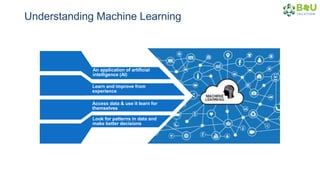
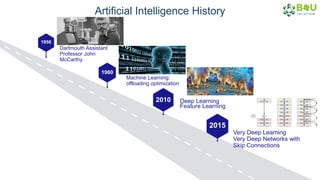
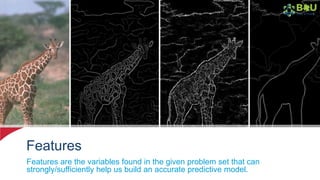
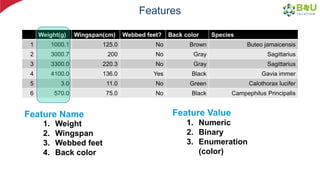
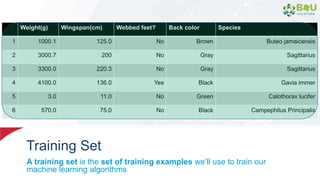
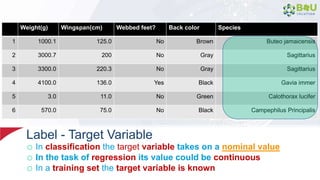
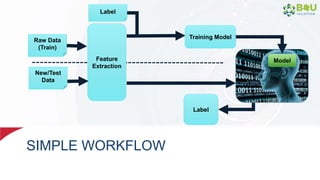
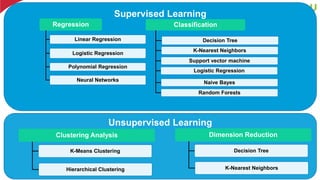
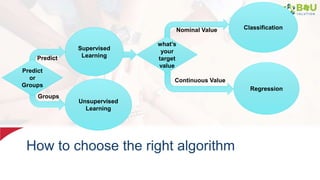
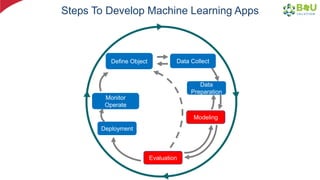
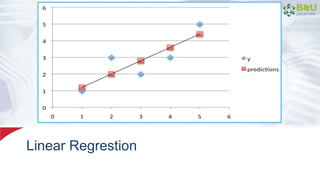
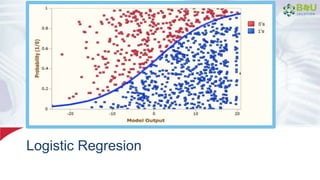
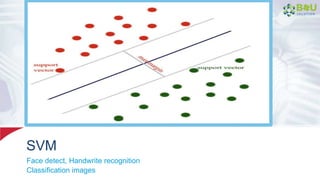
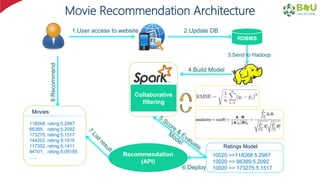
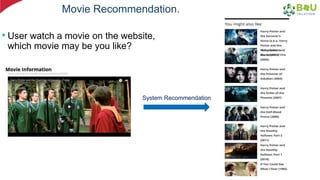
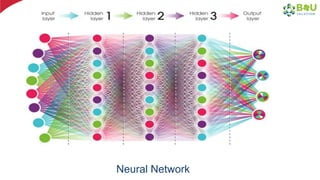
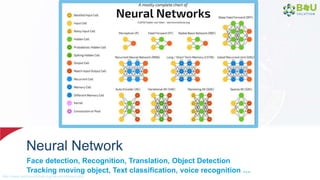
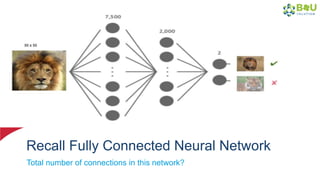
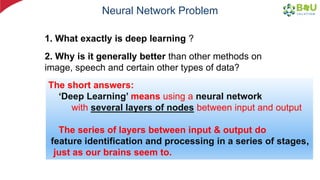
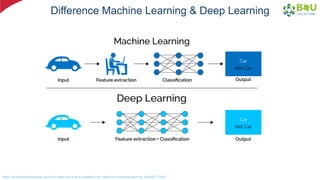
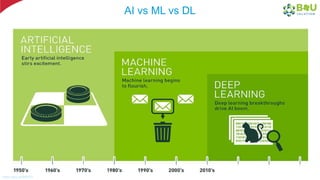
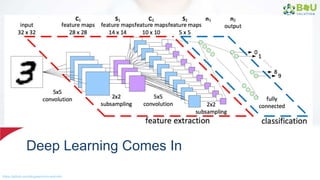
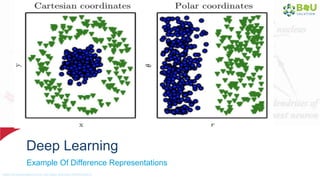
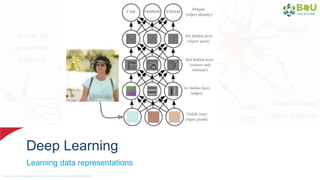
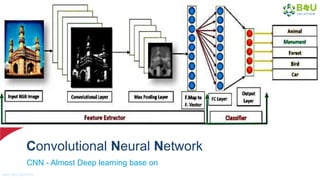
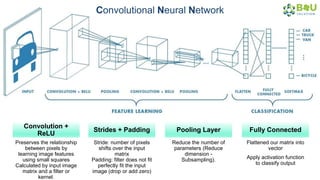
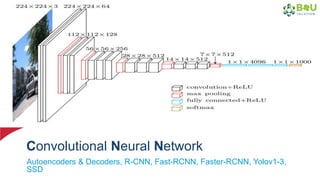
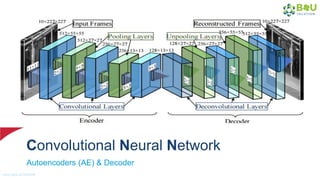
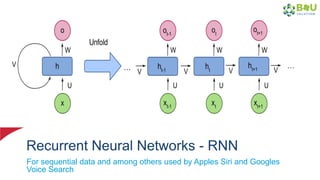
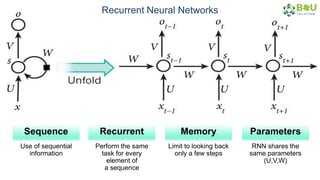
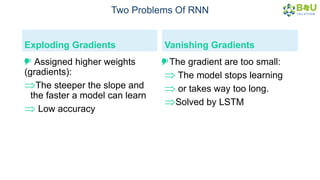
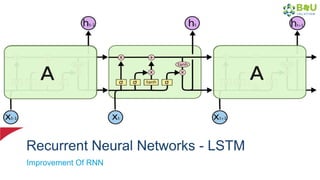
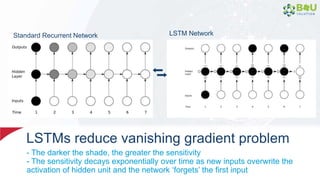
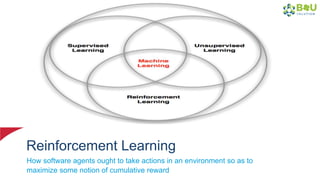
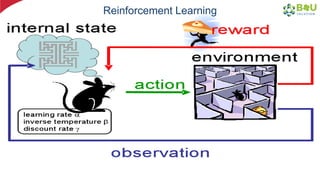
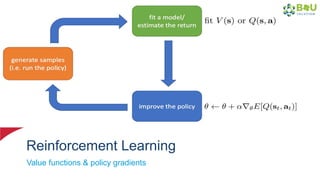
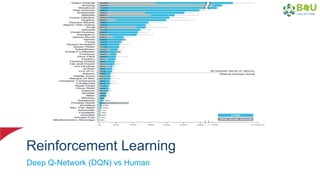
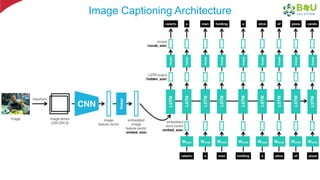
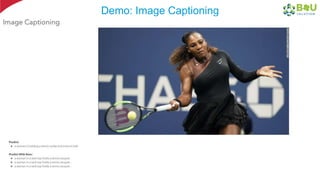
The document discusses machine learning and deep learning, focusing on their definitions, algorithms, and applications. It covers essential concepts such as training sets, classification, feature extraction, and different types of machine learning algorithms, including supervised and unsupervised learning. Additionally, the document highlights real-world applications like movie recommendations and image captioning using deep learning methods.