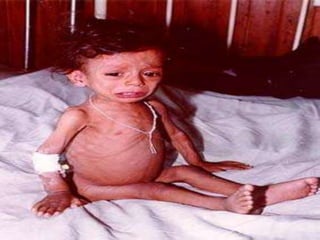
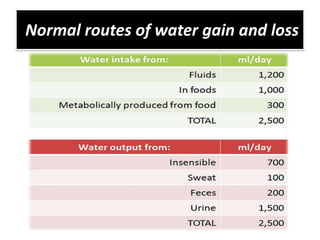
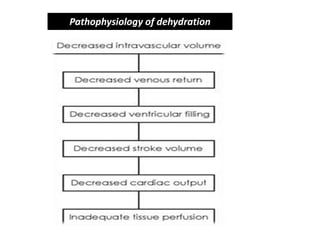
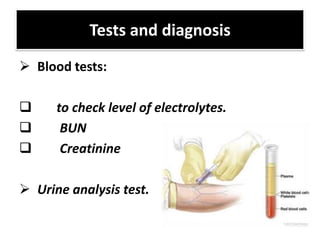
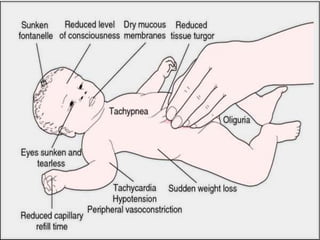
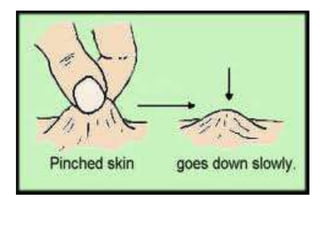
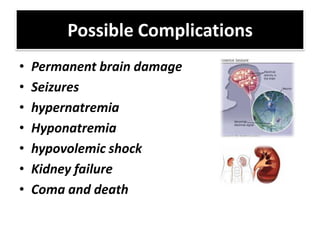
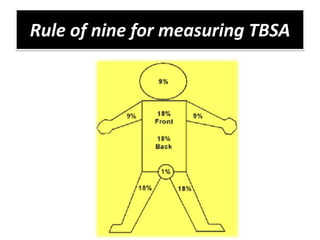
This document discusses dehydration in pediatrics. It defines dehydration and explains its pathophysiology and types based on severity and fluid/electrolyte loss. Causes of dehydration include diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, diabetes and burns. Diagnosis involves blood and urine tests to check electrolyte levels. Signs and symptoms range from mild thirst to severe complications depending on the percentage of fluid loss. Treatment involves oral or IV fluid replacement depending on severity. Nursing care focuses on monitoring fluid intake and output, providing skin care and educating families on prevention.