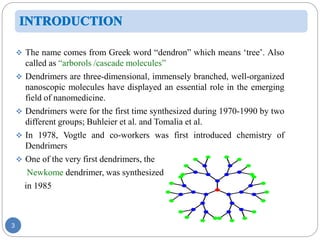
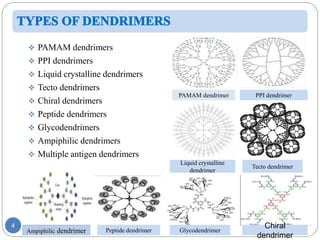
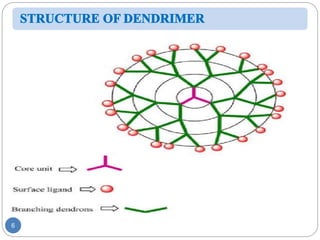
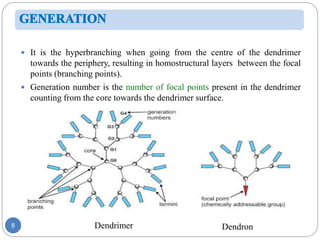
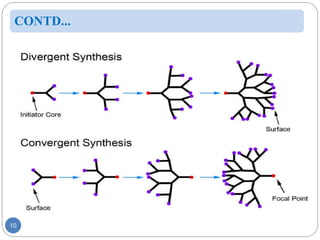
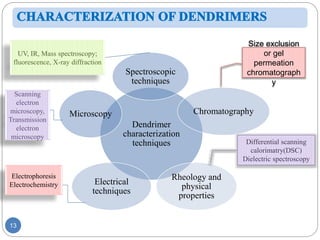
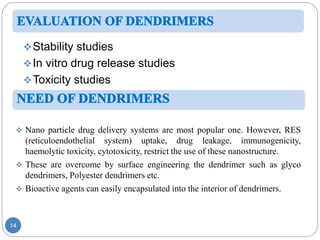
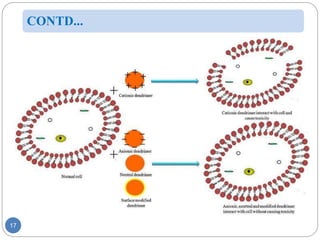
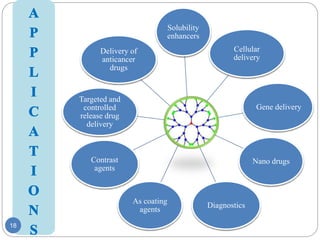
Dendrimers are nanoscale, tree-branching polymers that have potential applications as drug delivery agents. They are synthesized in a stepwise process that builds up branches around a core molecule. Dendrimers can encapsulate or conjugate to drug molecules, releasing them in a controlled manner. They have properties like water solubility and low toxicity that make them promising for targeted drug delivery. However, further research is still needed to address challenges like toxicity at high generations and scale up for commercialization before dendrimer-based drugs can be developed.