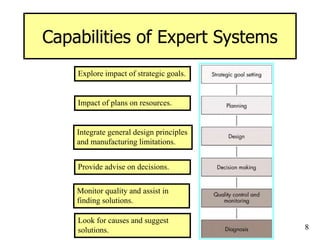
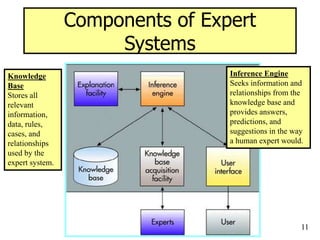
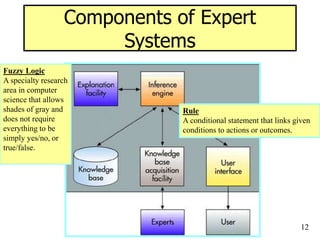
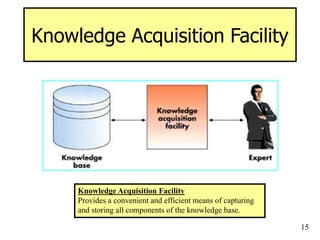
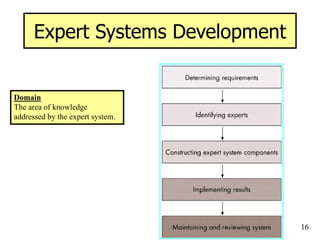
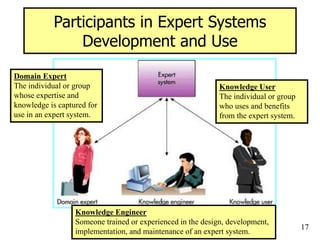
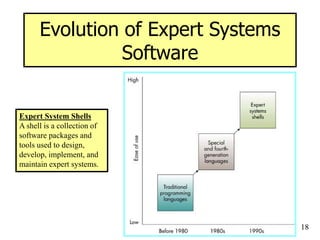
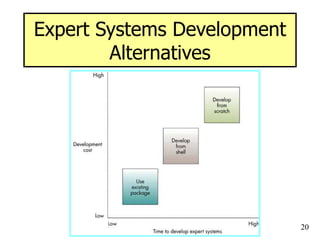
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and expert systems, detailing their capabilities, branches, and components. It outlines the use of expert systems in various fields, their benefits, limitations, and the roles of participants in their development. Additionally, it highlights applications of AI and expert systems in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and information management.