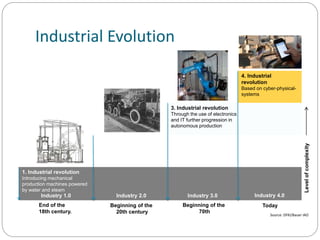
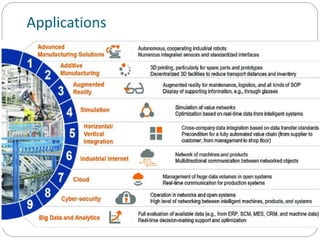
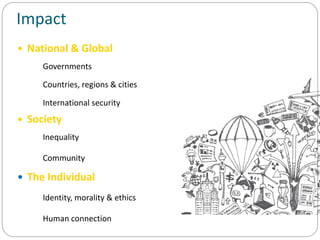
The document discusses the evolution of industry, focusing on the Fourth Industrial Revolution characterized by cyber-physical systems and their applications. It outlines key principles and building blocks of Industry 4.0, such as interoperability and real-time capabilities, and highlights its impacts on the economy, business, and society. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of evolving skills for individuals to remain relevant in this new industrial landscape.