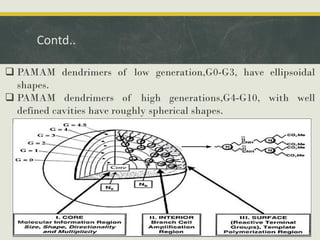
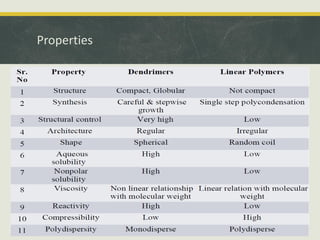
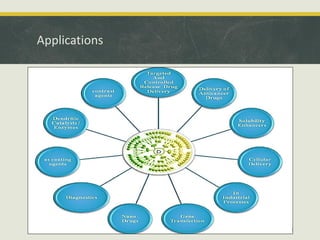
Dendrimers are synthetic, highly branched macromolecules that were first introduced in 1978. They are characterized by their highly branched 3D structure that provides a high degree of surface functionality. There are two main methods for synthesizing dendrimers - the divergent method, which starts from the core and extends outward, and the convergent method, which starts from the surface groups and progresses inward. Dendrimers can encapsulate drug molecules within their interior or attach drugs to their surface, making them useful for drug delivery applications by protecting drugs and controlling their release. Their properties and applications depend on their type, generation, and functional groups.