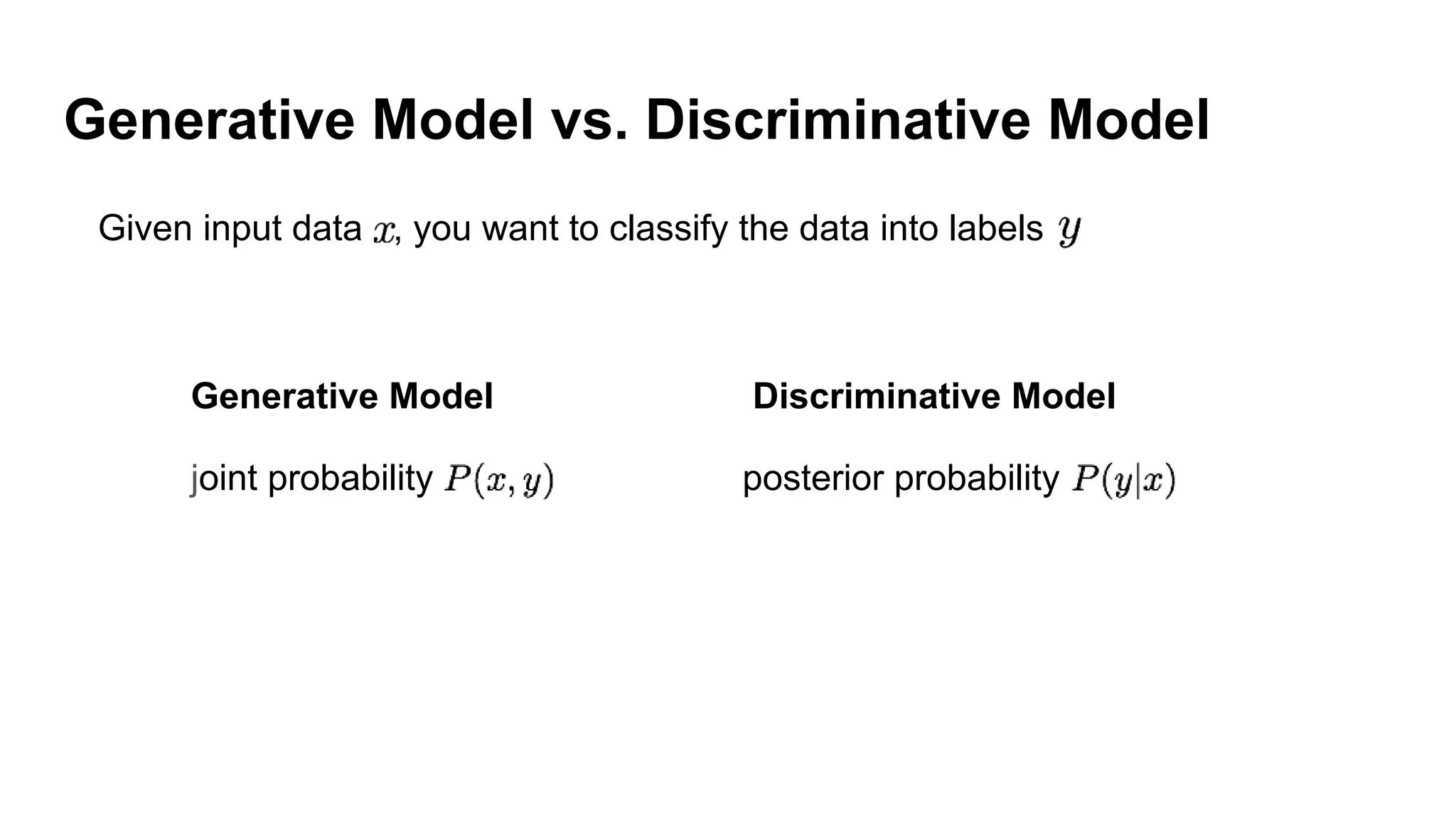
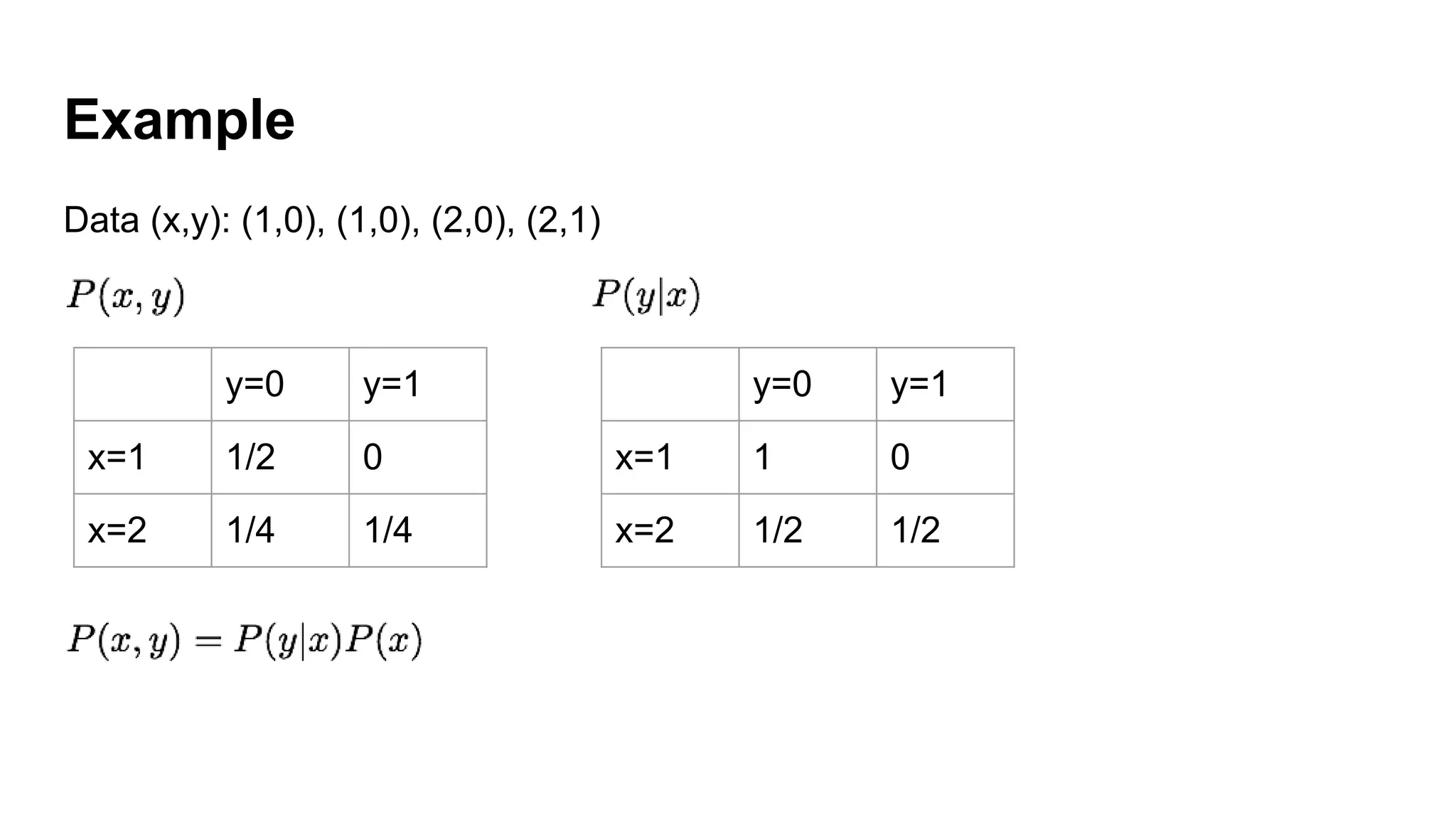
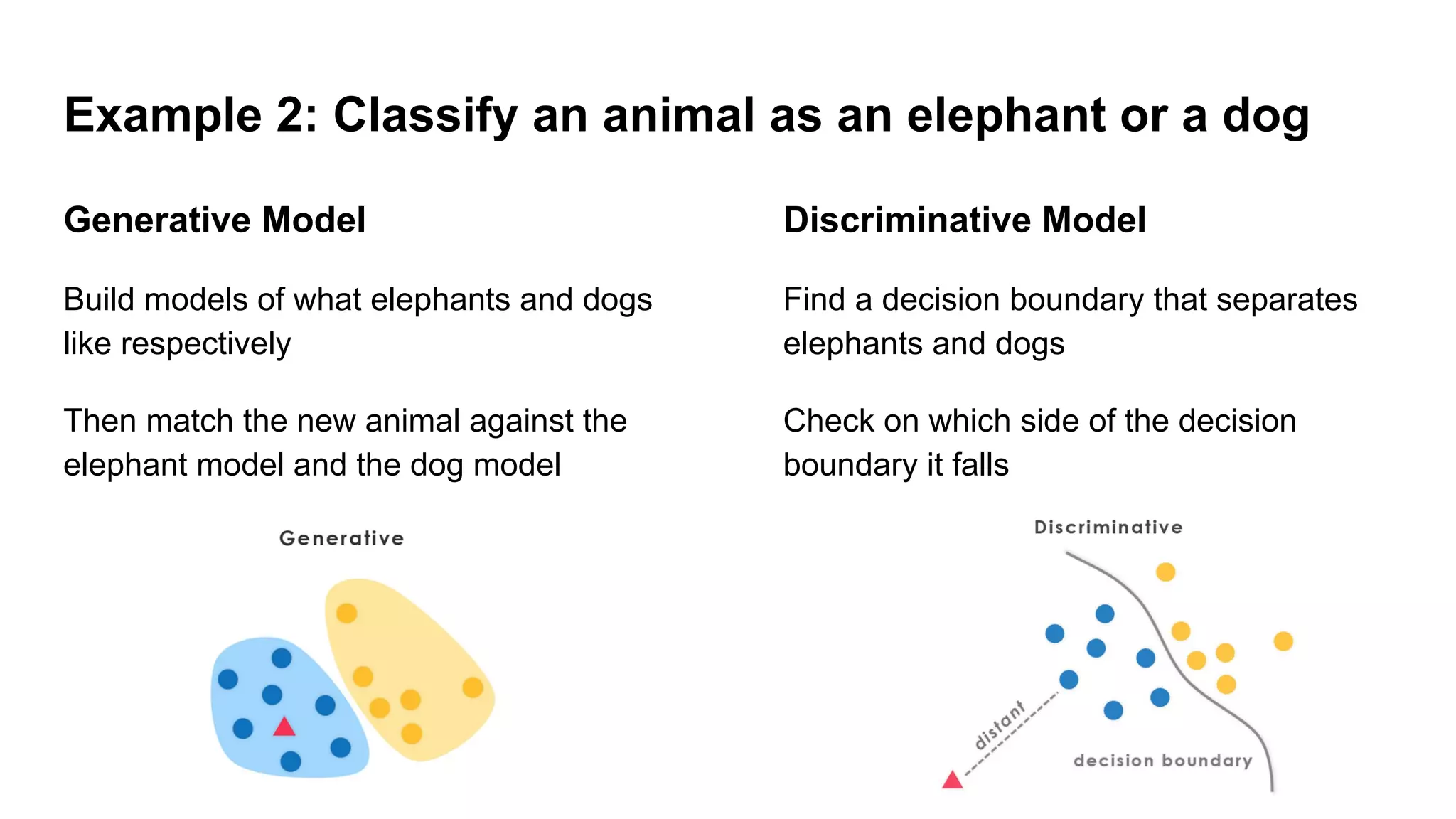
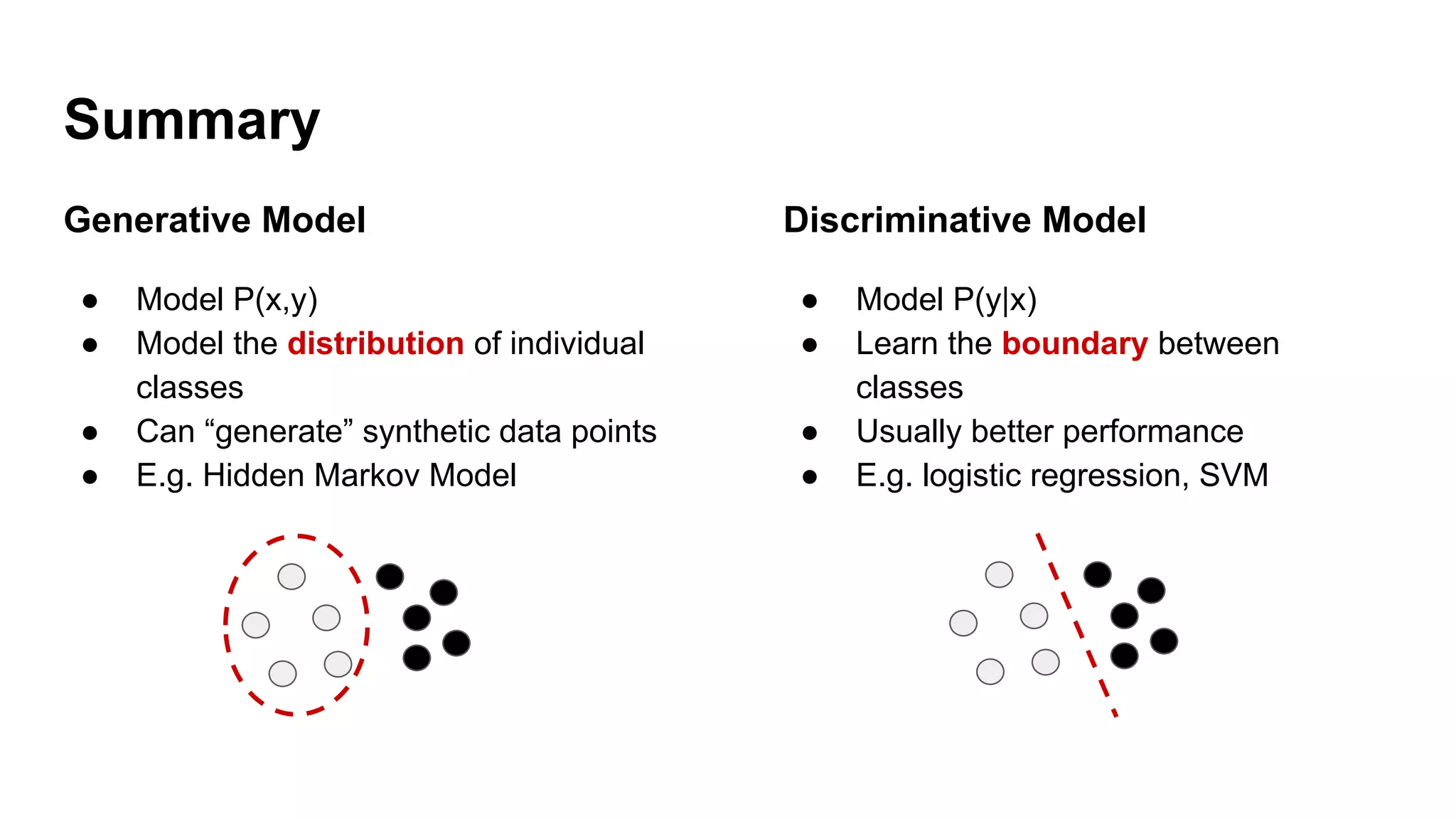
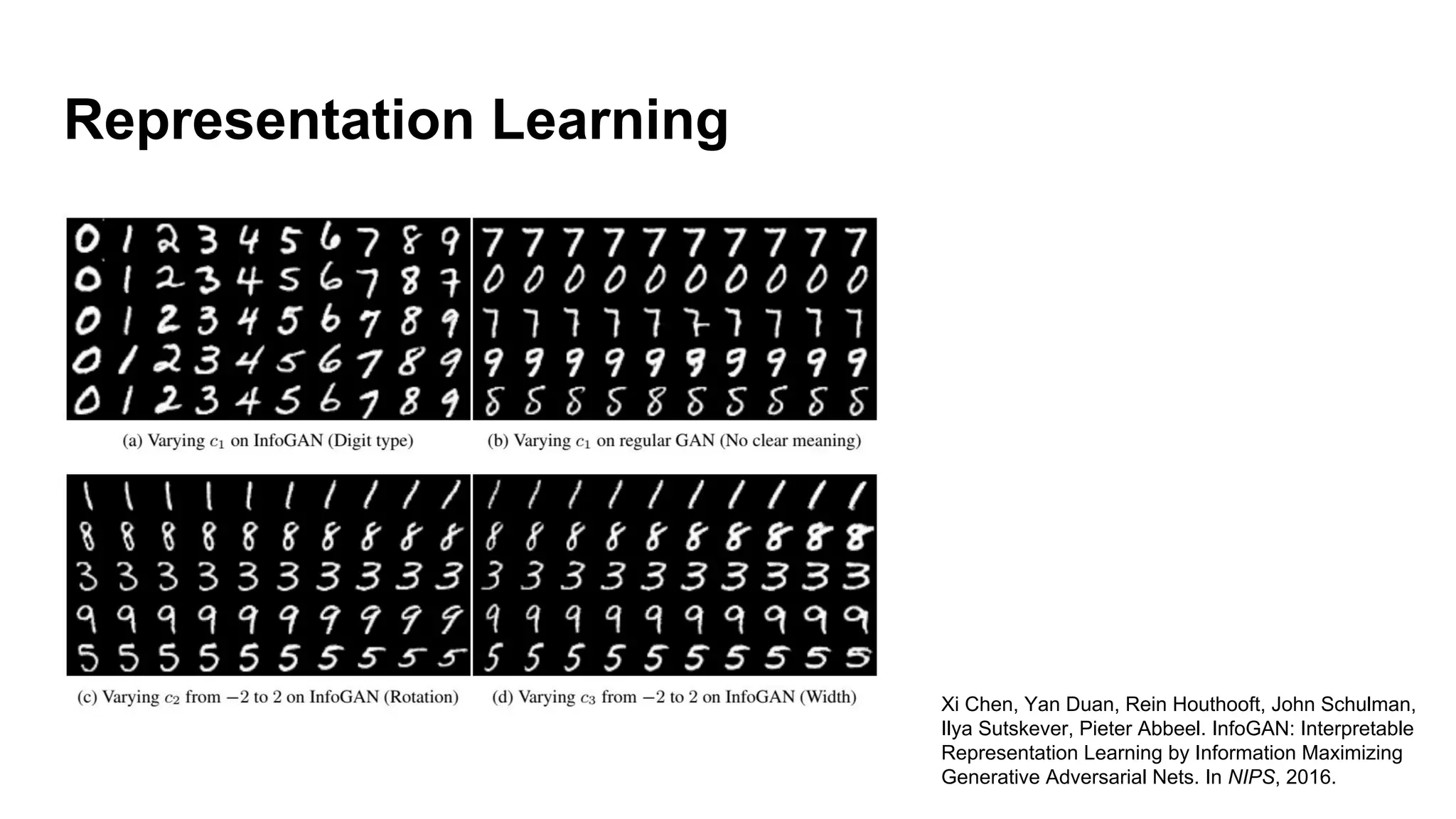
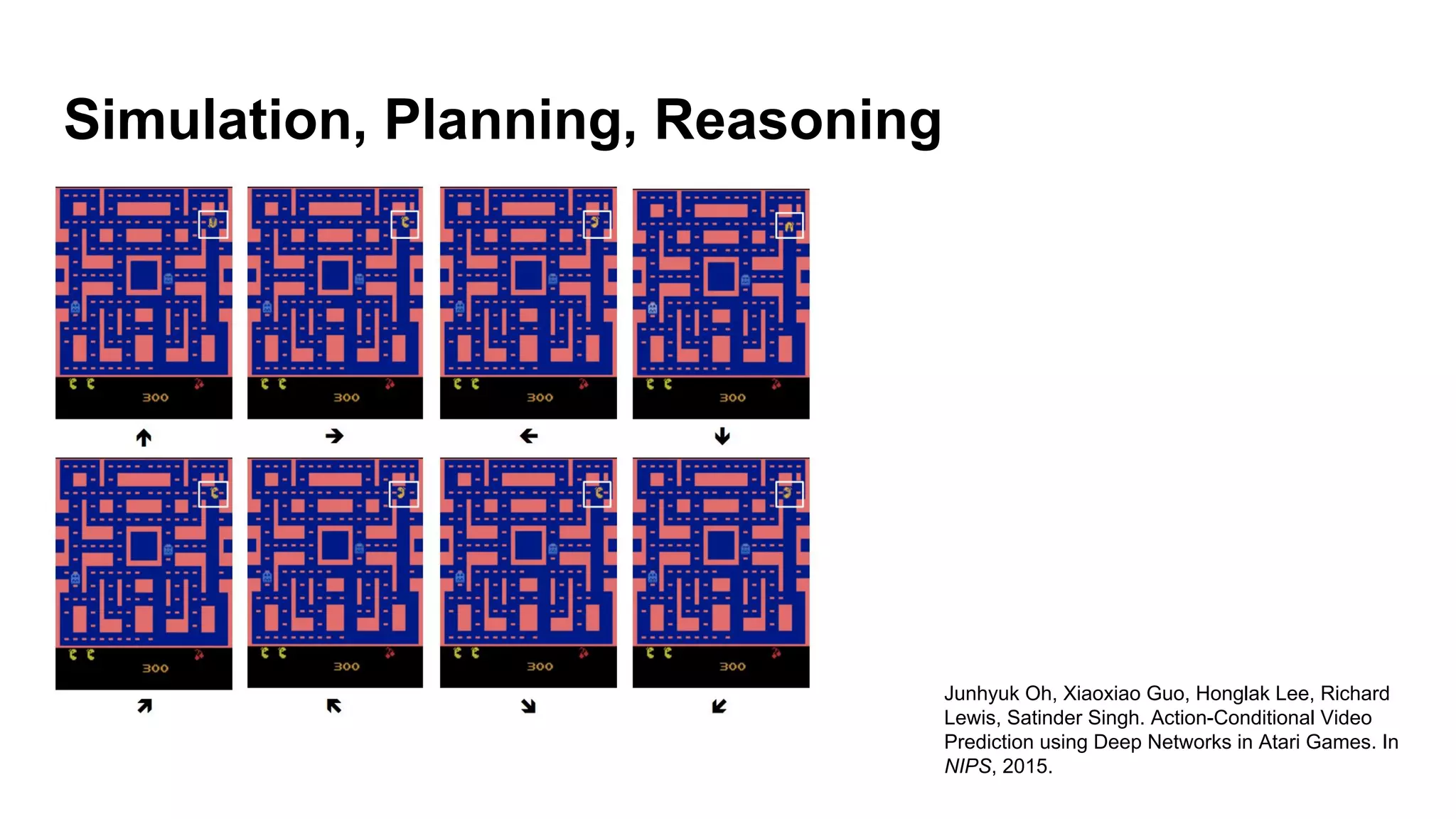
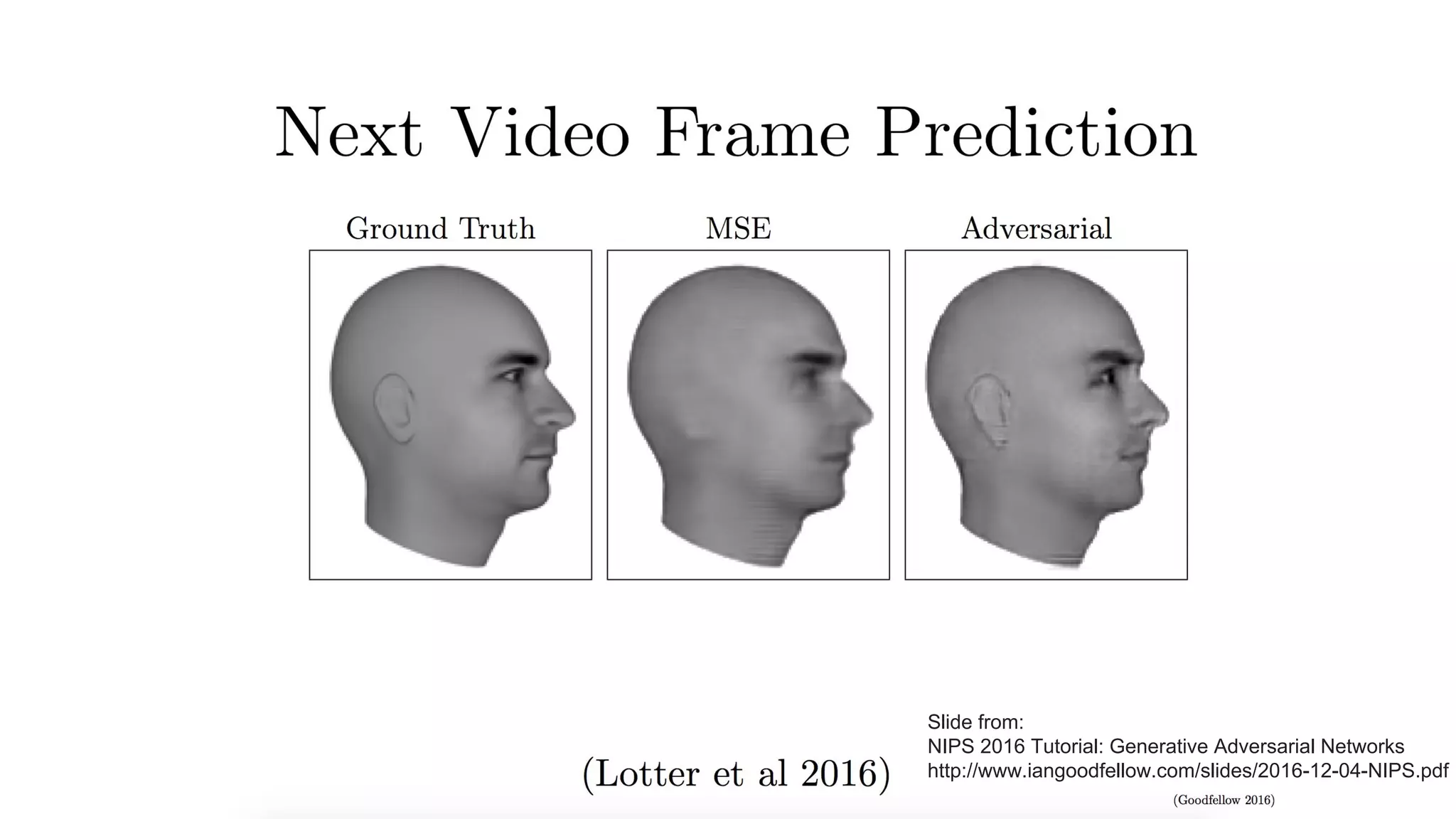
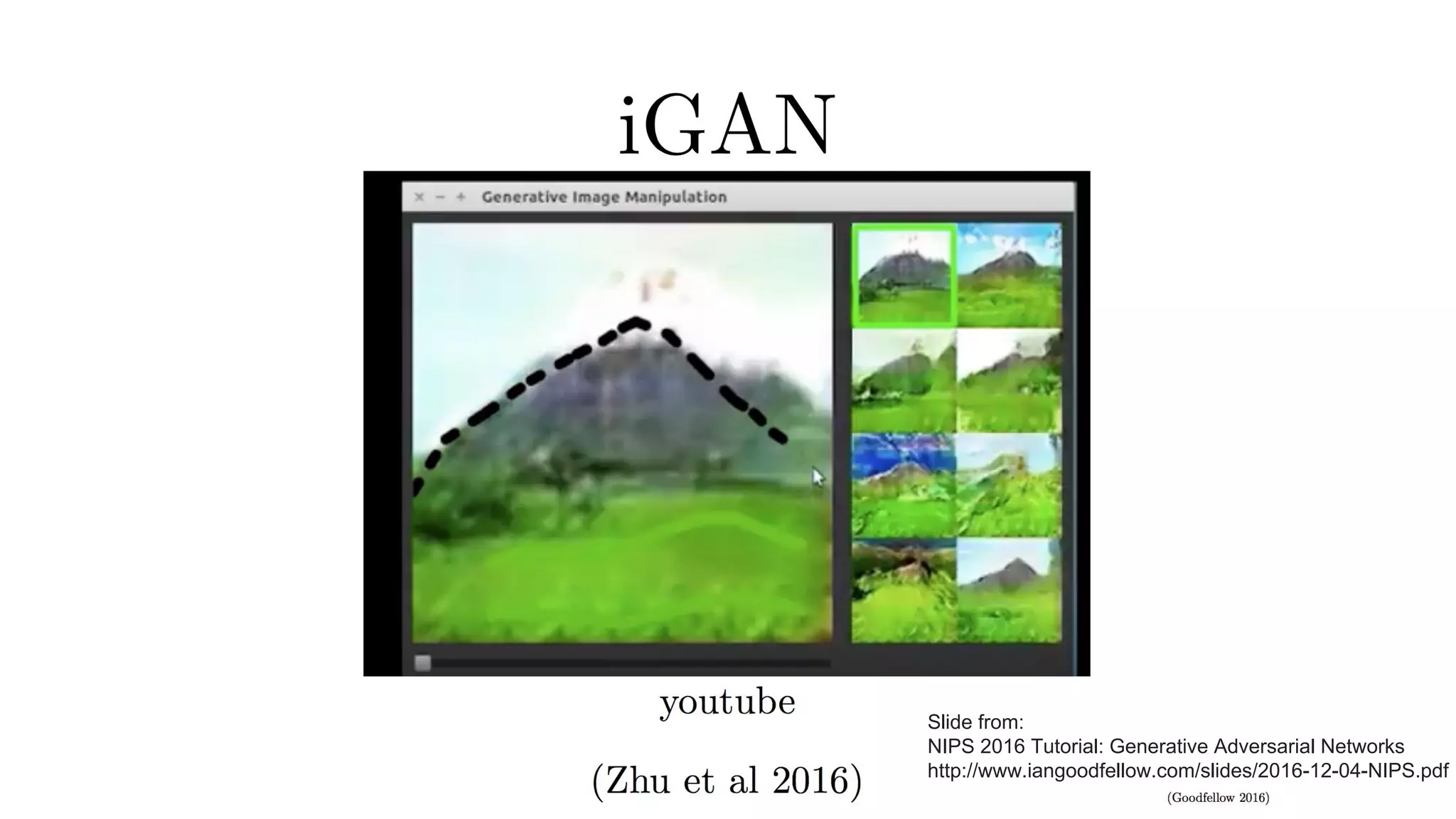
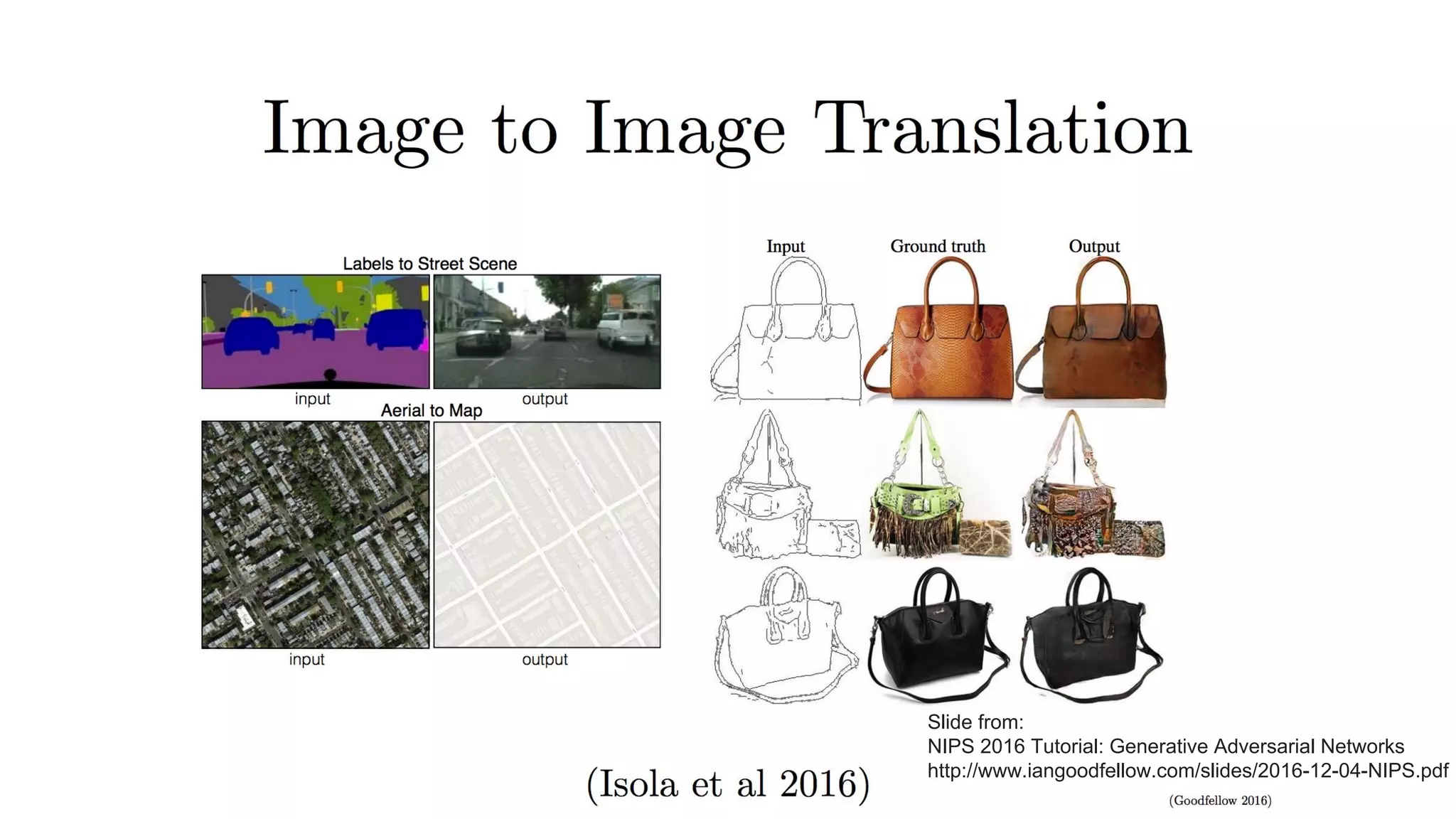
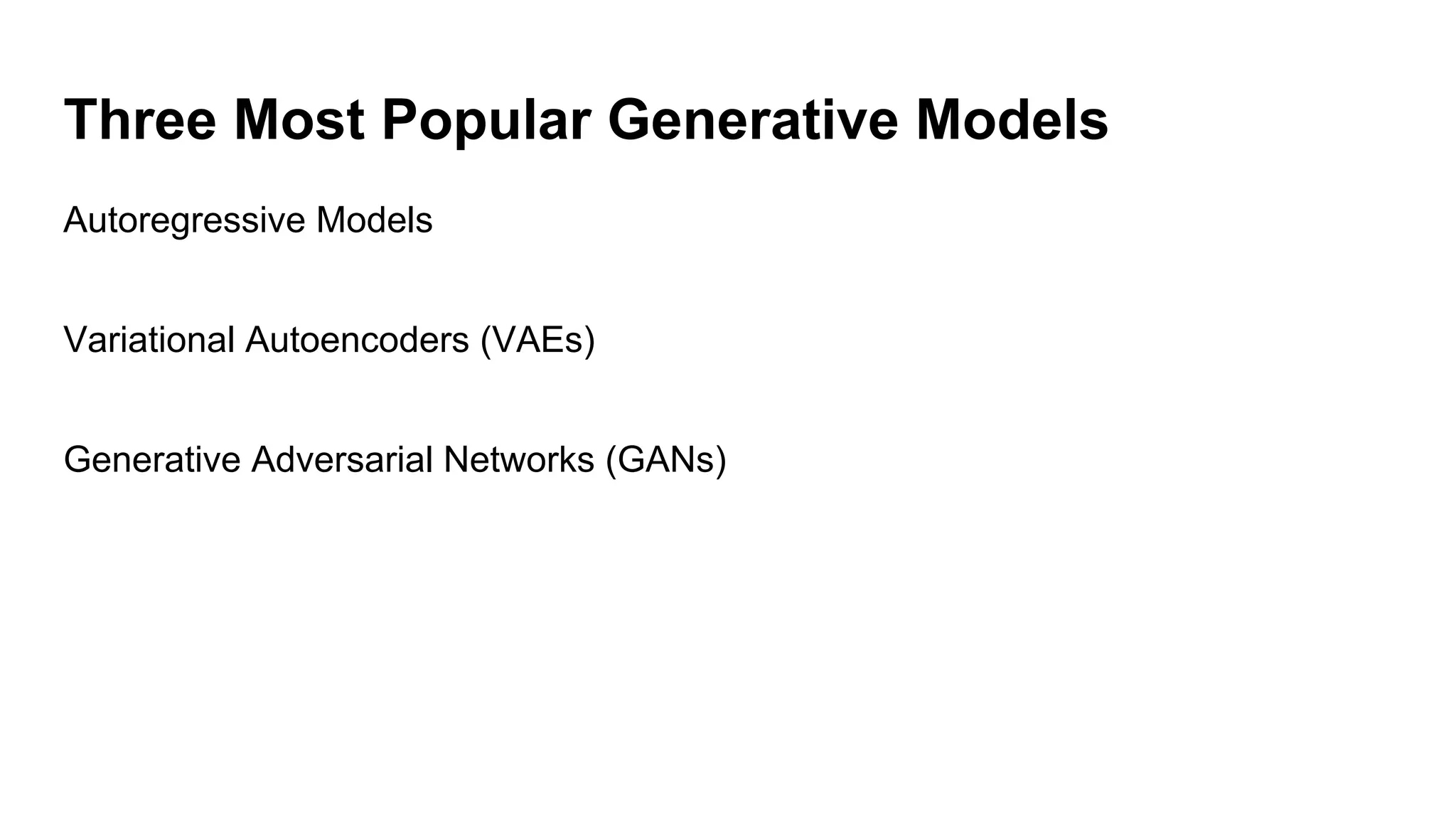
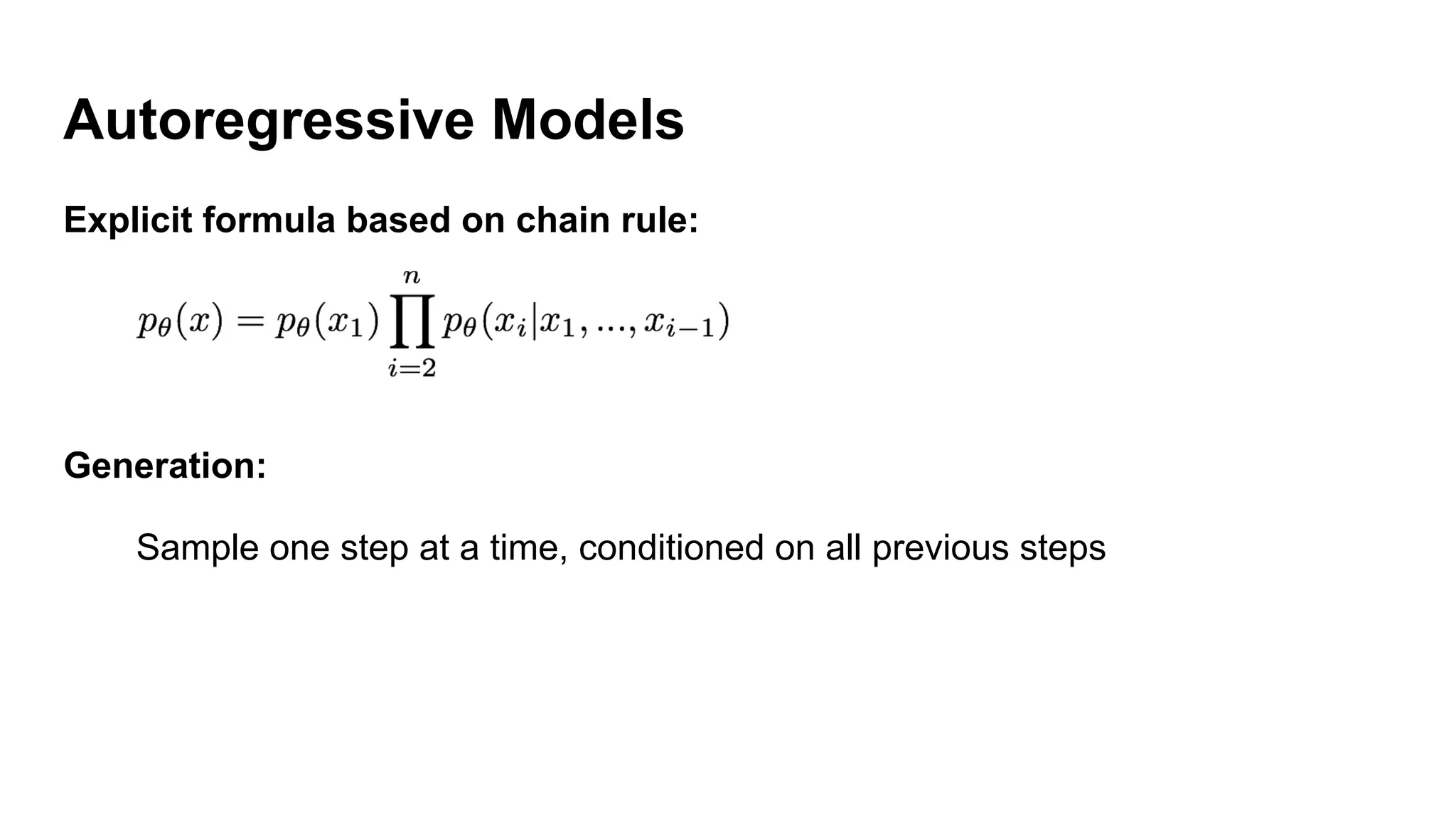
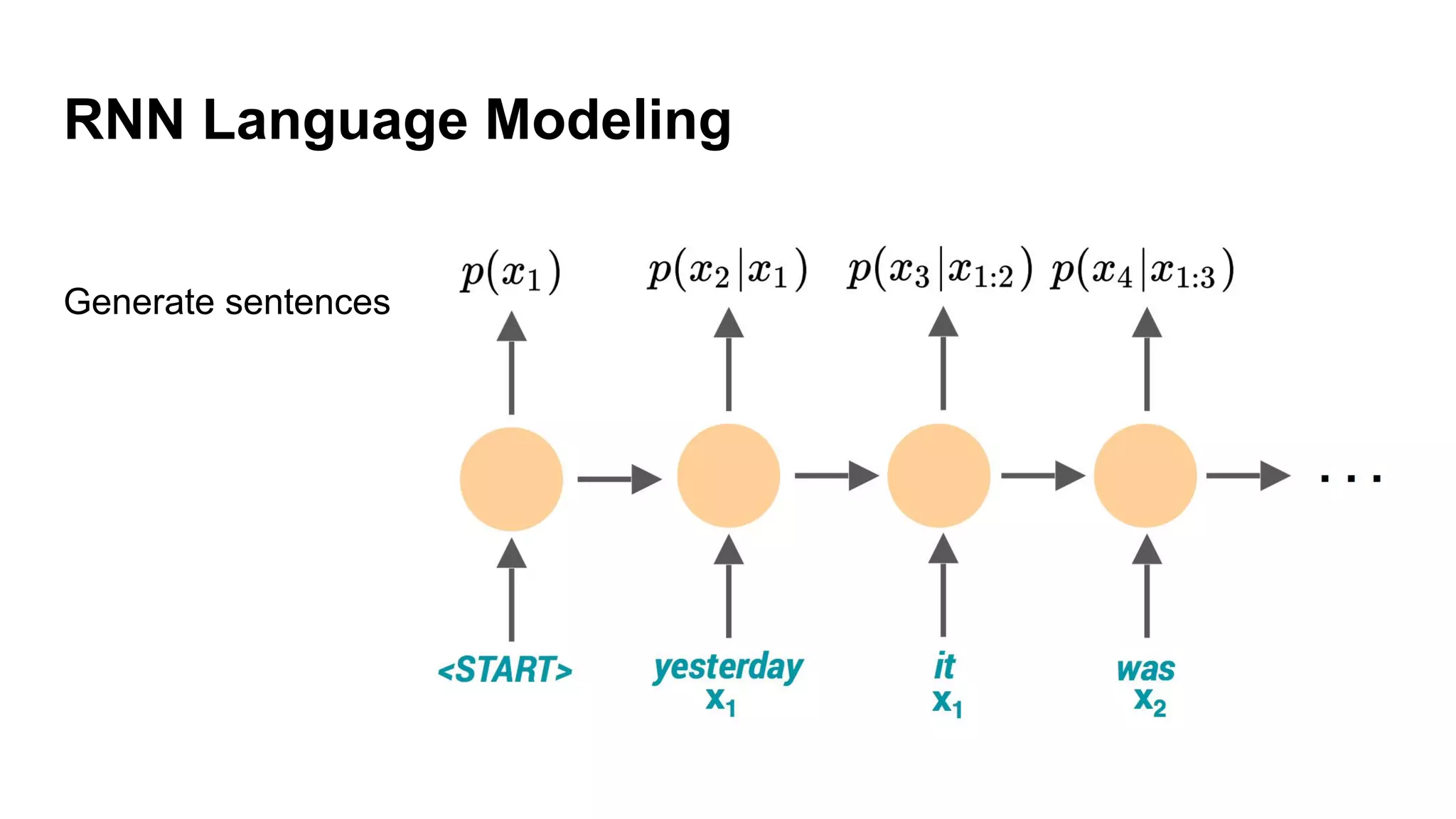
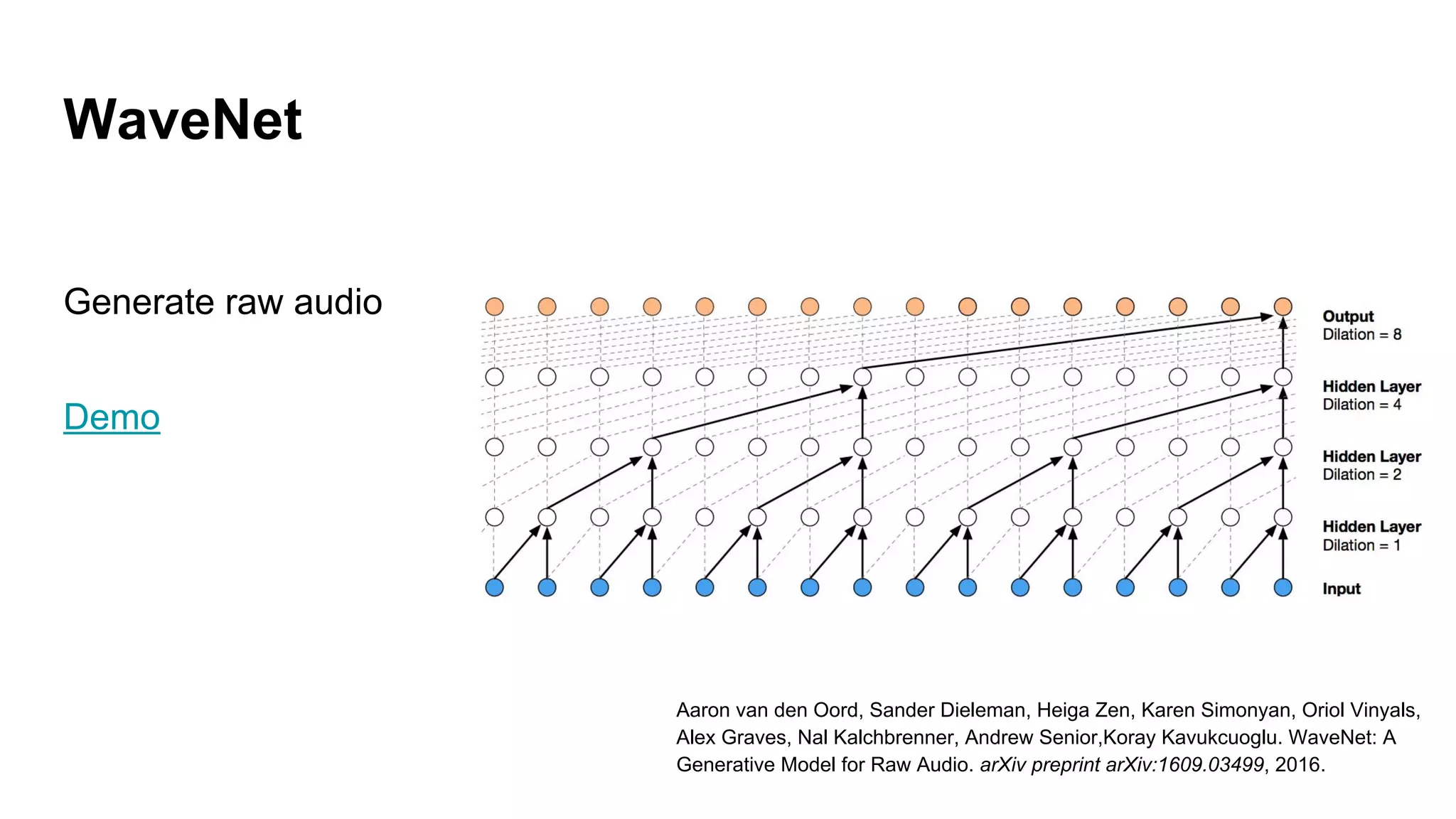
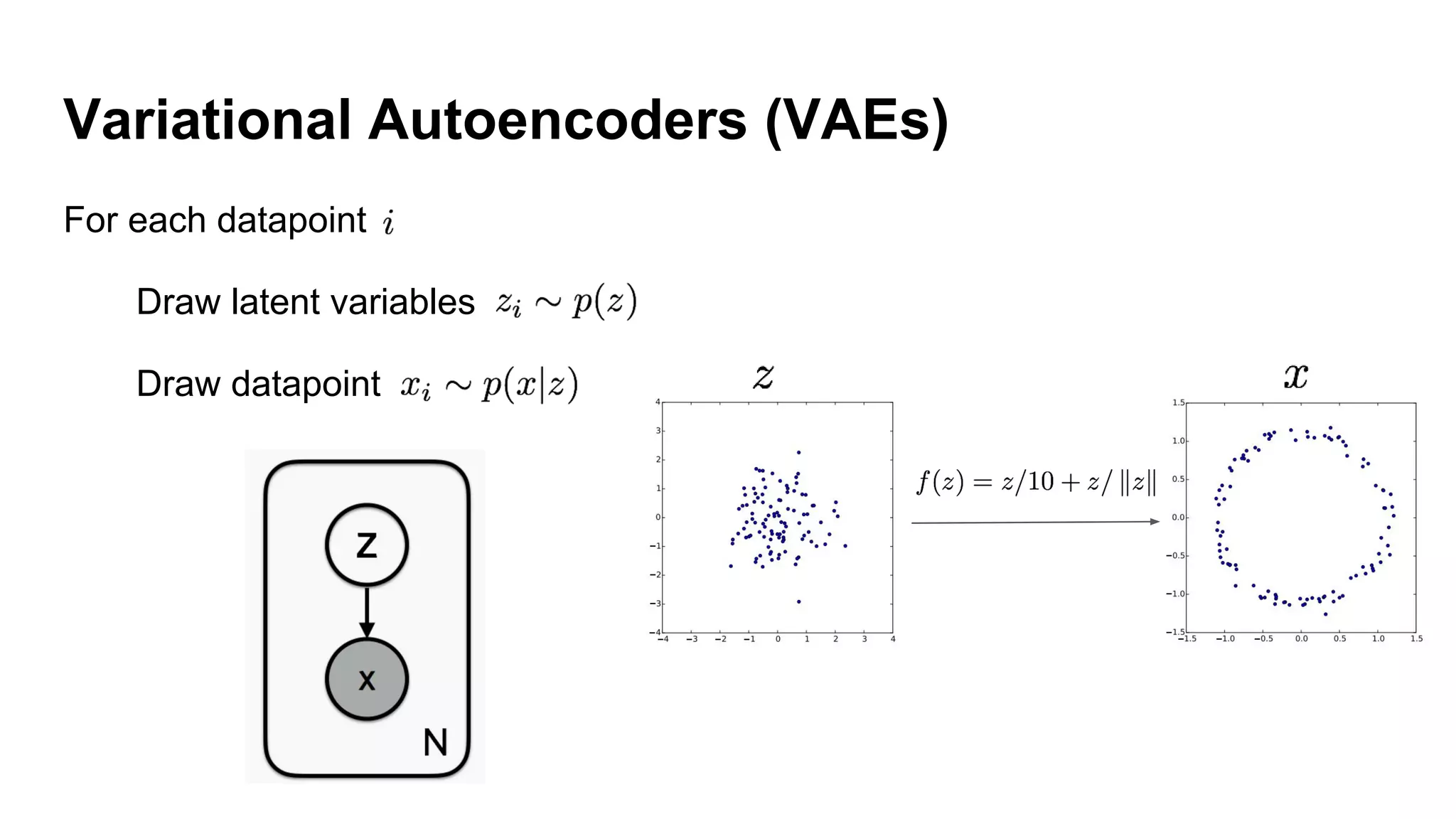
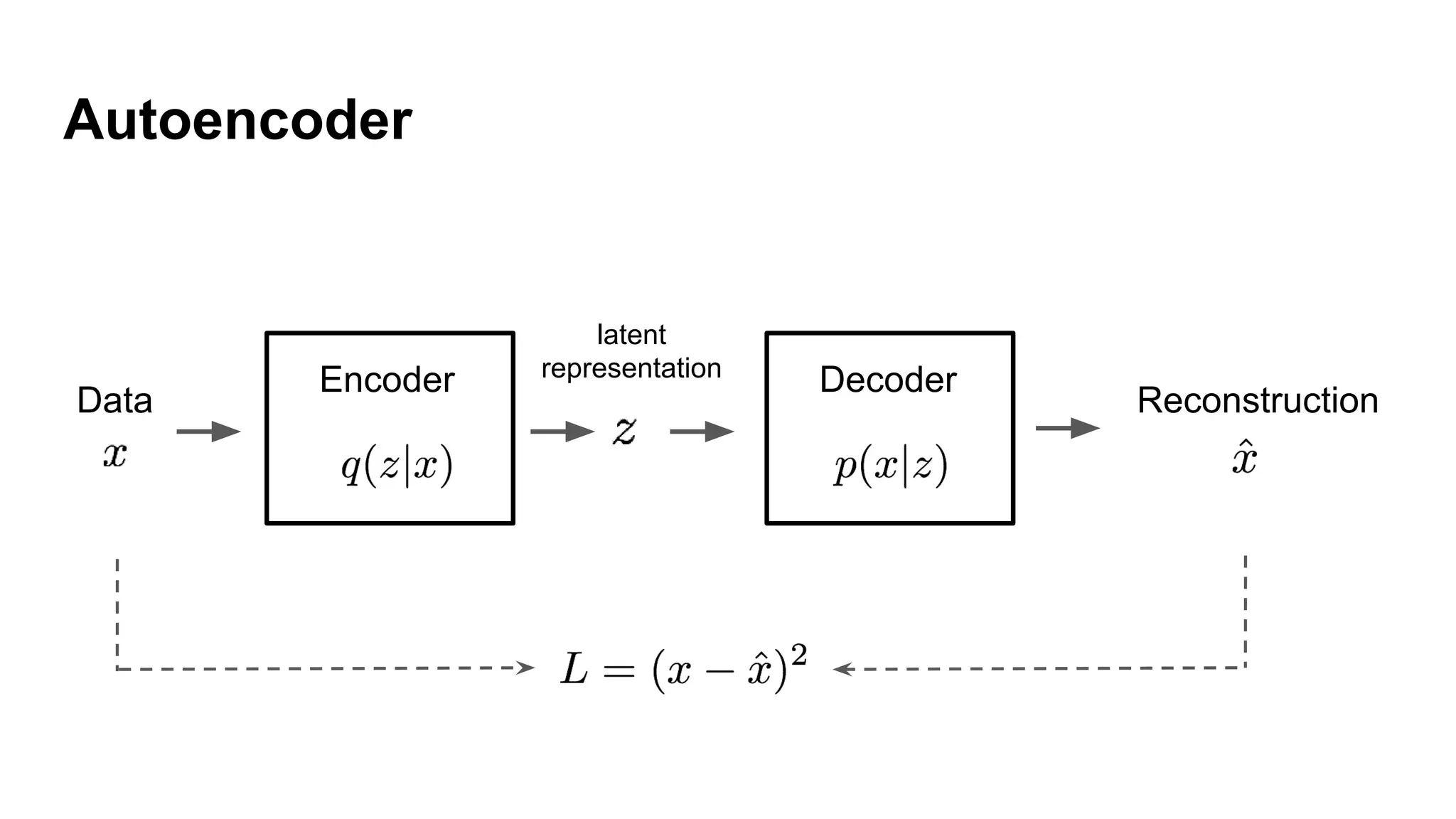
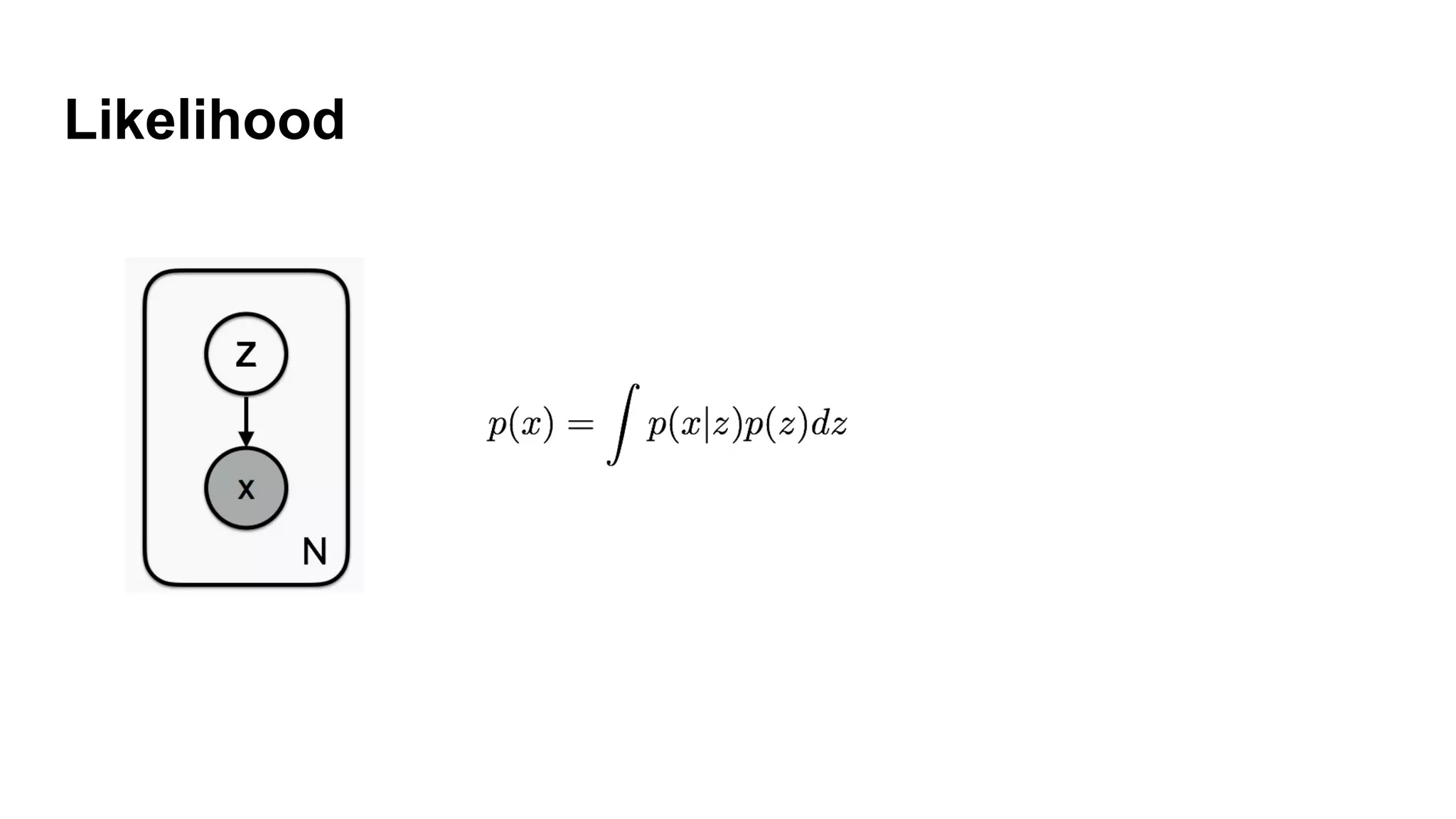
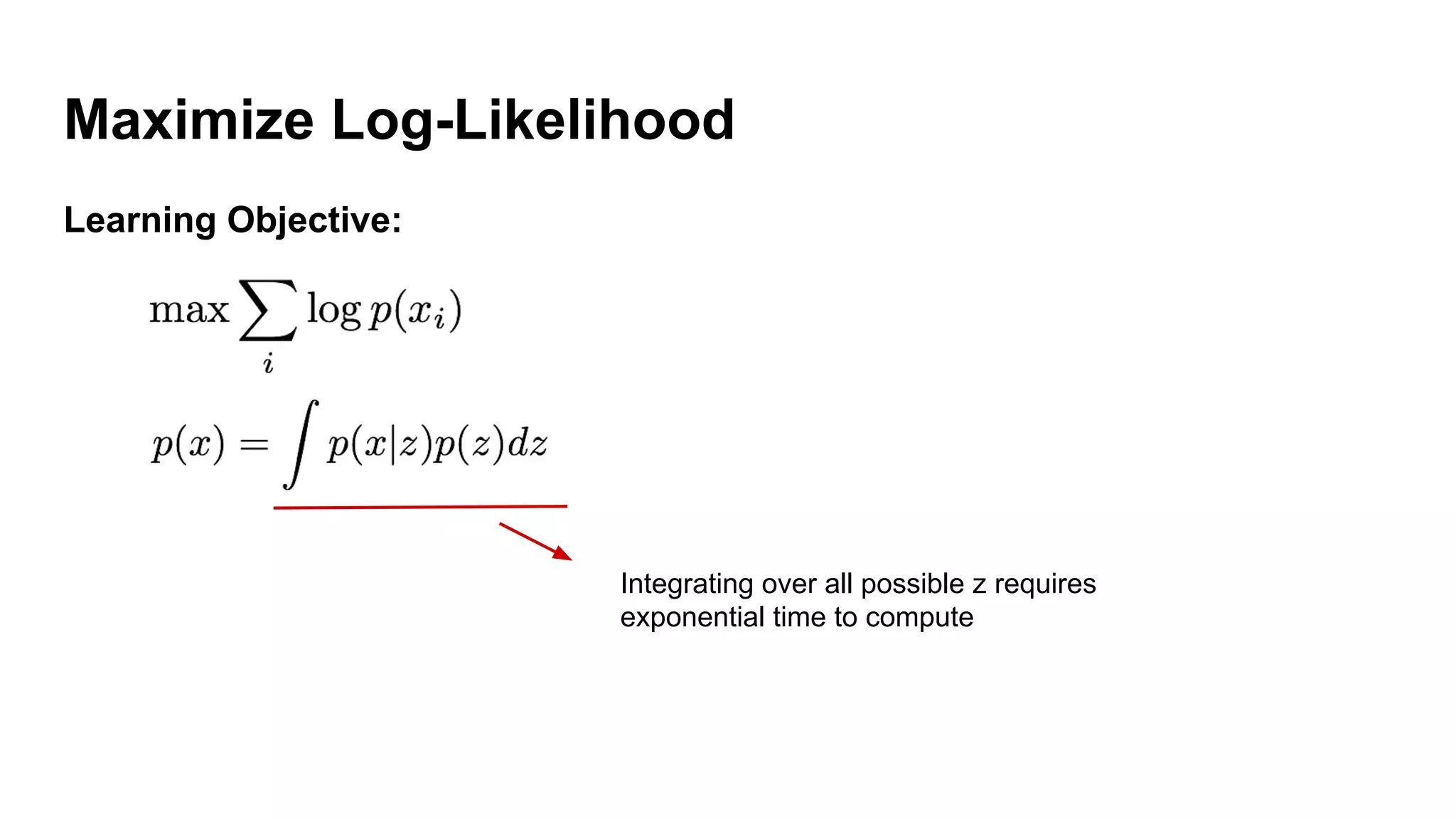
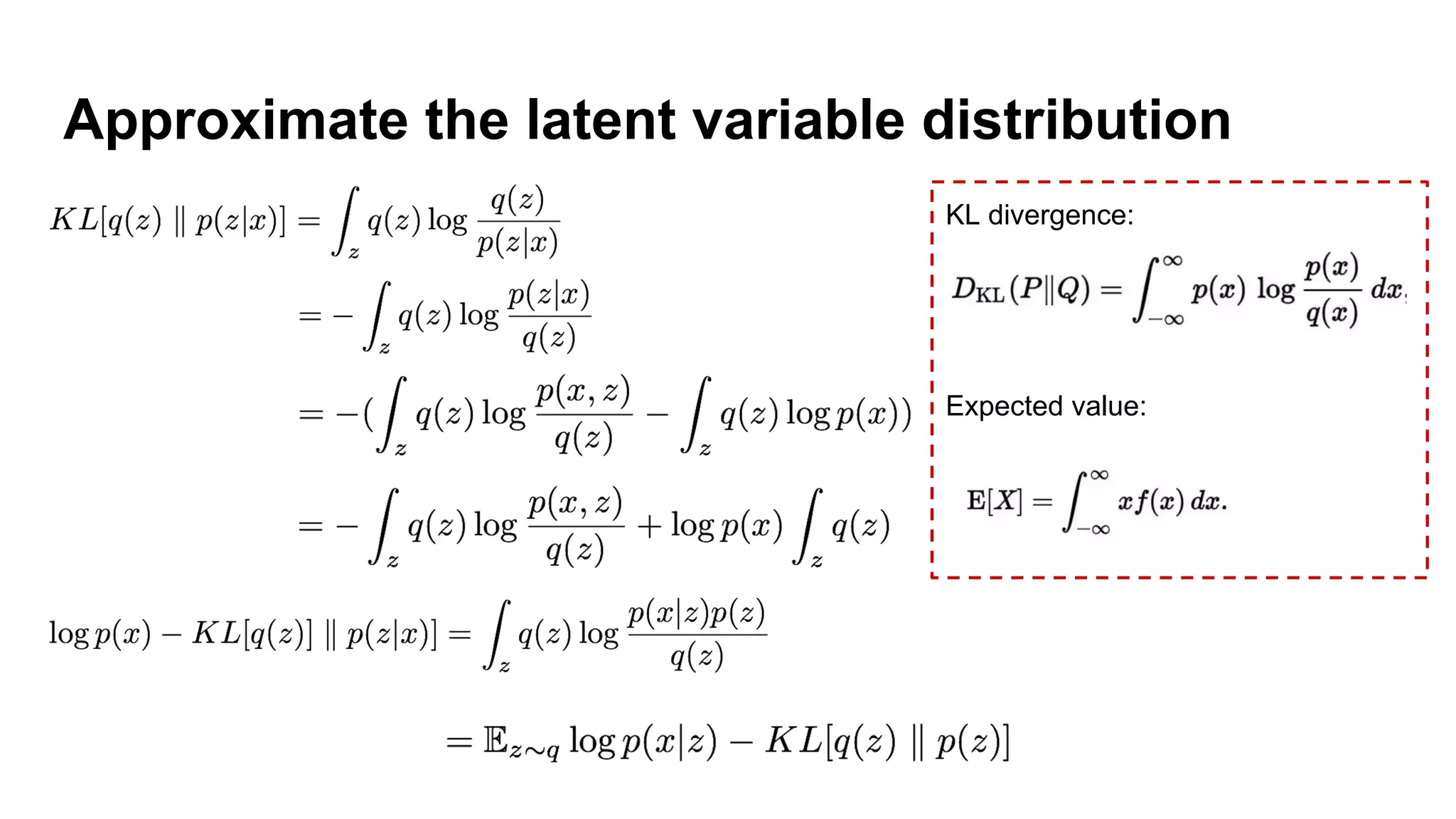
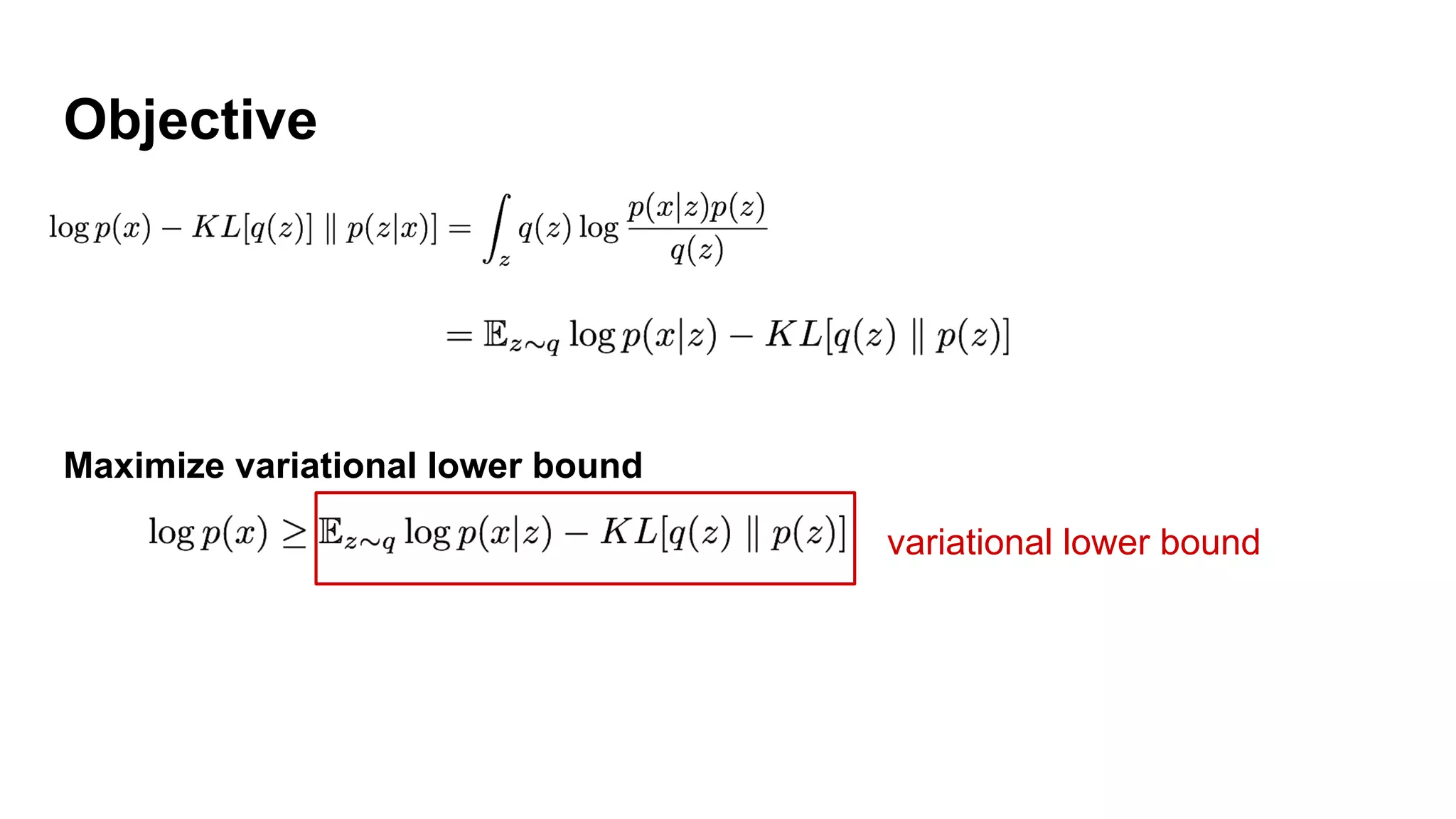
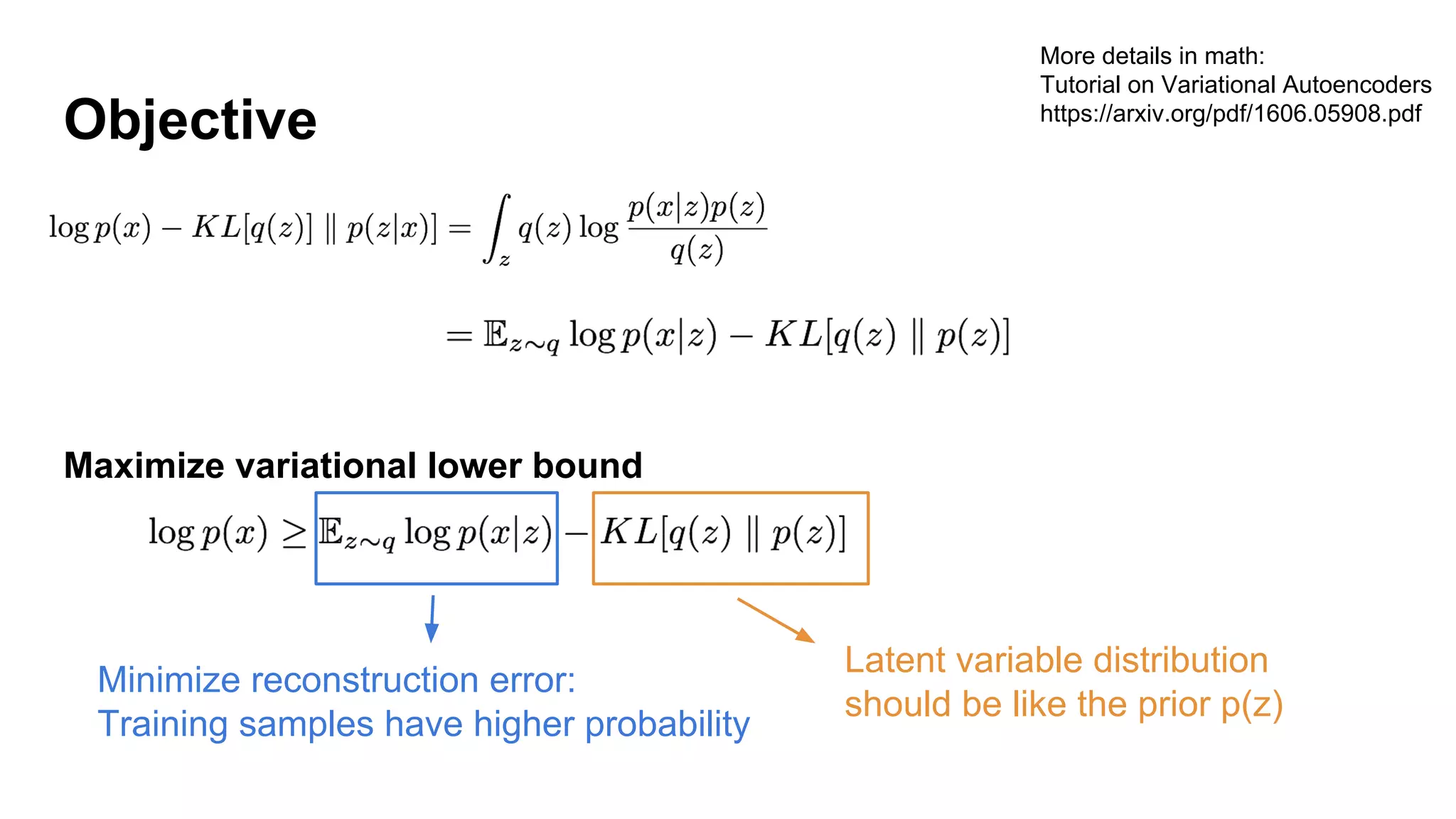
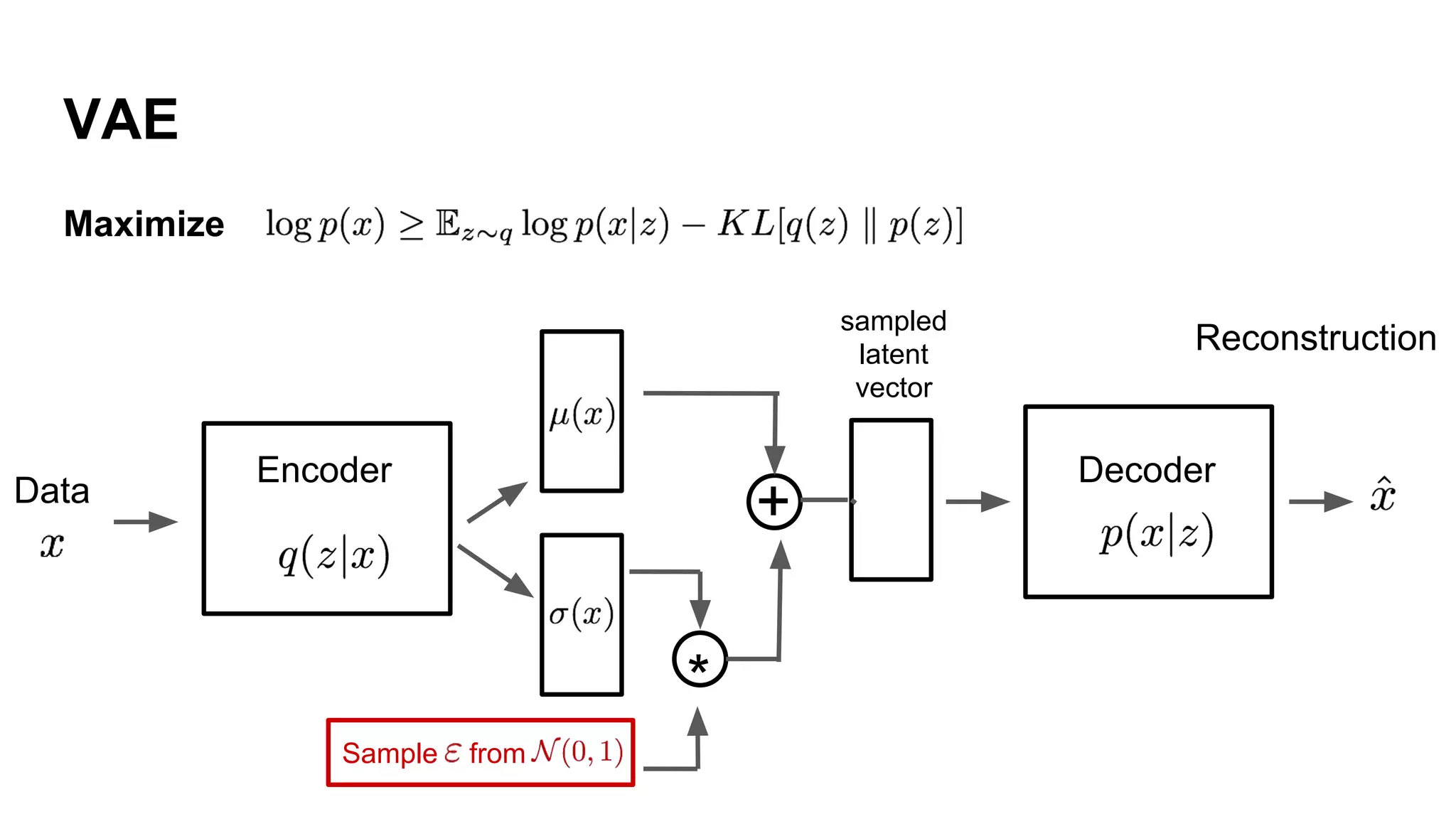
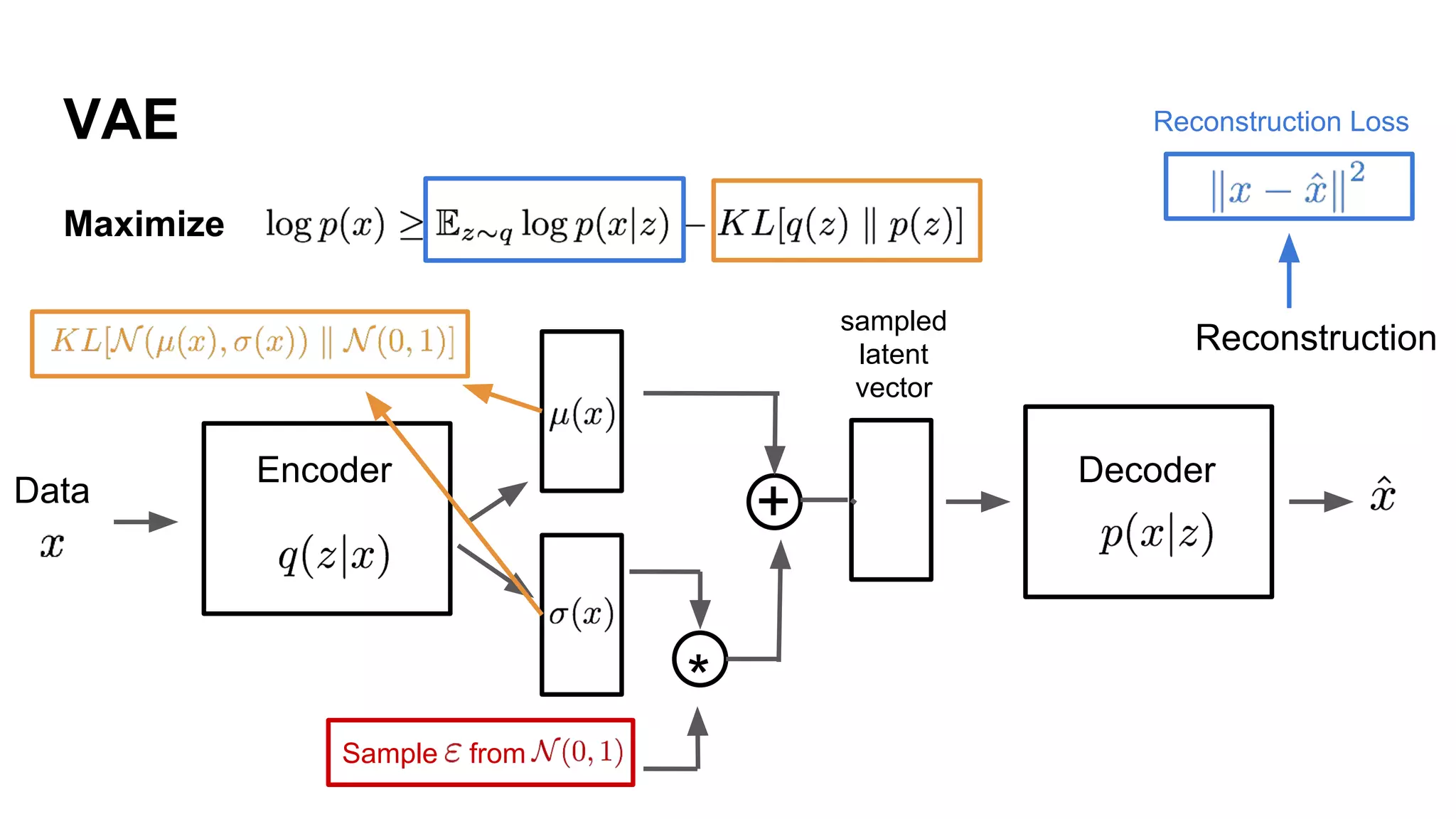
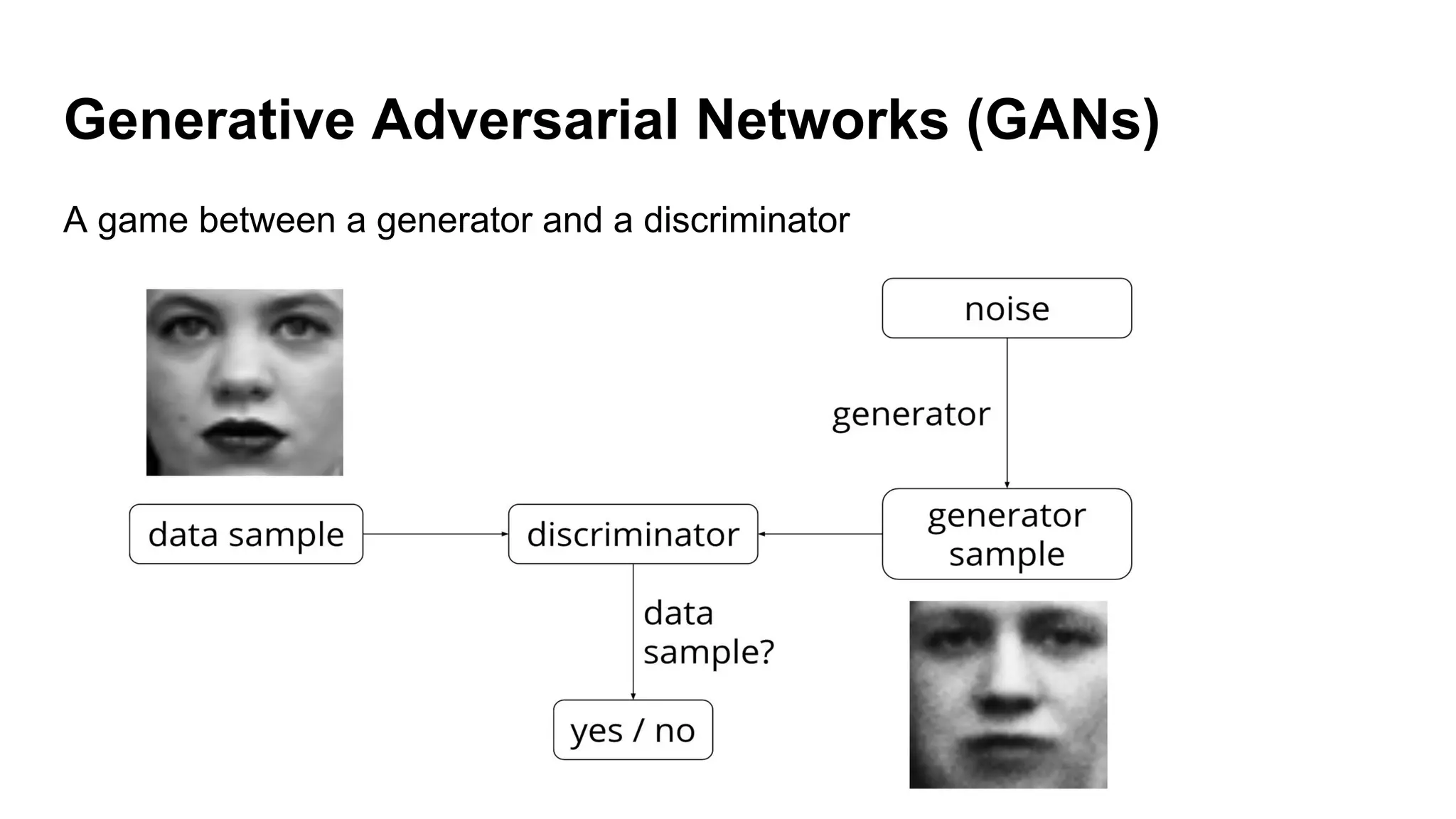
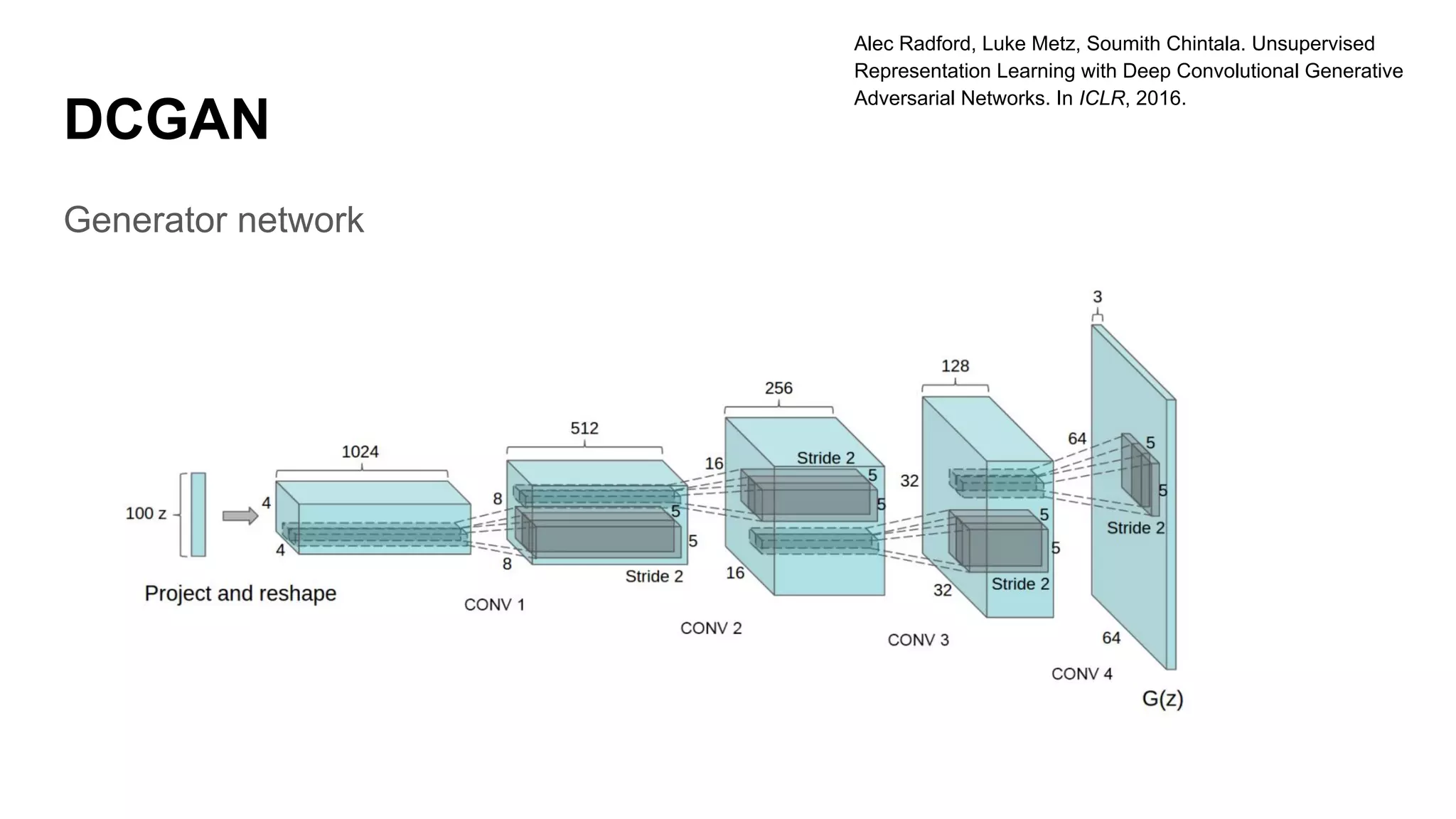
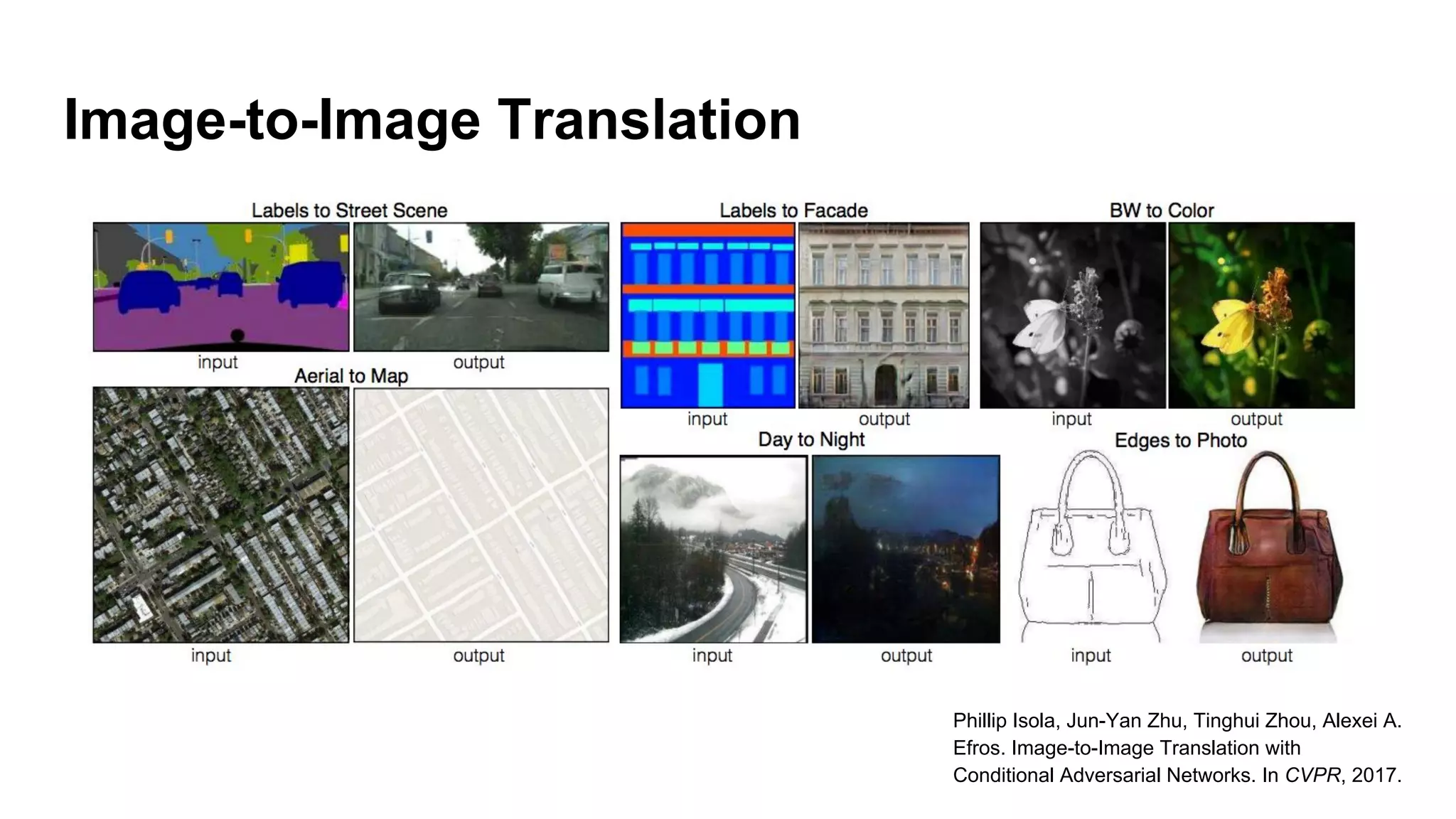
Deep generative models can generate synthetic images, speech, text and other data types. There are three popular types: autoregressive models which generate data step-by-step; variational autoencoders which learn the distribution of latent variables to generate data; and generative adversarial networks which train a generator and discriminator in an adversarial game to generate high quality samples. Generative models have applications in image generation, translation between domains, and simulation.