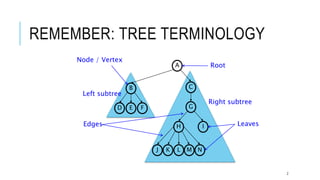
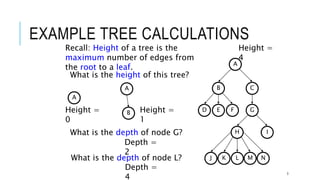
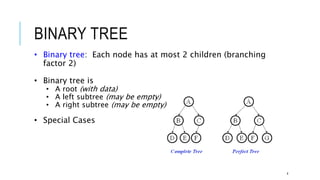
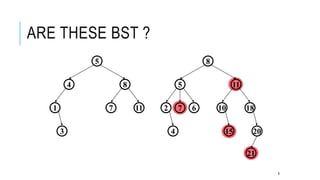
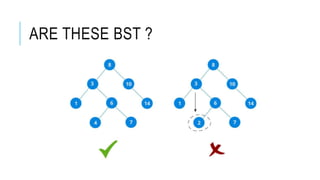
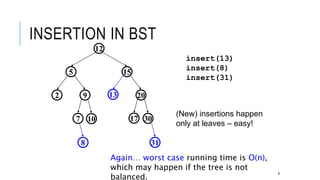
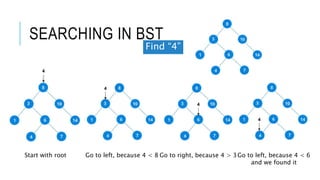
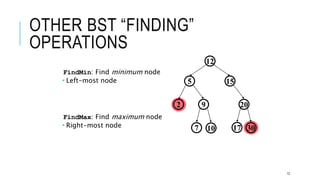
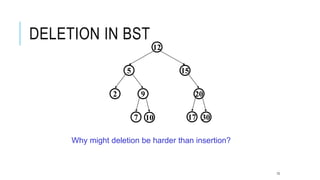
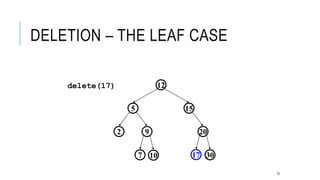
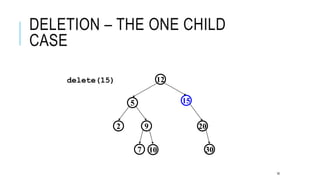
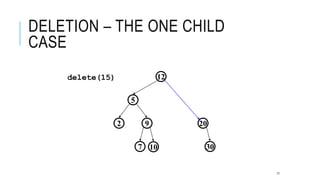
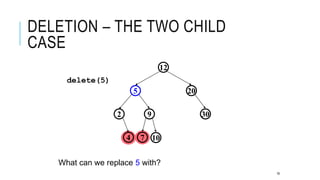
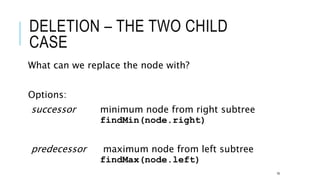
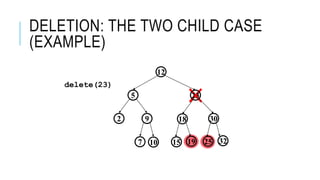
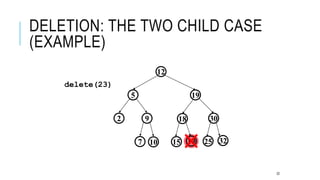
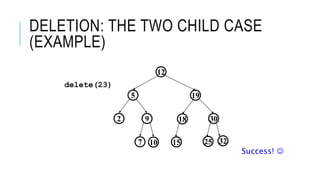
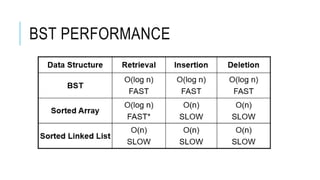
The document explains the binary search tree (BST) algorithm and data structure, detailing key concepts like tree terminology, properties of binary trees, and specific operations such as insertion, searching, and deletion in BSTs. It highlights the challenges of deletion compared to insertion and provides algorithms for managing different cases during deletions. The content is supported by references to academic slides and external resources.