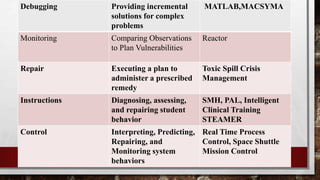
This document provides an agenda on expert systems that includes an introduction, definition, history, components, advantages, disadvantages and applications. It defines an expert system as a computer program that simulates human judgment to solve complex problems. The key components are a knowledge base that stores information and rules, and an inference engine that applies rules to deduce answers. Expert systems emerged in the 1970s and proliferated in the 1980s, being among the earliest successful forms of artificial intelligence. They are used in fields like healthcare, manufacturing and games.











![ 1970S
The concept of expert system was first developed in the 1970s by Edward
Feigenbaum [ professor and founder of the Knowledge Systems Laboratory at
Stanford university].
Father of expert systems.
Data processing to knowledge to “knowledge processing”.
By new processor technology and computer architectures .
Two early expert systems:-
Health care space for medical diagnoses
Helped chemists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esne-170109163043/85/expertsystem-pptx-email-13-320.jpg)