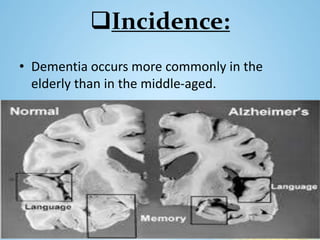
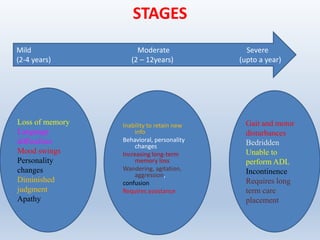
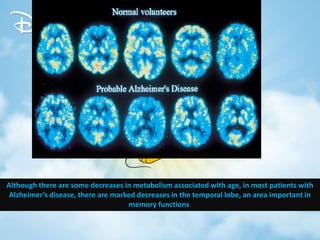
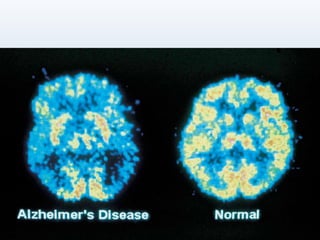
The document discusses dementia, defining it as an acquired impairment of intellect and memory, and classifying various types and disorders associated with it. It details the history, incidence, etiology, warning signs, clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment modalities for dementia, along with stages of the condition. It emphasizes the importance of awareness and education for both healthcare providers and individuals regarding dementia's signs, symptoms, and management strategies.