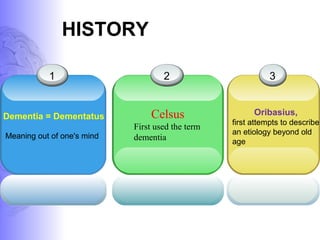
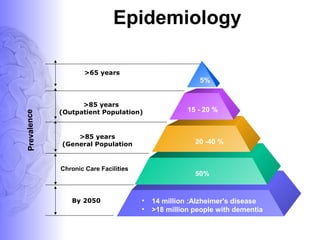
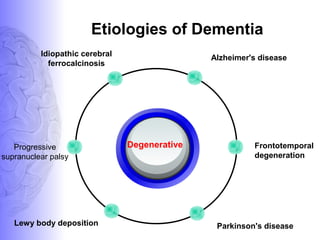
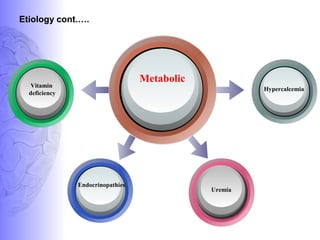
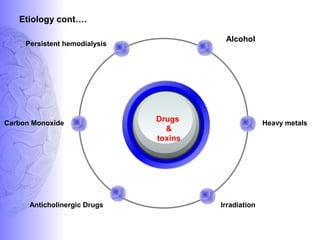
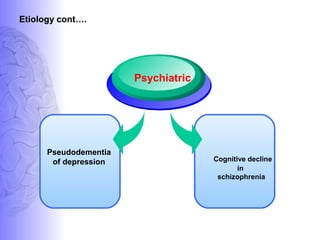
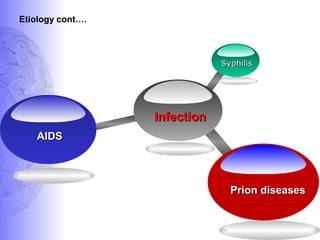
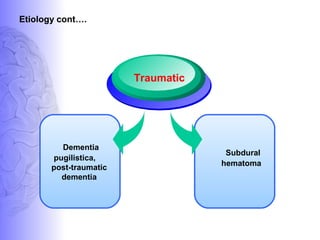
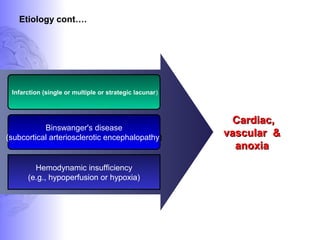
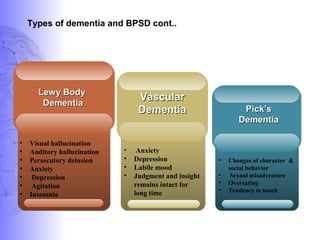
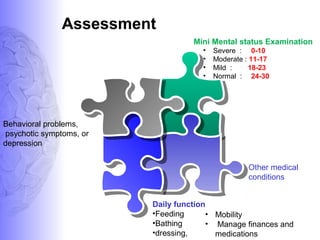
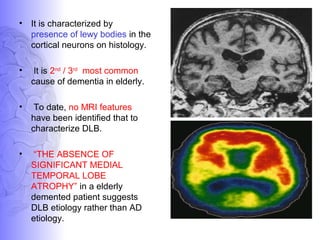
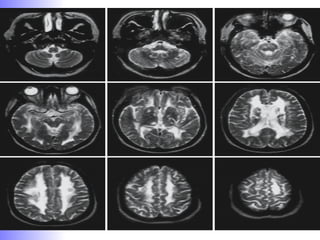
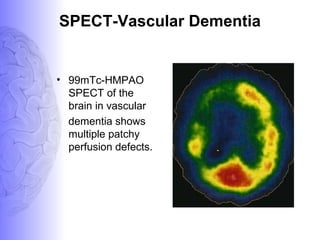
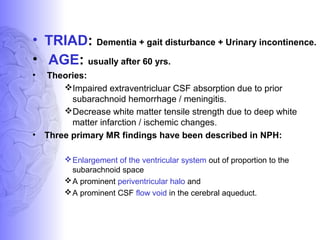
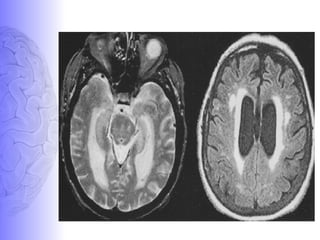
1. Dementia is defined as a progressive impairment of cognitive functions occurring in clear consciousness. The most common causes are Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal dementia, and vascular dementia.
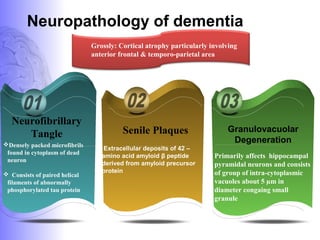
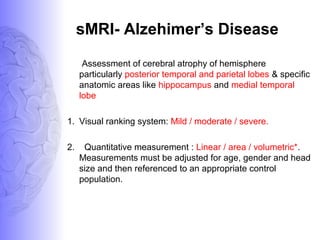
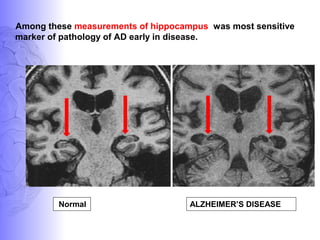
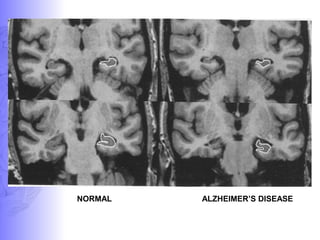
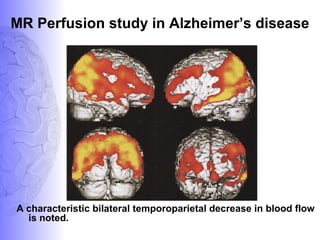
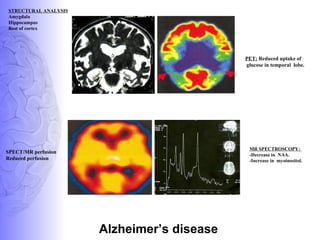
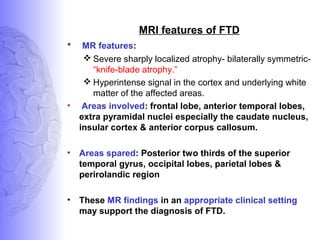
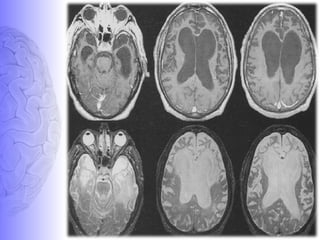
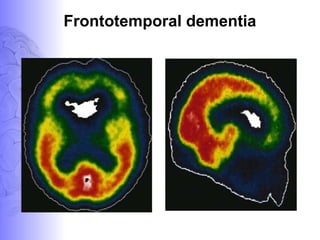
2. Neuroimaging and neuropathological findings help characterize different dementias. Alzheimer's disease shows hippocampal and temporal lobe atrophy on MRI and beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles microscopically. Frontotemporal dementia presents with frontal and anterior temporal lobe atrophy.
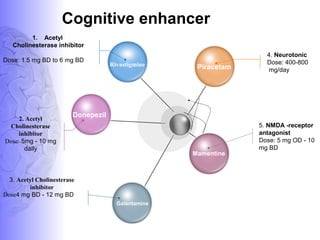
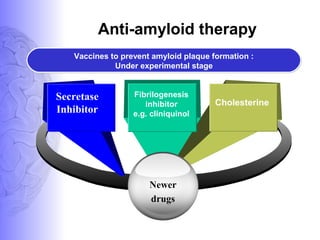
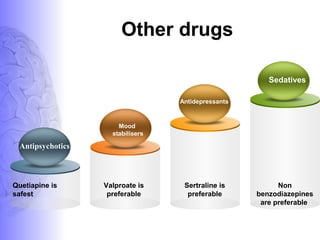
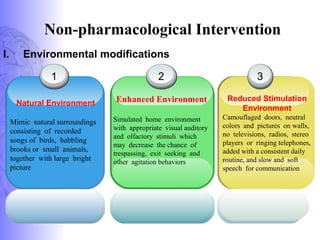
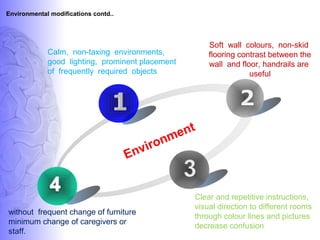
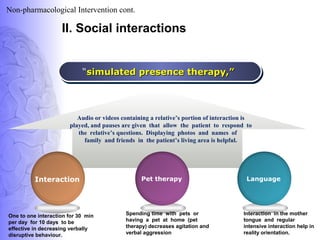
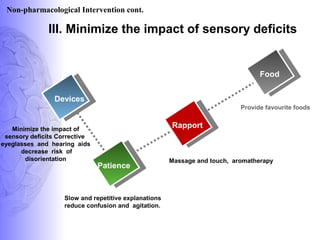
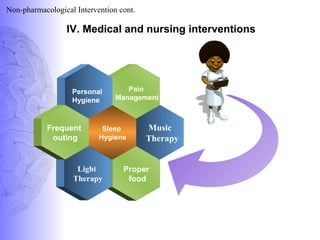
3. Treatment involves pharmacological interventions like cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for Alzheimer's, as well as non-pharmacological approaches like cognitive stimulation, environmental modifications, and