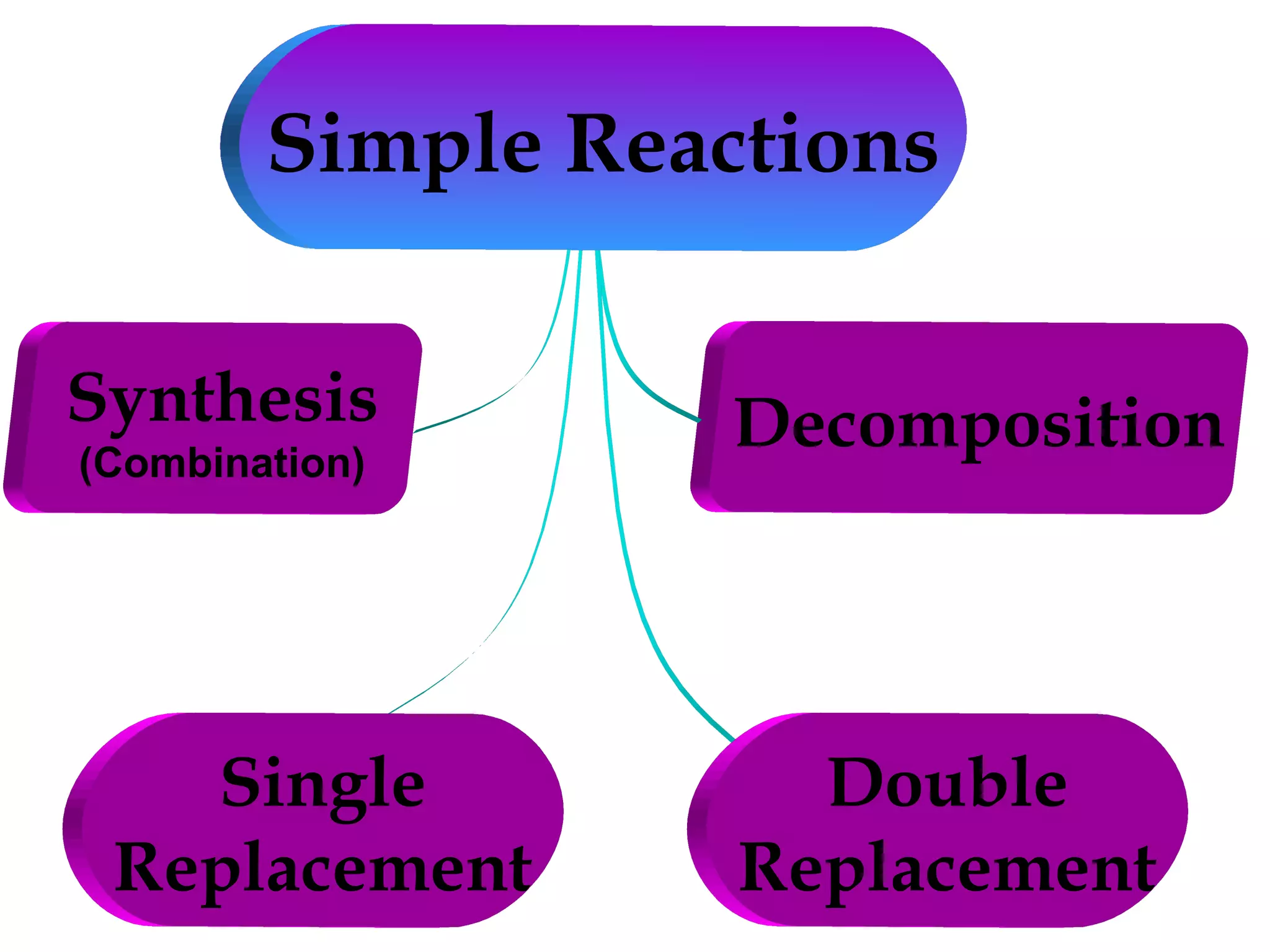
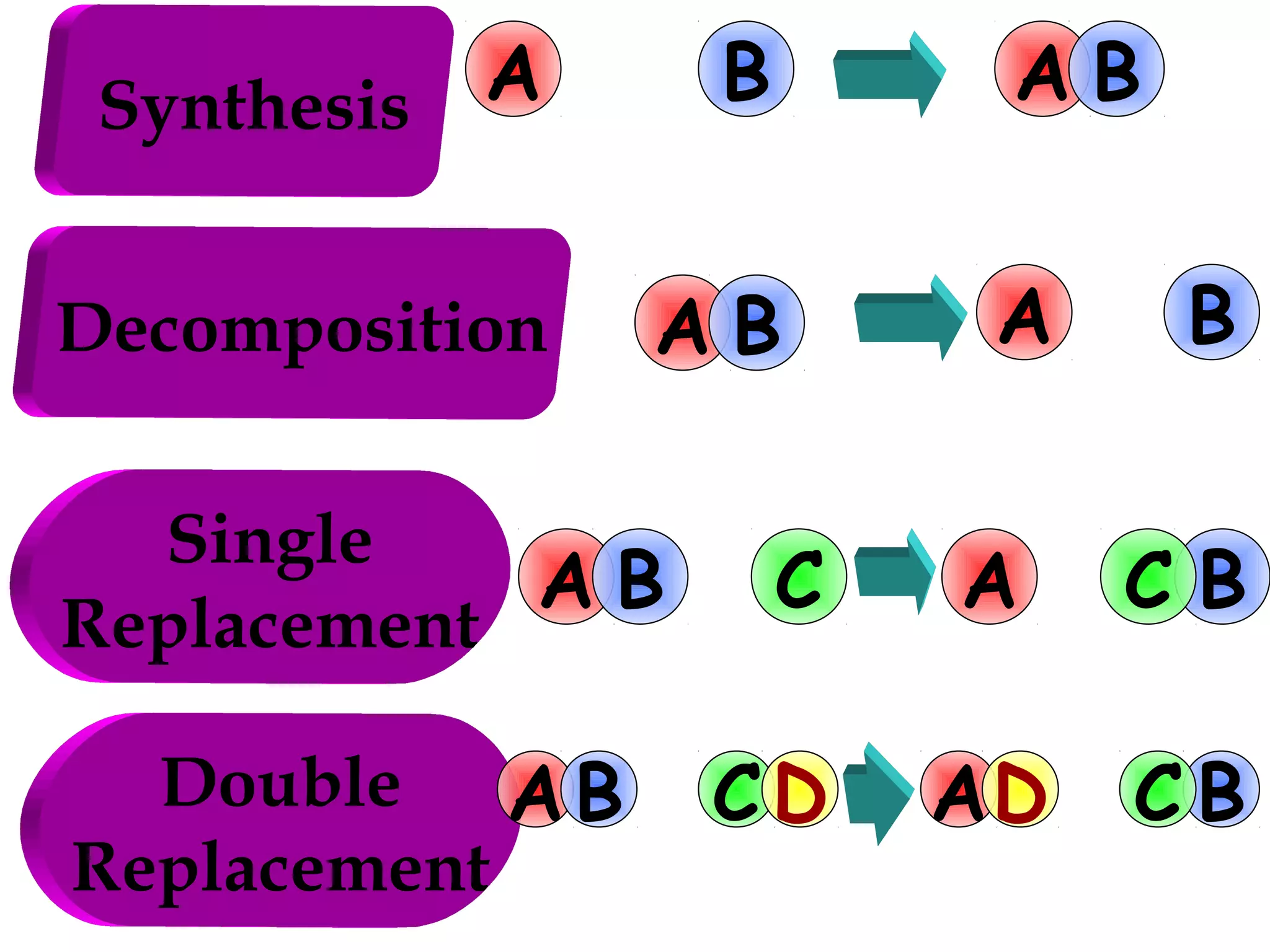
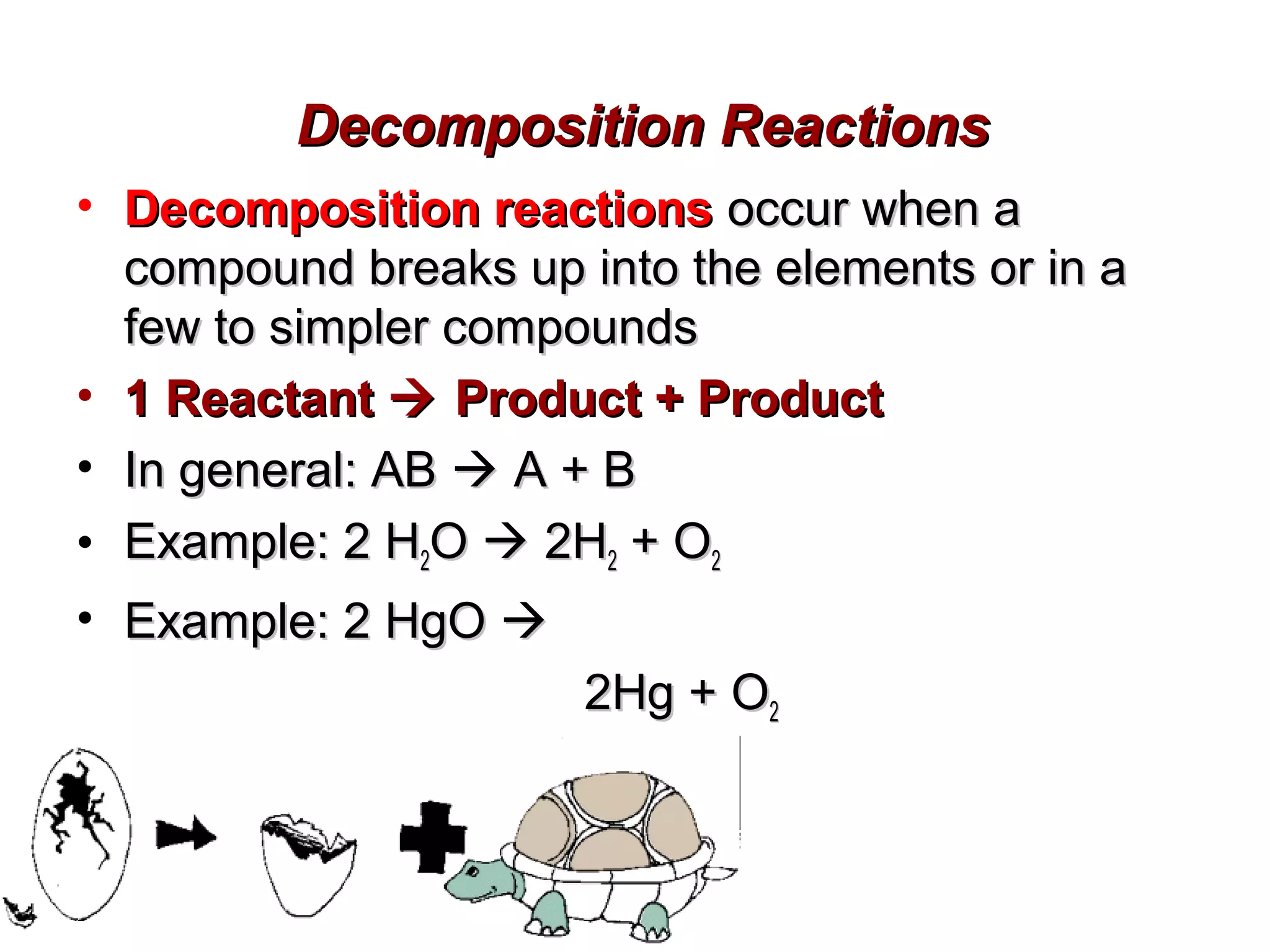
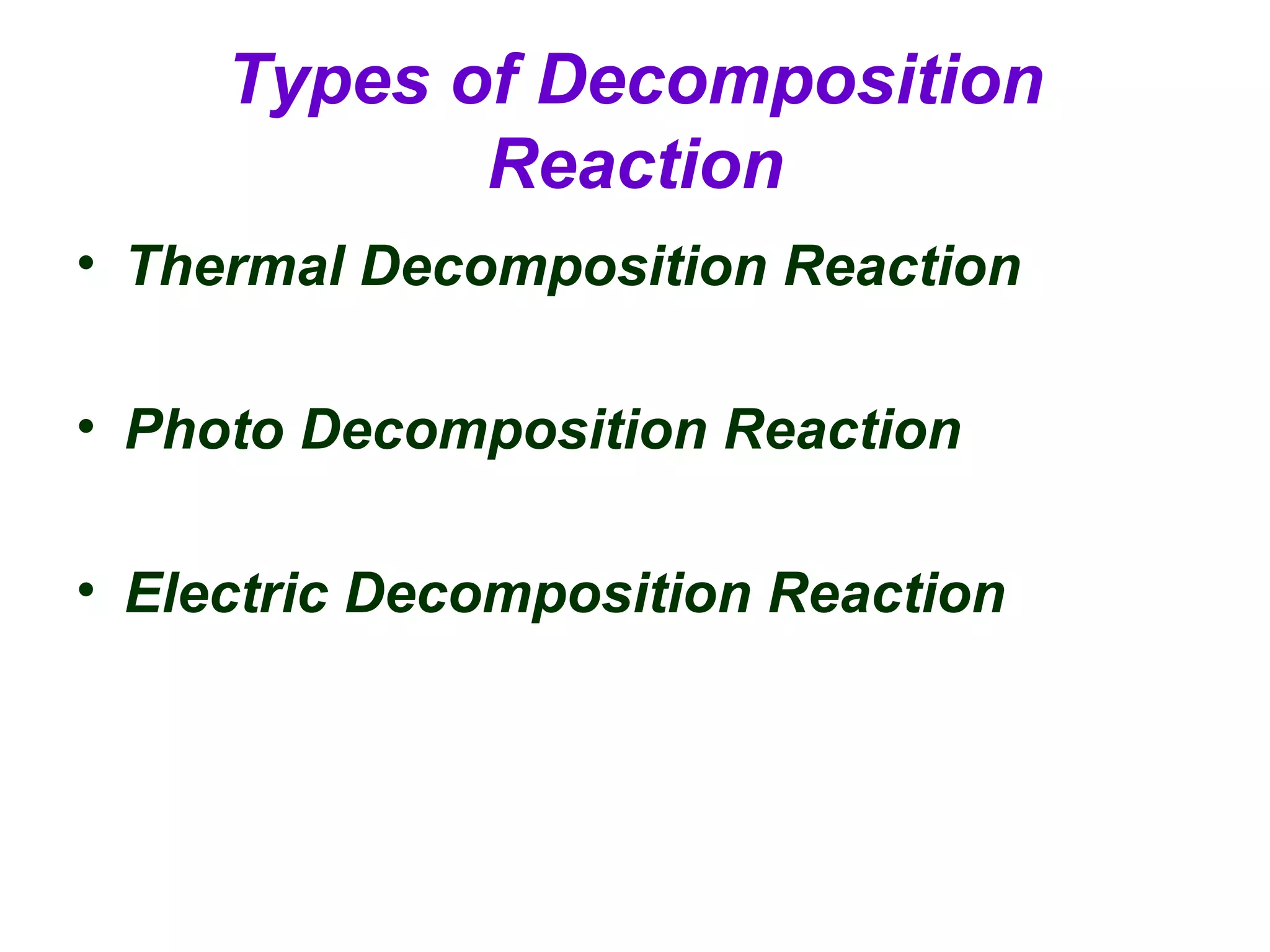
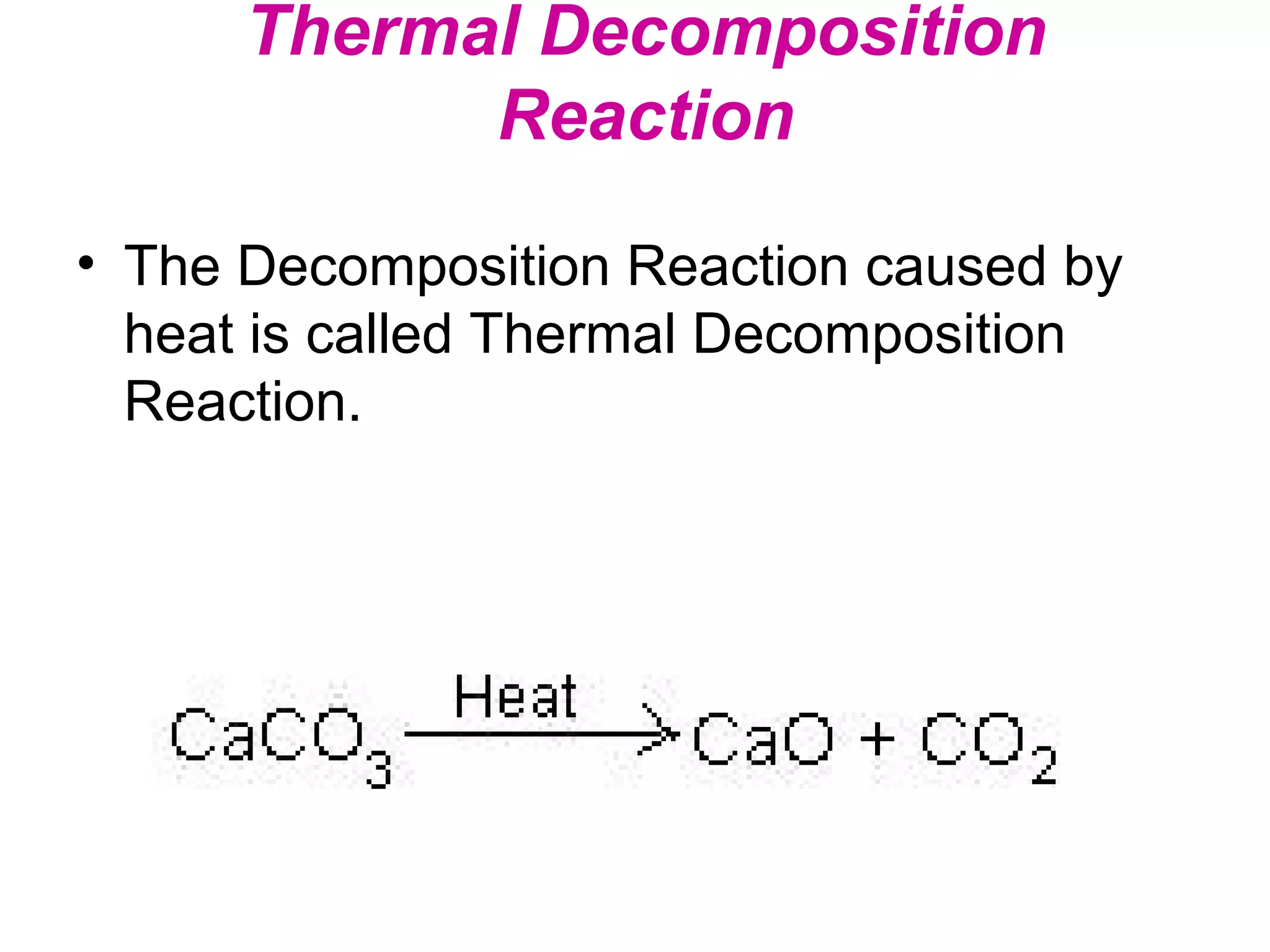
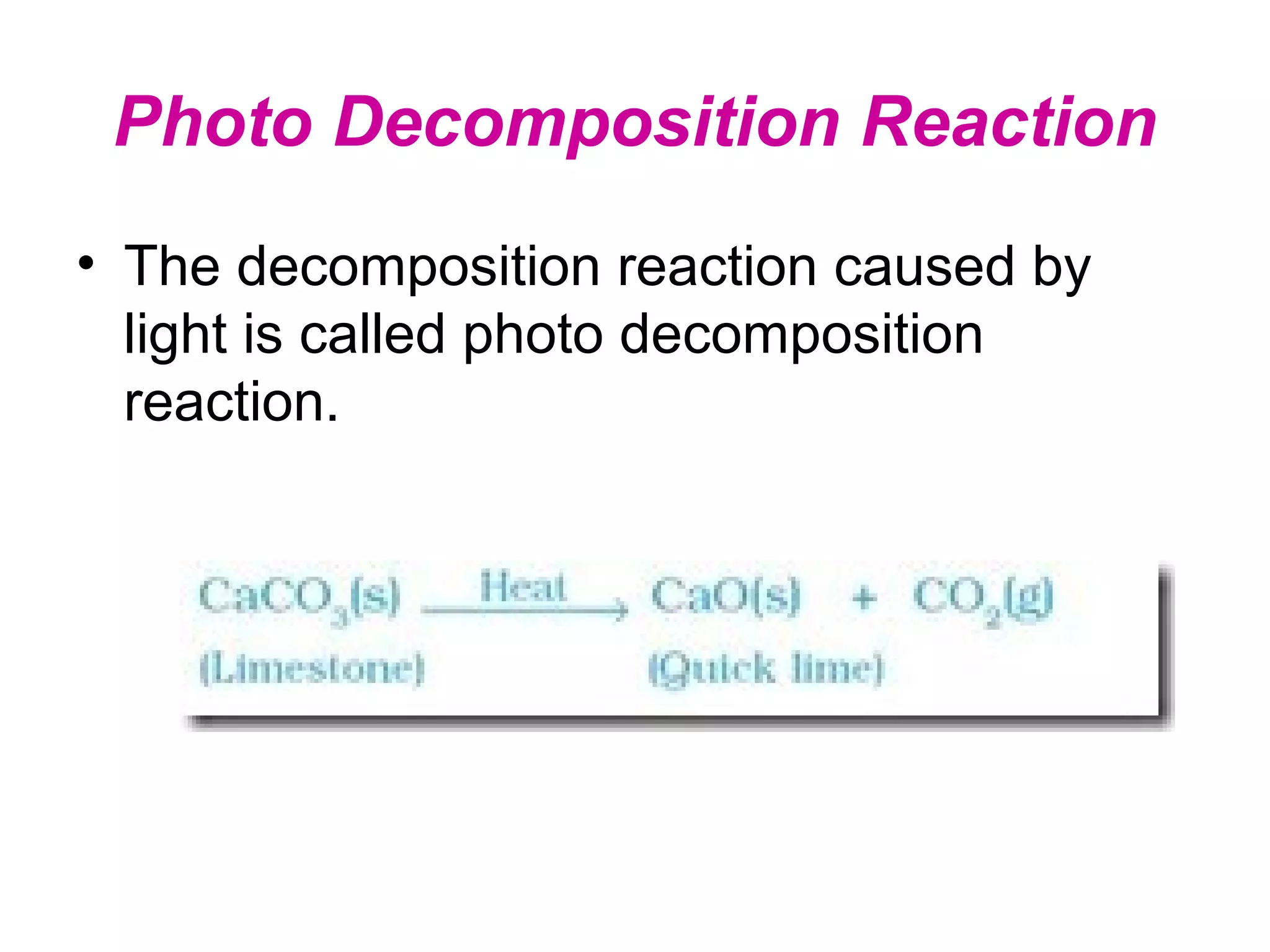
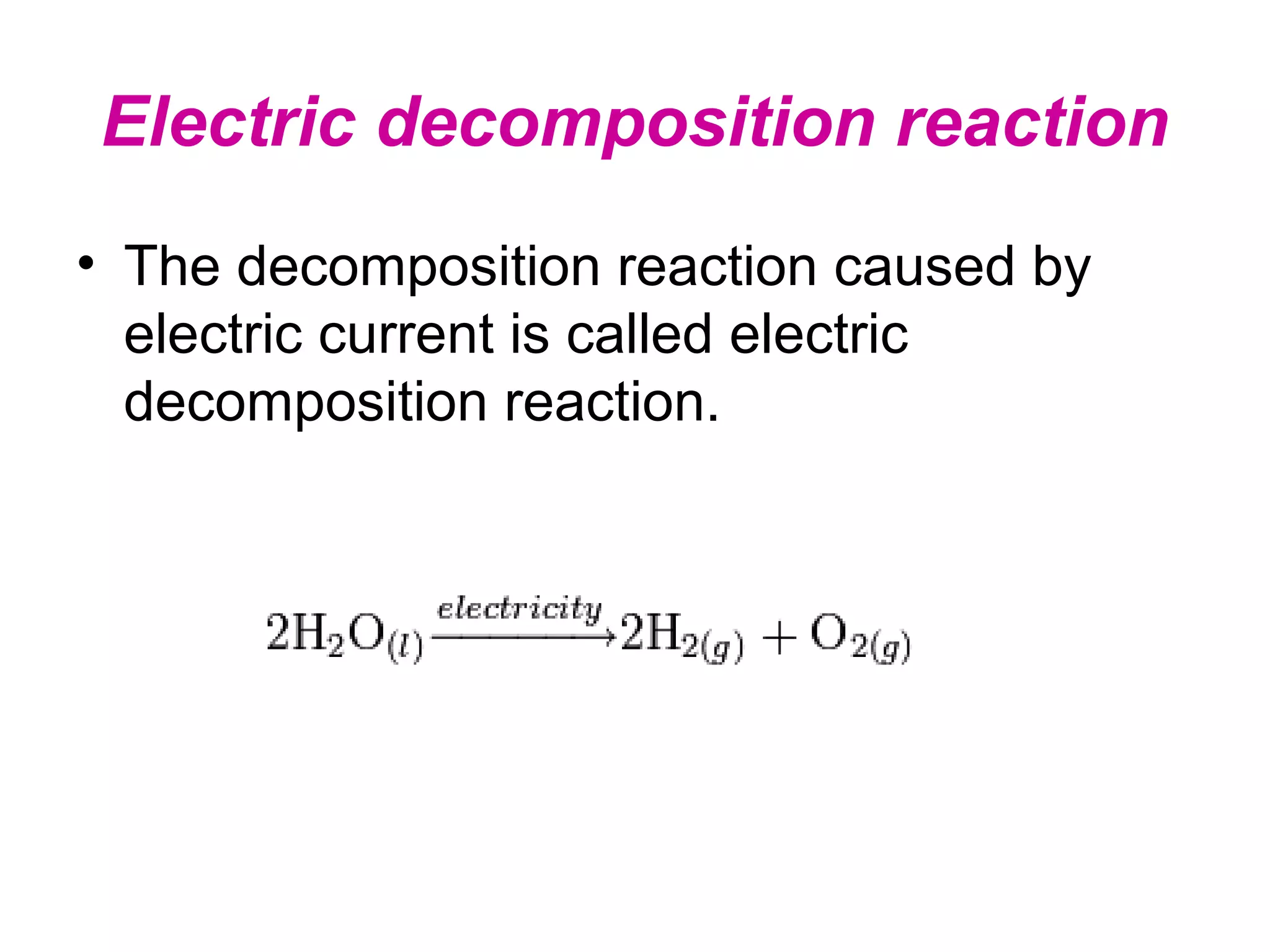
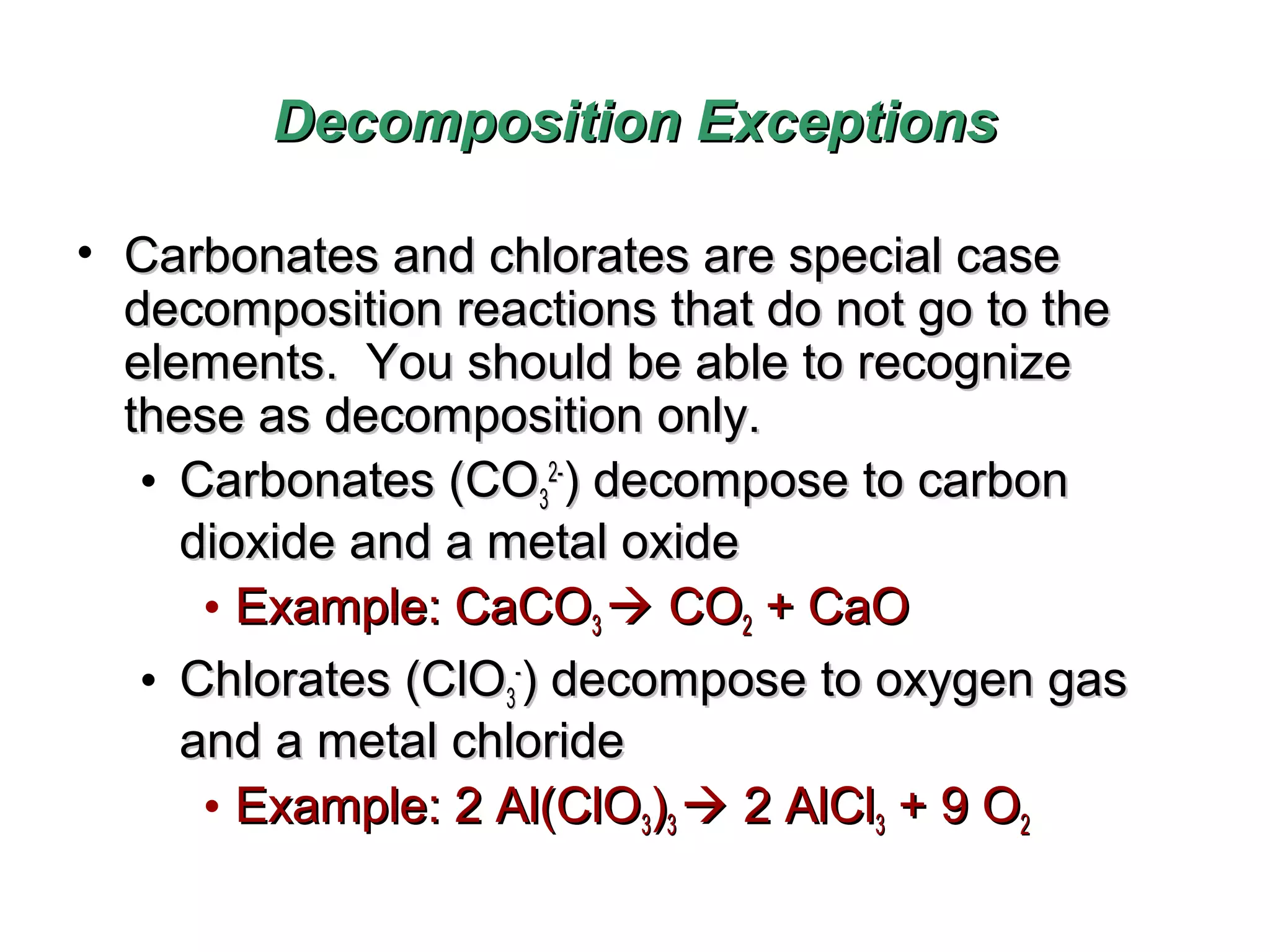
Decomposition reactions occur when a compound breaks down into simpler substances like elements or other compounds. There are three main types of decomposition reactions: thermal decomposition caused by heat, photo decomposition caused by light, and electric decomposition caused by an electric current. An example of a decomposition reaction is when water breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen gases.