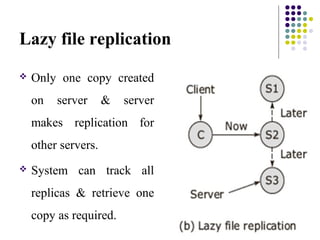
This document discusses key aspects of distributed file systems including file caching schemes, file replication, and fault tolerance. It describes different cache locations, modification propagation techniques, and methods for replica creation. File caching schemes aim to reduce network traffic by retaining recently accessed files in memory. File replication provides increased reliability and availability through independent backups. Distributed file systems must also address being stateful or stateless to maintain information about file access and operations.