This document contains a series of questions about concepts related to gravity, including:
- How the weight of an object changes as it moves closer to or farther from Earth.
- How weight and mass are different on the moon compared to Earth.
- Factors that determine gravitational force and how it relates to mass.
- Graphs showing changes in weight over time or distance from massive objects.
- Calculating weight and force on different celestial bodies given their gravitational acceleration.
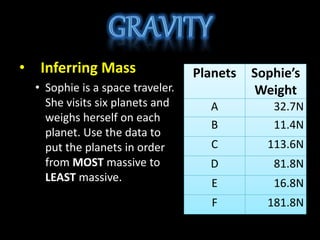
- Inferring the relative masses of planets based on an astronaut's measured weight.
- How gravitational force varies with distance and mass between objects.
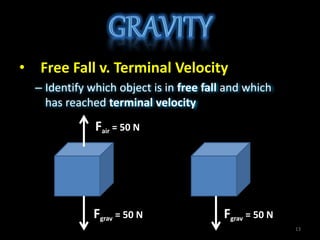
- Identifying examples of objects in free fall versus at terminal velocity.
- The