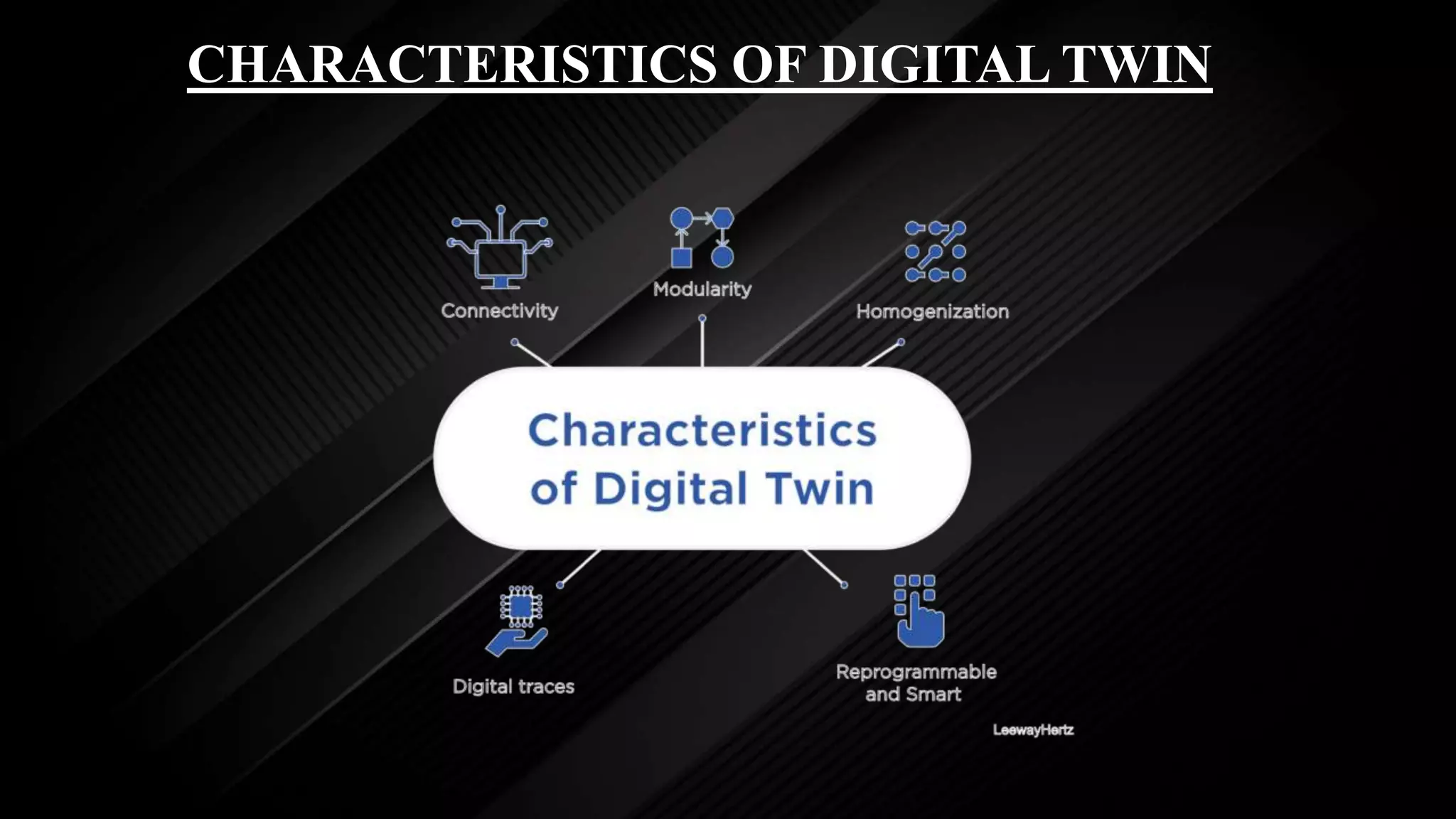
This document discusses digital twin technology. It defines a digital twin as a virtual representation of a physical object that can accurately mimic the performance of the physical object. The document outlines the characteristics, architecture, features, advantages, and applications of digital twins. Digital twins are used across industries like manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, and smart cities to improve design, monitoring, predictive maintenance, and more. The success of digital twins depends on connectivity to real-time data from physical objects and sensors.