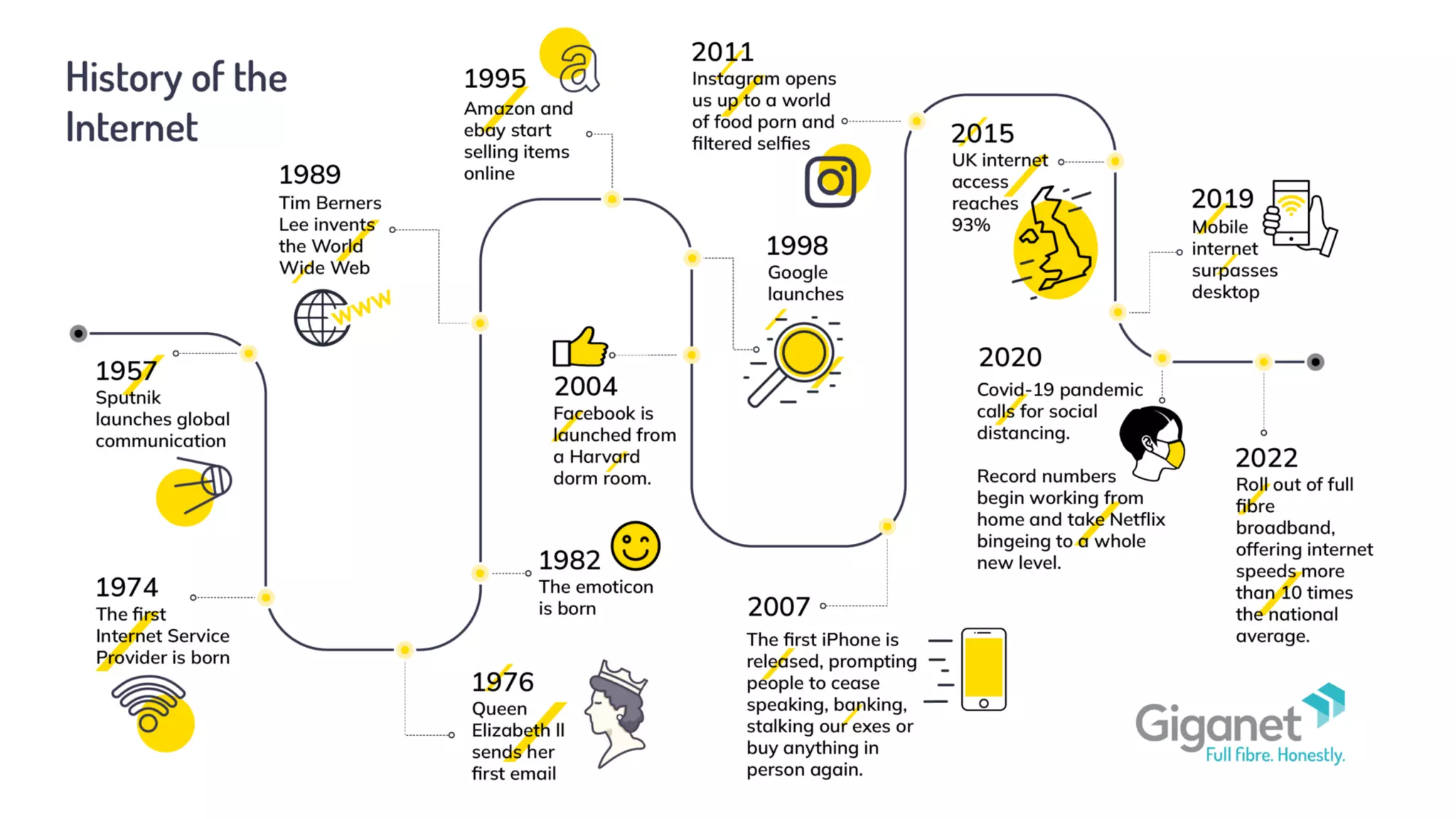
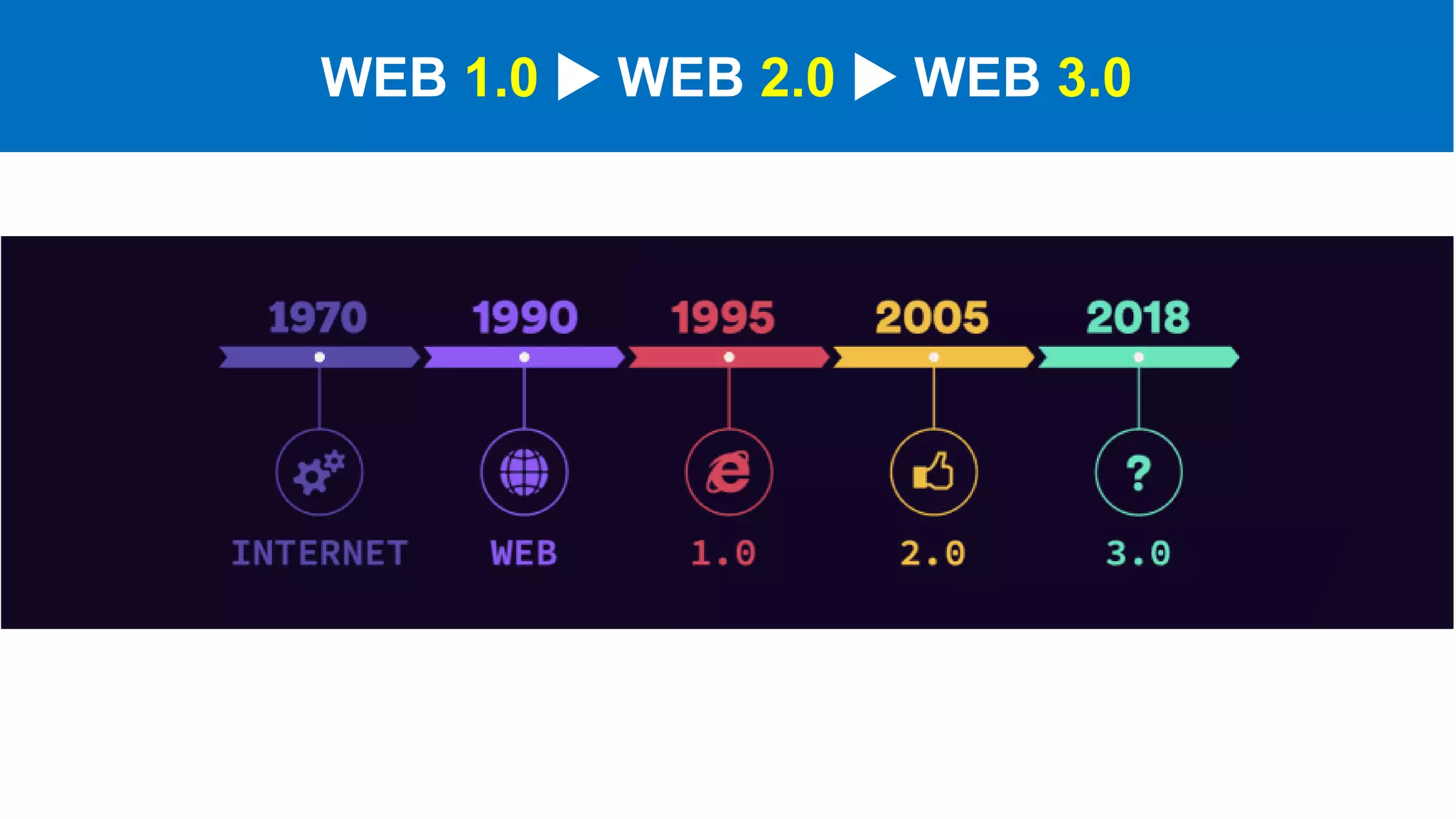
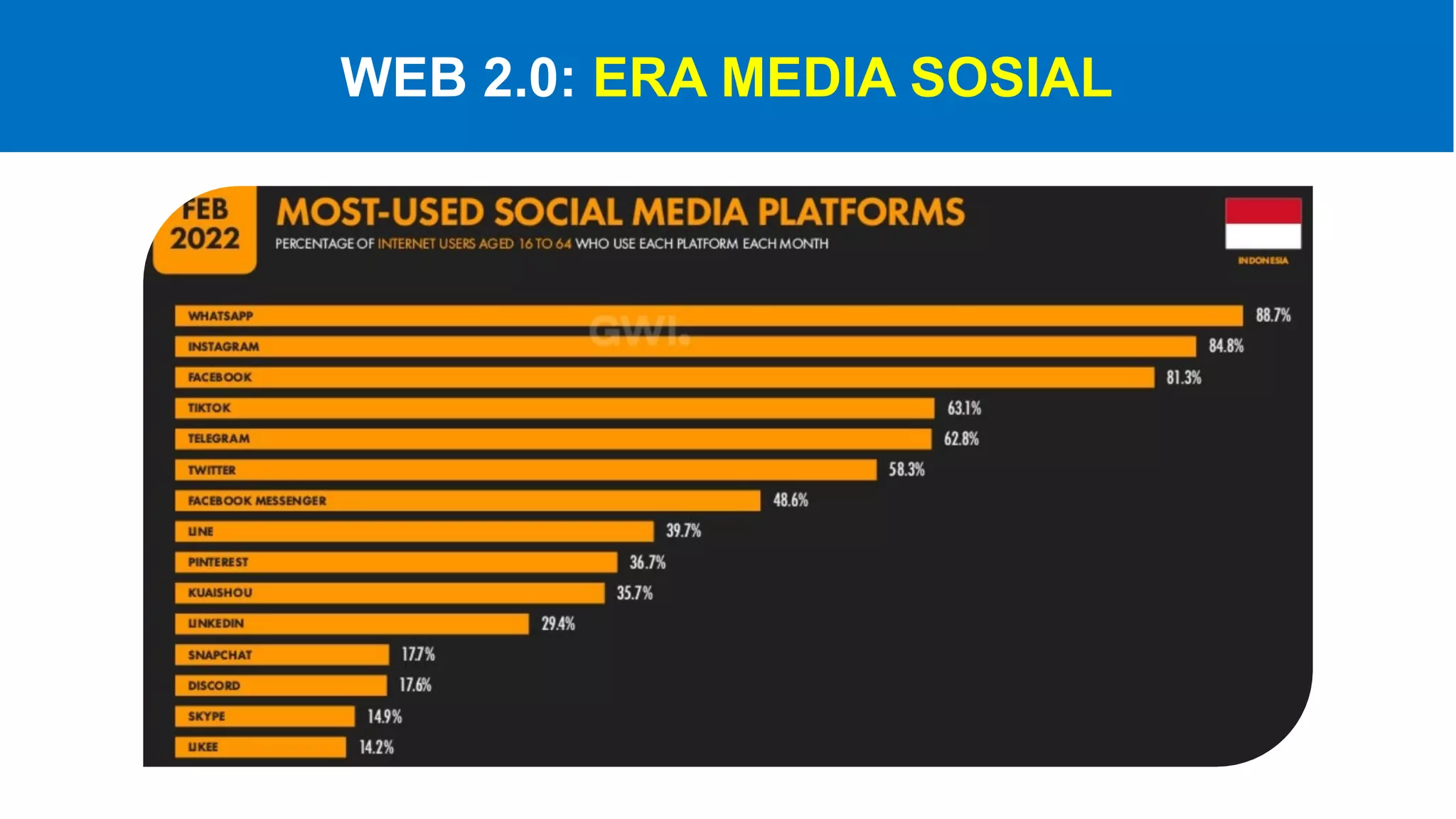
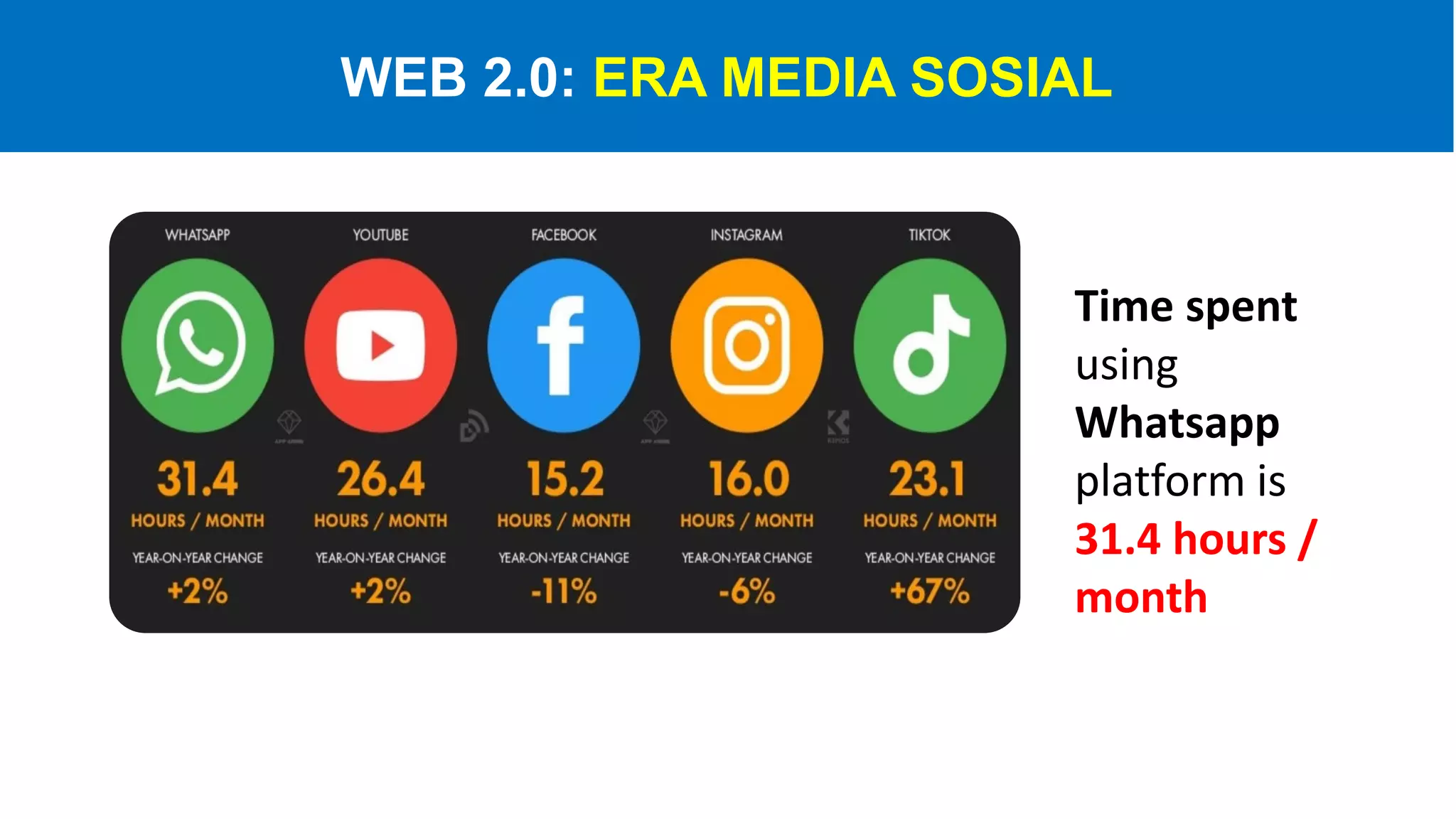
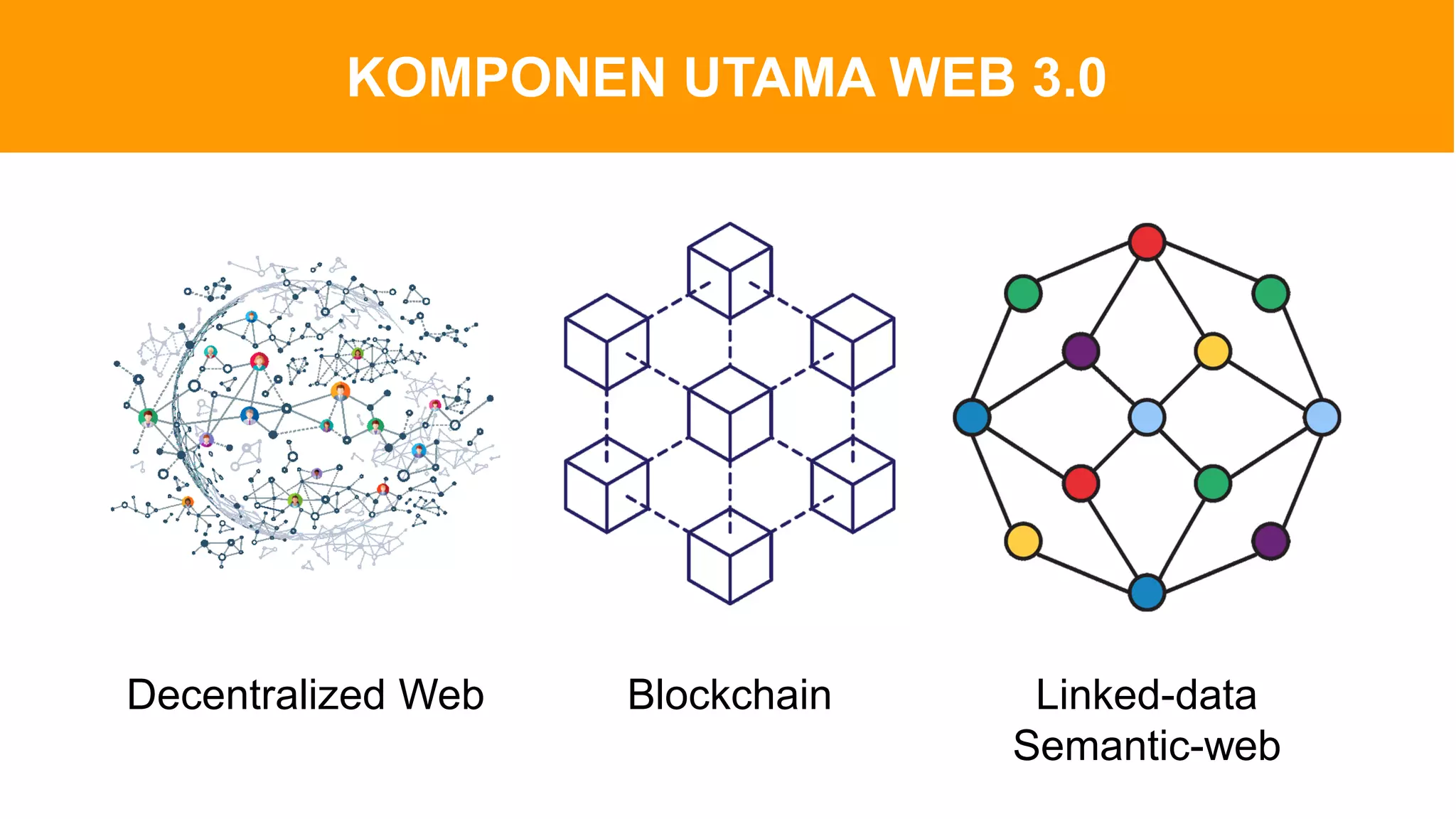
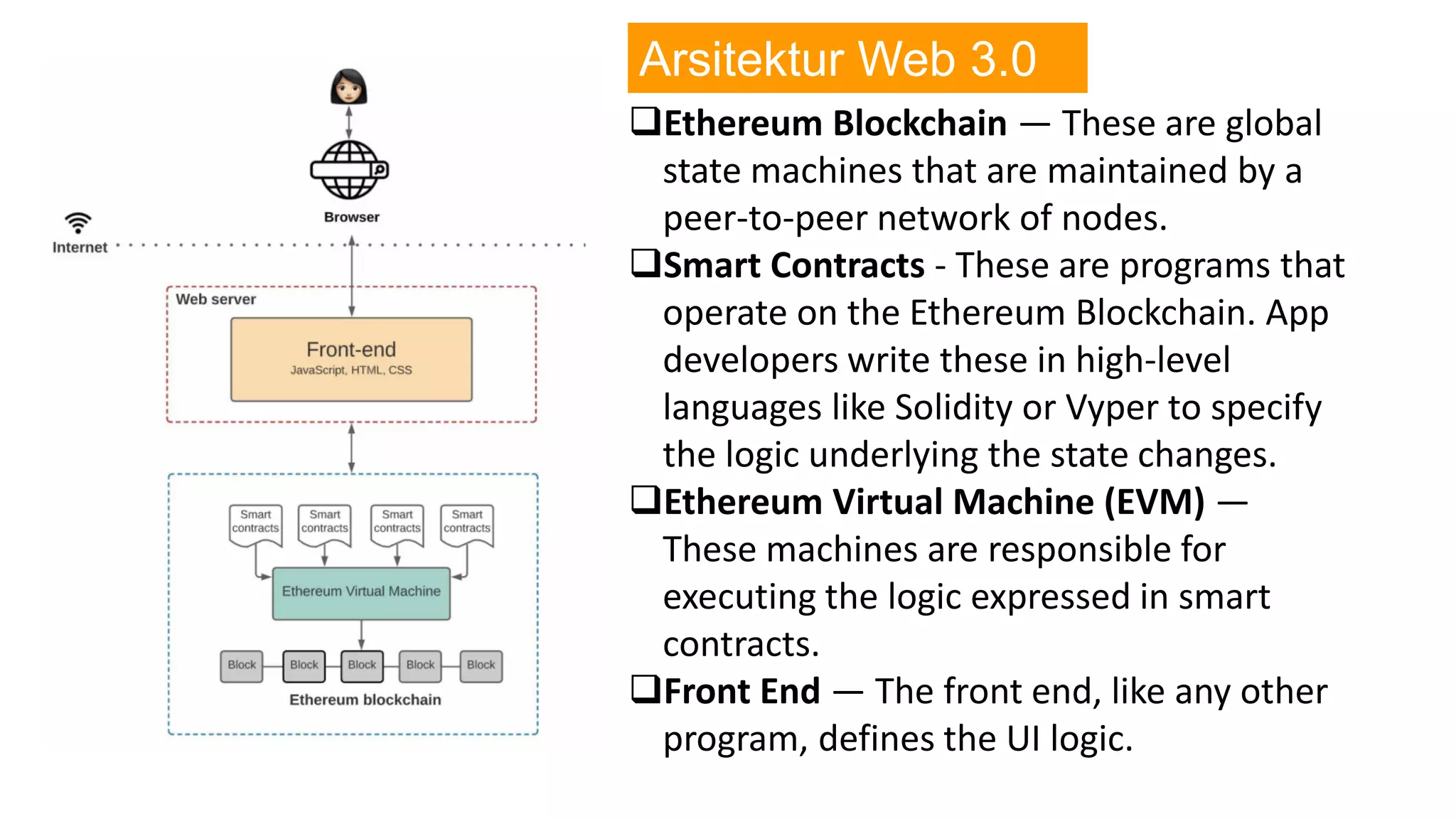
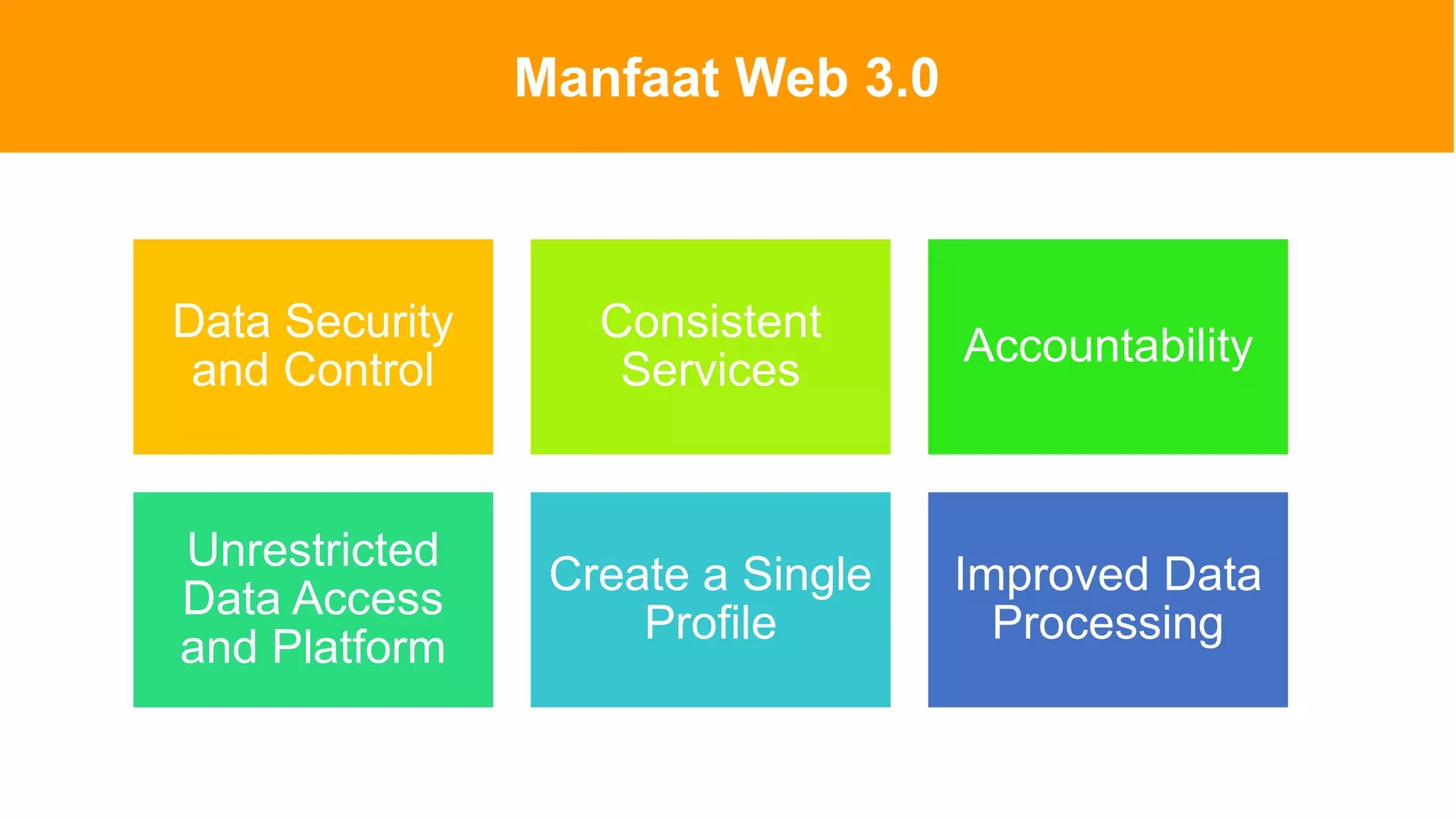
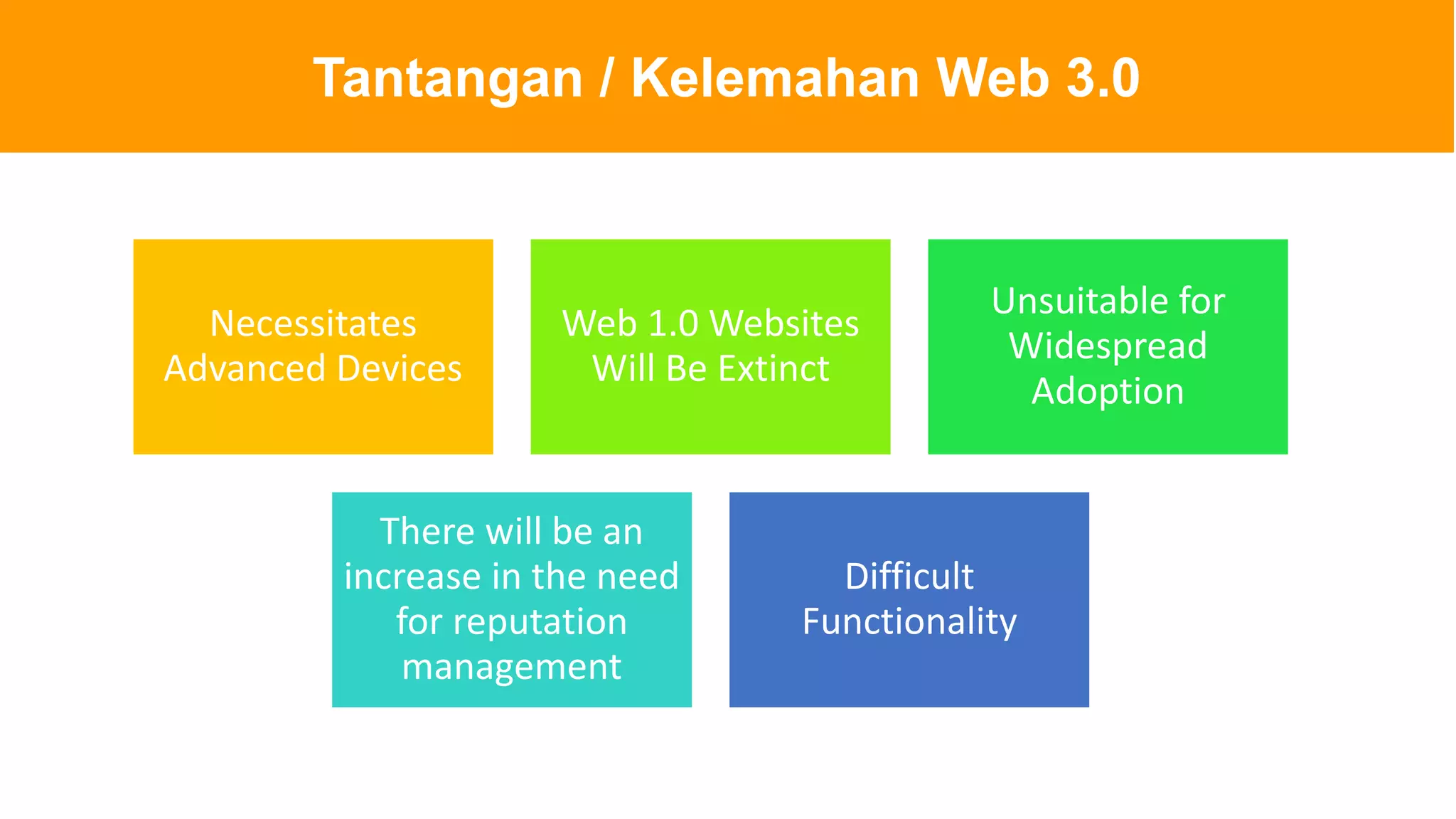
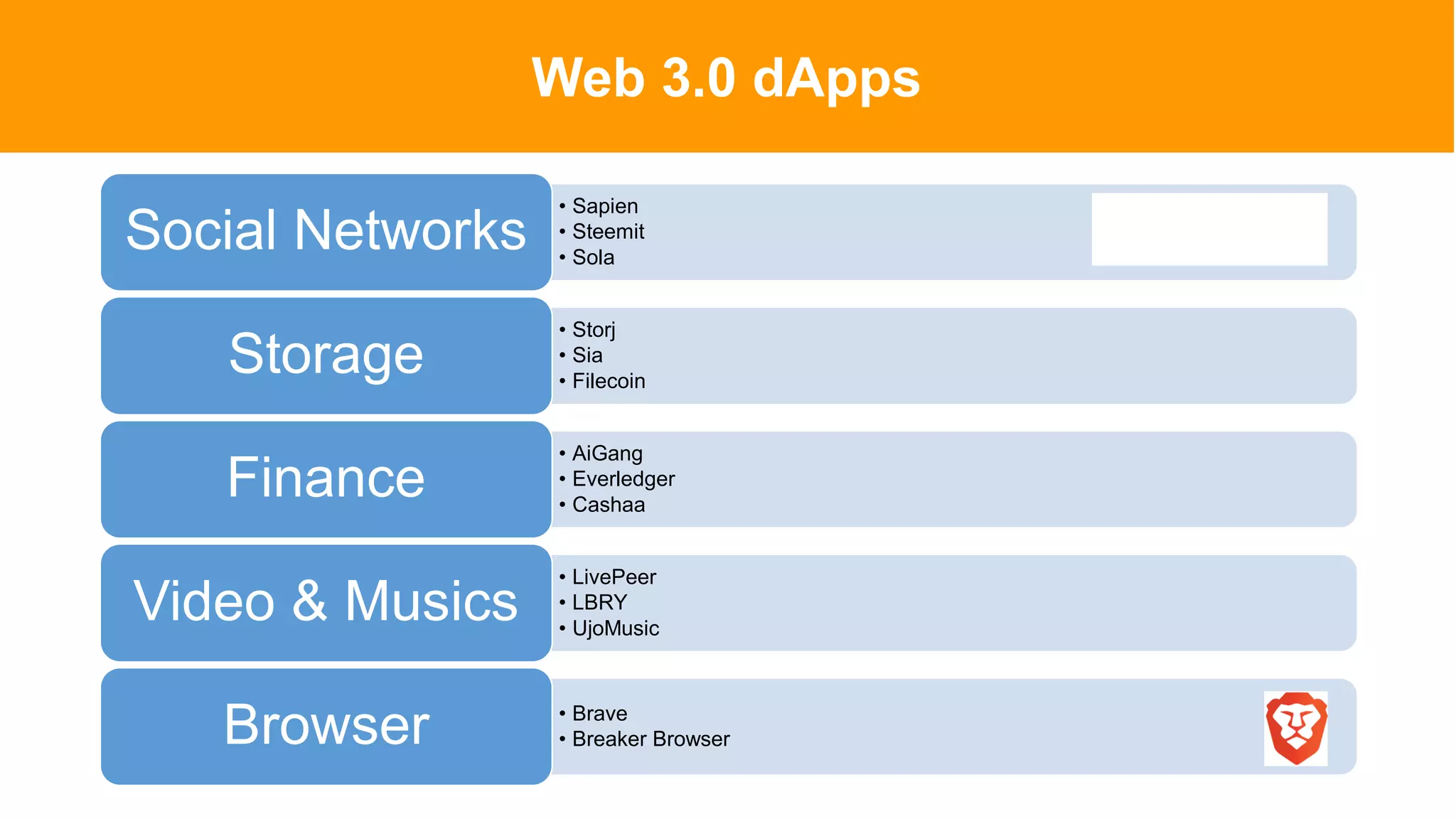
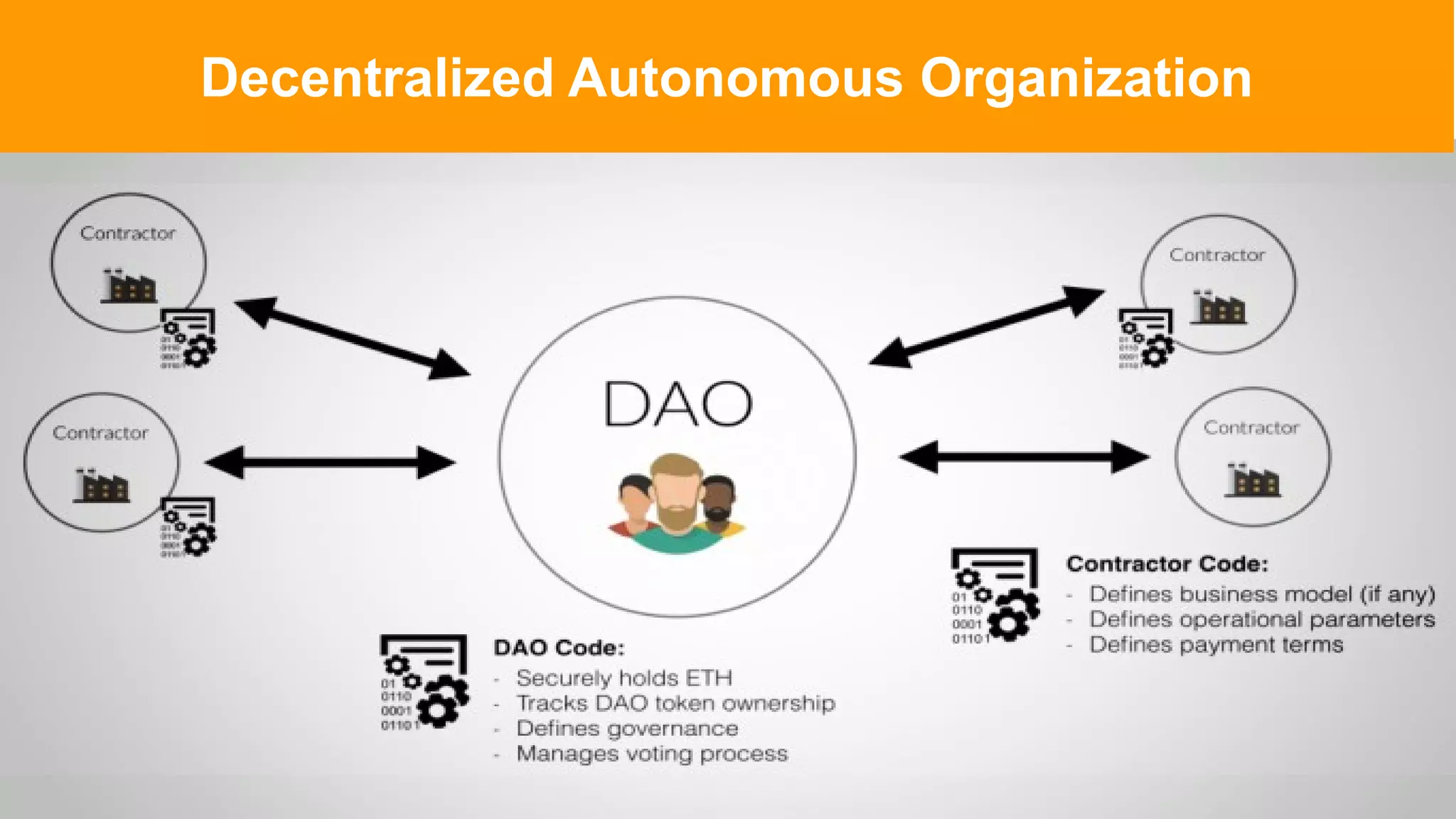
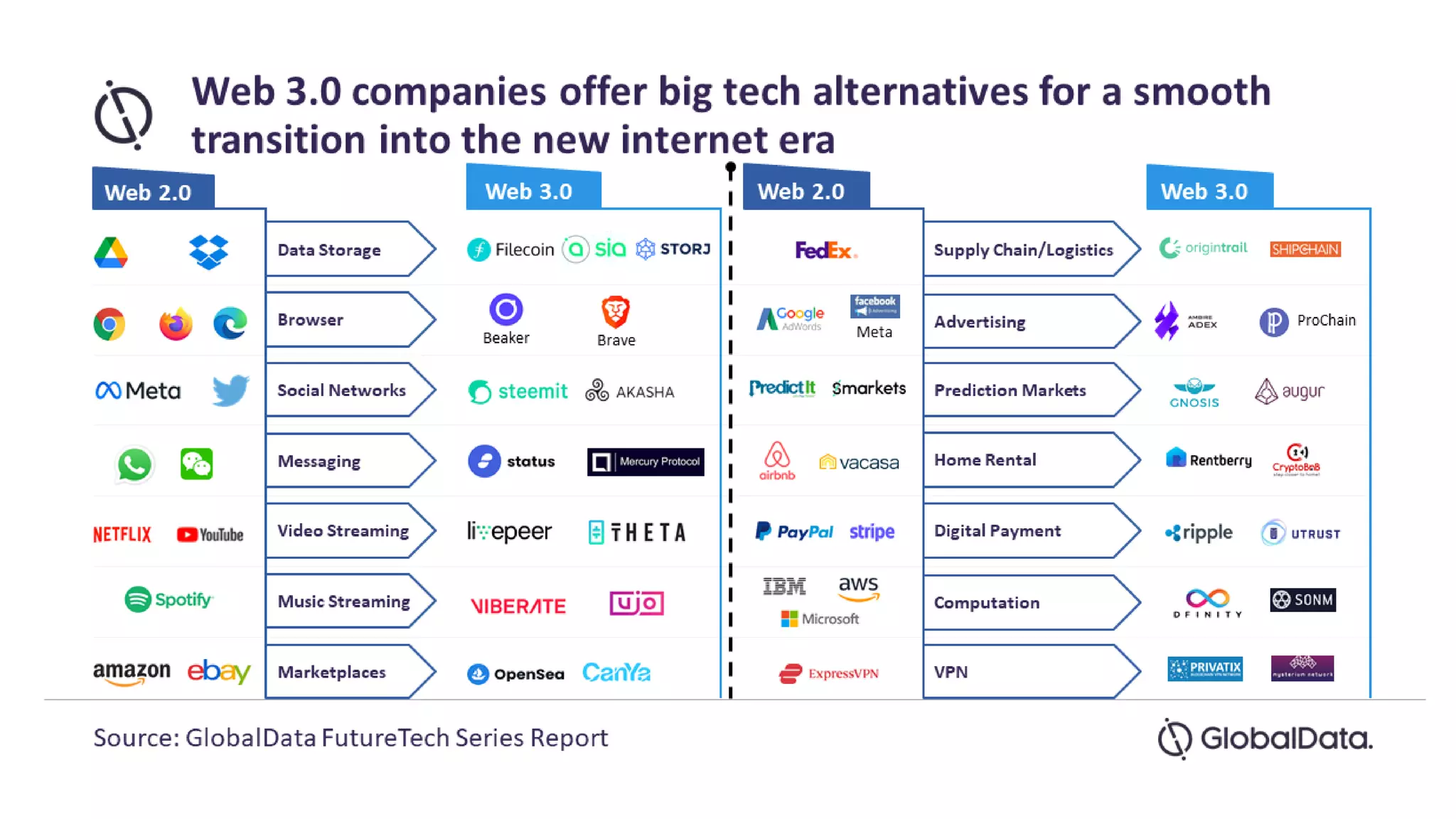
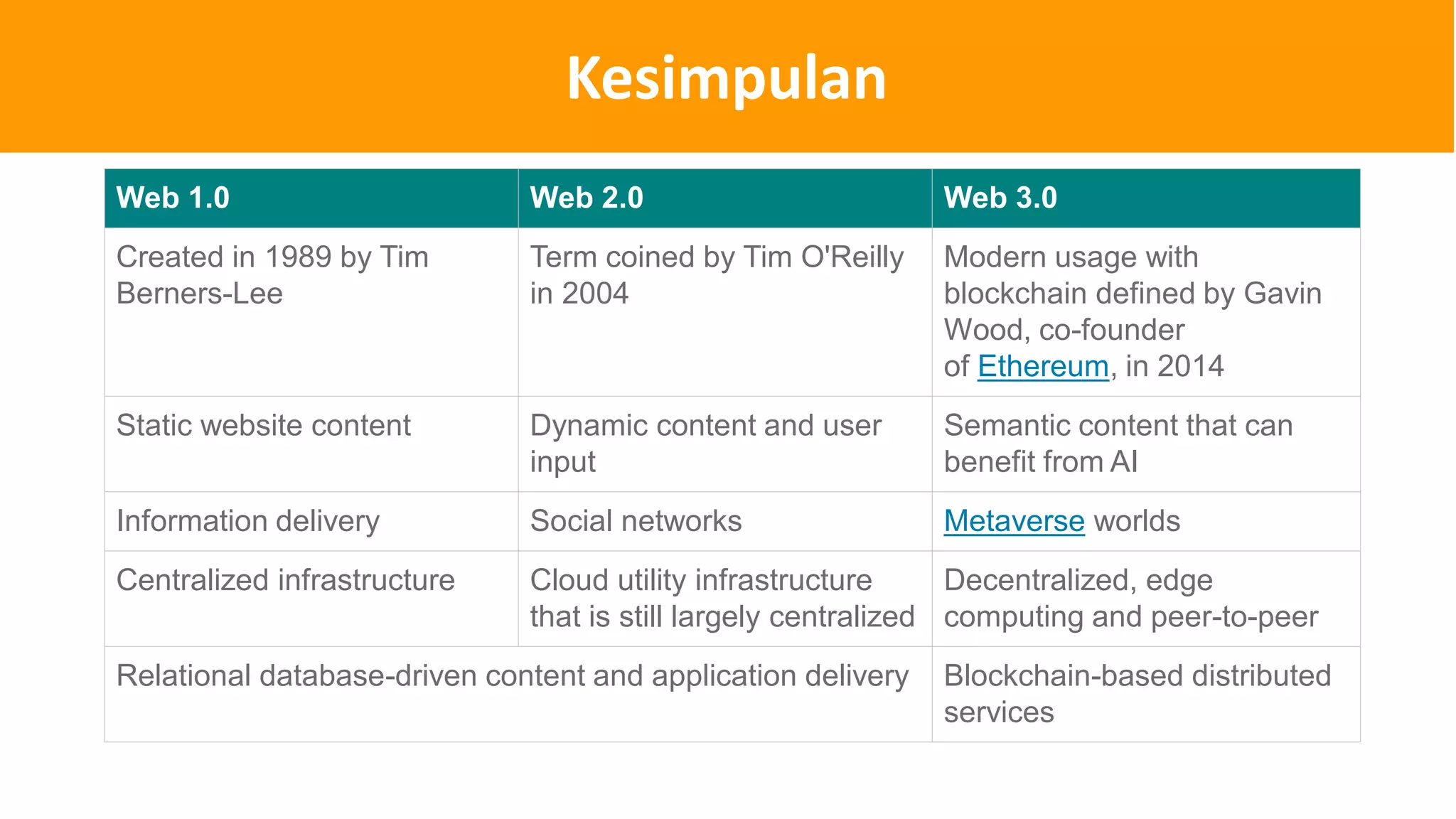
The document introduces Web 3.0, detailing its evolution from Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, emphasizing decentralized applications and user control over data. It outlines the key characteristics and components of Web 3.0, including blockchain, NFTs, and decentralized finance. The author urges continuous learning in related technologies to stay relevant in the evolving digital landscape.