document provides an overview of different types of derivatives, including examples. It discusses forwards, futures, options, and swaps. Forwards are customized bilateral contracts where the parties agree to buy or sell an asset at a future date for a predetermined price. Futures are standardized exchange-traded contracts that are cash settled. Options provide the right but not obligation to buy or sell an asset by a specified date at a predetermined price. Swaps involve exchanging cash flows of one party's financial instrument for those of the other party. The document defines key terms and concepts for each type of derivative and provides examples to illustrate how they work.