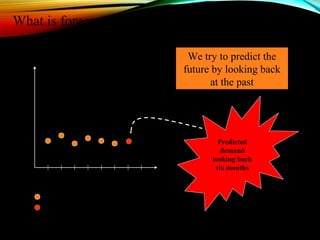
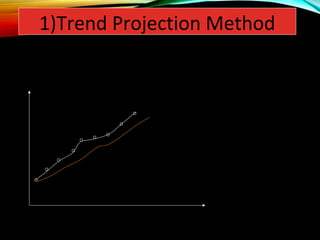
Demand forecasting involves using past demand information to predict future demand. It is important for production planning, acquiring supplies, financial planning, pricing strategies, and advertising. Both qualitative and quantitative techniques are used. Qualitative techniques like expert opinion and surveys are used when little historical data exists, while quantitative time series analysis of trends, seasons, cycles, and random variations is used for existing products. Forecasting allows production to match demand and helps businesses plan effectively.