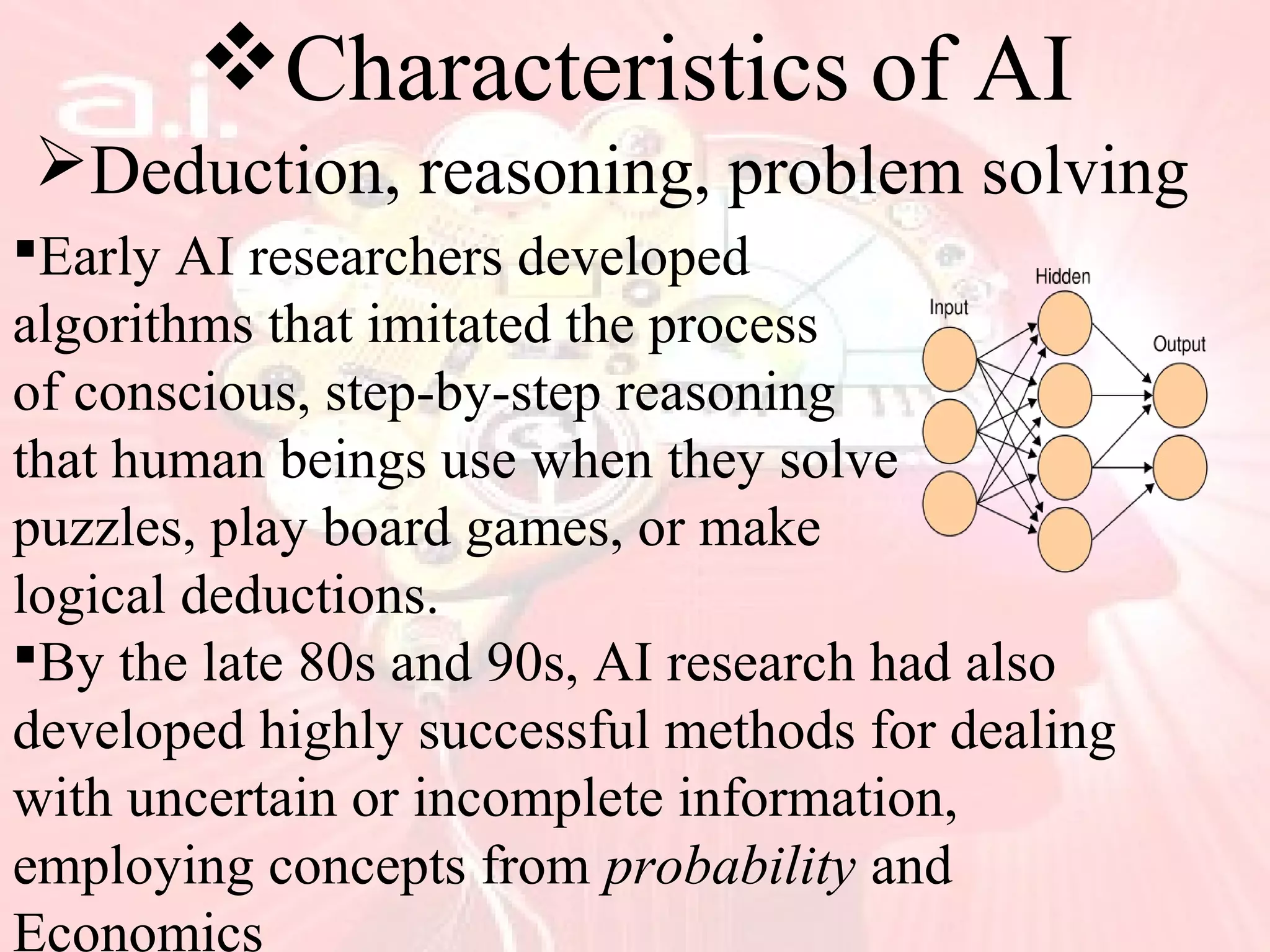
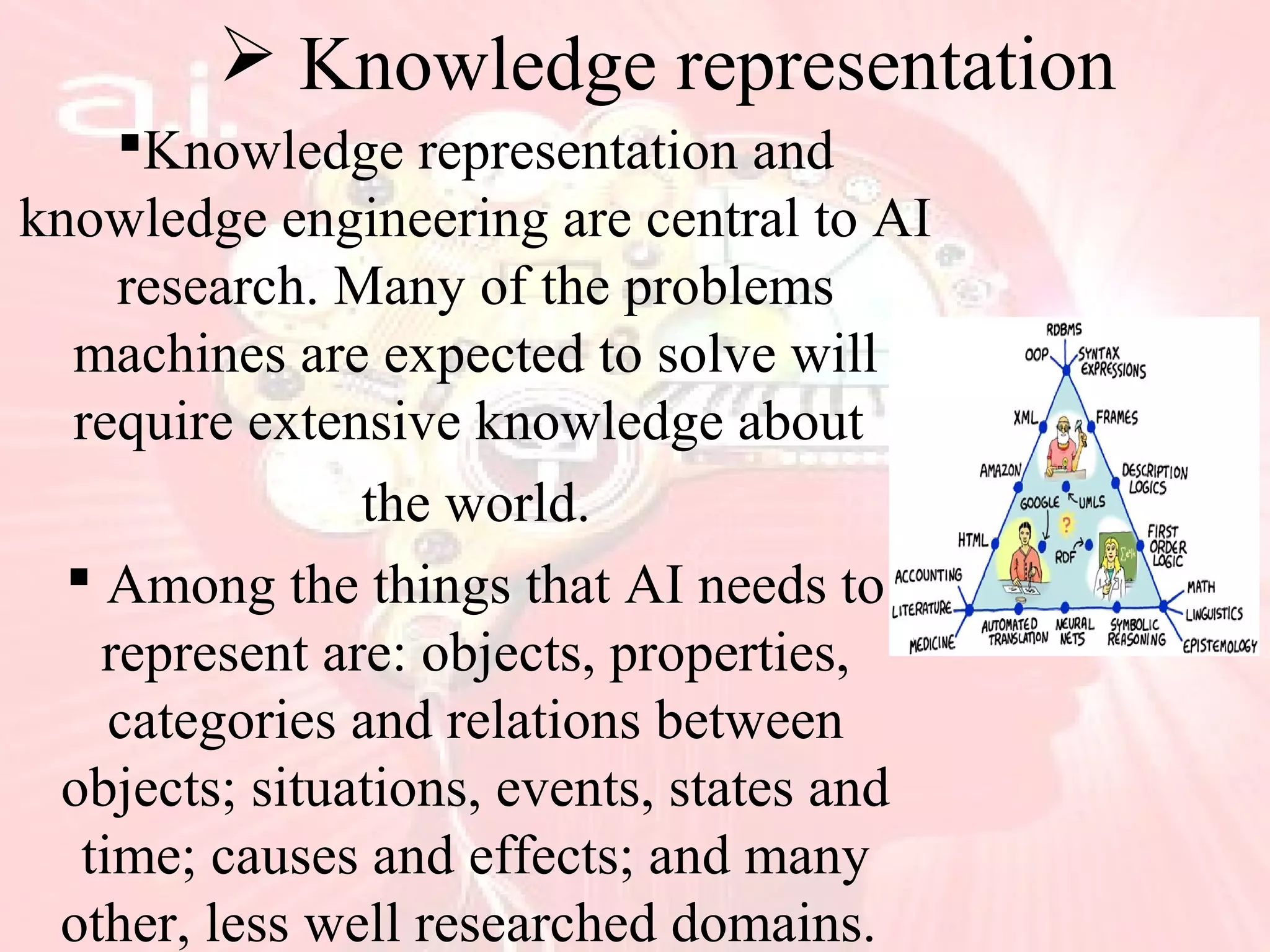
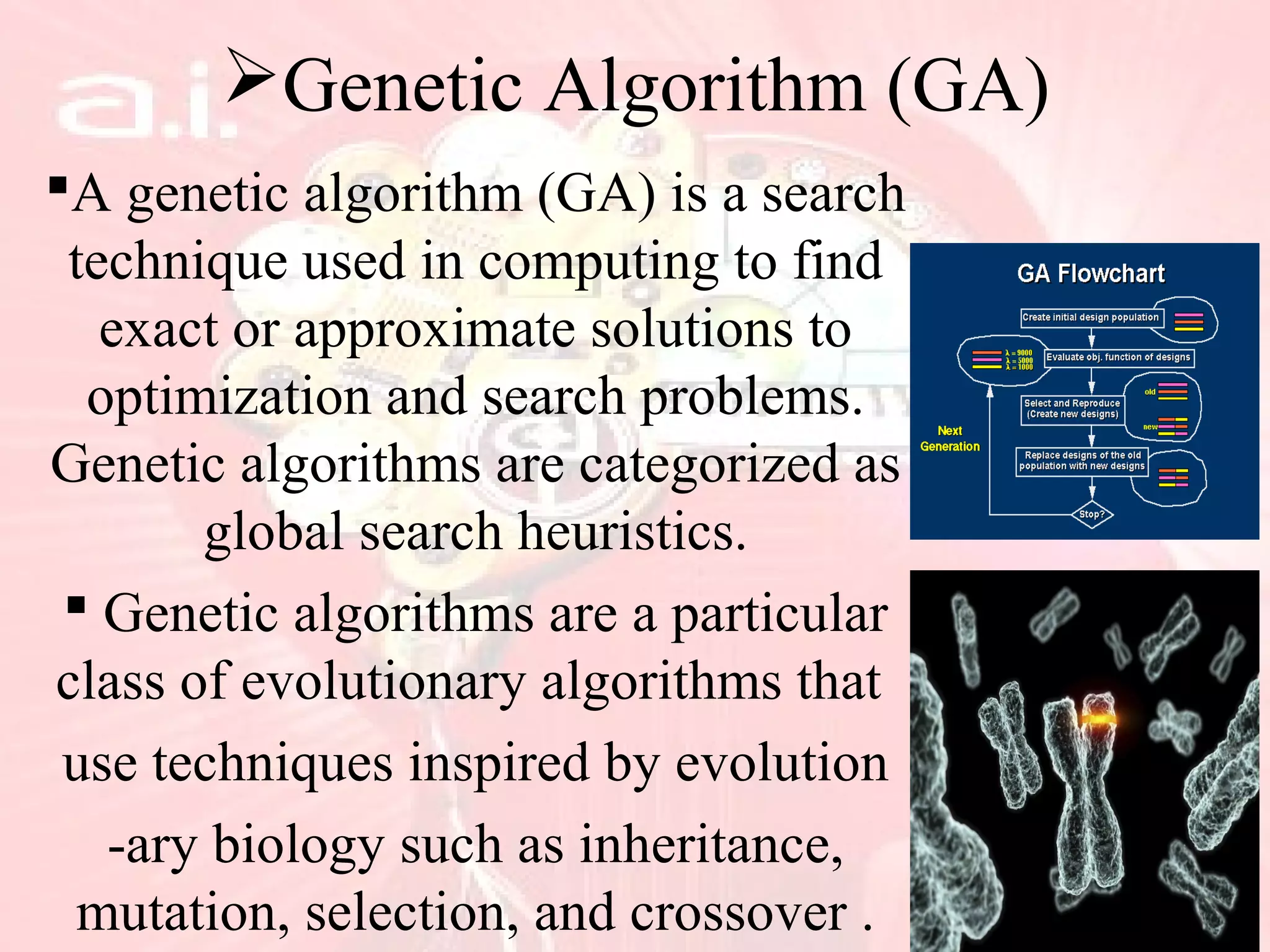
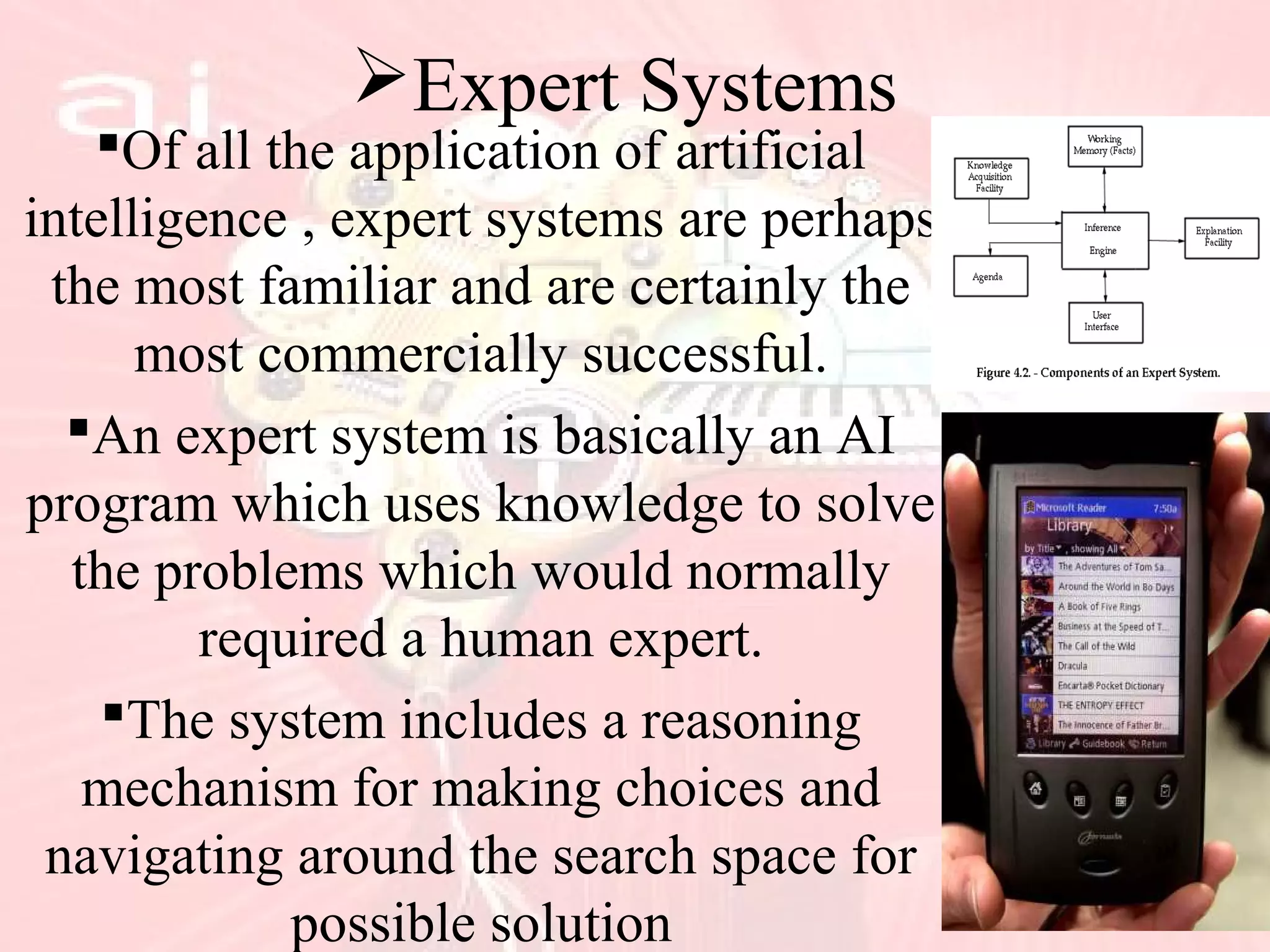
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence, including its history, key concepts like neural networks and fuzzy logic, characteristics such as problem solving and learning, applications in fields like finance and medicine, and programming languages commonly used in AI like Lisp and Prolog. While AI has made impressive advances, it has yet to achieve human-level intelligence and abilities like autonomous learning from diverse, real-world experiences. Future progress may require better integration of existing techniques.