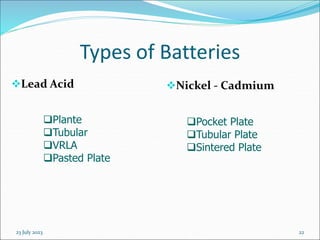
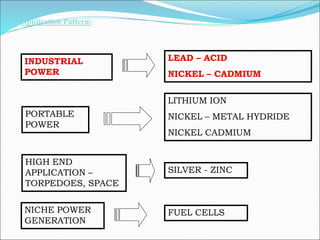
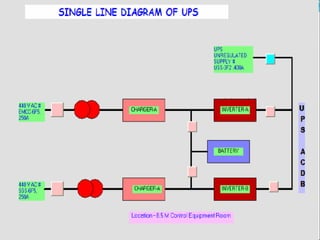
The document discusses the importance of reliable DC power supply systems in power stations. It notes that failure of the station's DC supply could have catastrophic consequences by rendering protection and control systems inoperative. The DC supply system is designed to minimize this risk of failure. The protection philosophy assumes DC failures are unlikely events. The DC system aims to provide continuous, high quality power under normal and abnormal operating conditions, acting as the ultimate backup power source when total AC supply fails.










![23 July 2023 19
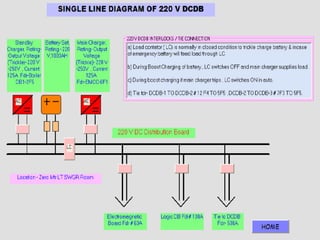
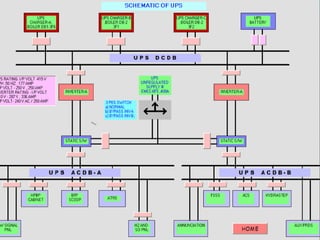
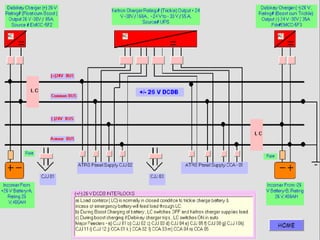
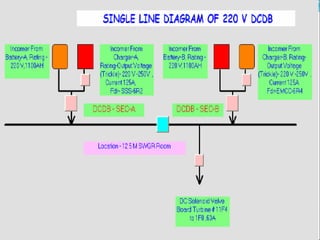
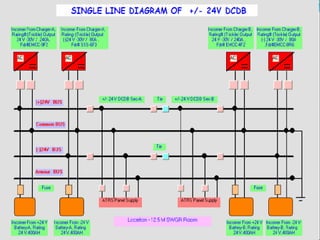
DC SYSTEM
BATTERY CHARGERS [TWO/THREE]
BATTERY BANKS [ONE/TWO]
DC DISTRIBUTION BOARDS [ONE/TWO]
DC FUSE BOARDS
UN EARTHED SYSTEM
CHARGER TROUBLE, DC EARTH FAULT AND DC
VOLTAGE ABNORMAL ALARMS IN UCB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcsupplysystem-230723055638-89786446/85/DC-SUPPLY-SYSTEM-ppt-19-320.jpg)