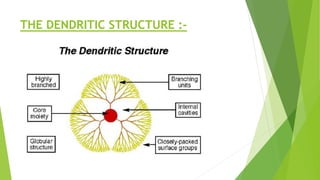
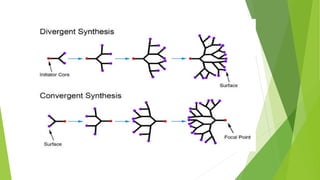
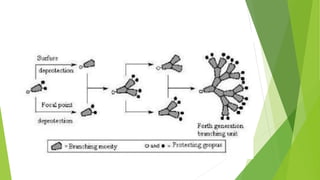
Dendrimers are synthetic, highly branched polymers with three distinct components: a core, interior layers, and an exterior surface. They are synthesized using either a divergent or convergent method. Dendrimers have many potential applications including as drug delivery systems, solubility enhancers, and in gene therapy due to their highly branched structure which allows encapsulation of bioactive molecules in their interior. They are characterized using techniques like spectroscopy, scattering, chromatography and microscopy. Common uses include delivery of anticancer drugs, enhancing drug solubility, and cellular delivery of therapeutic agents.