Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times

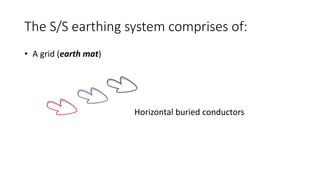


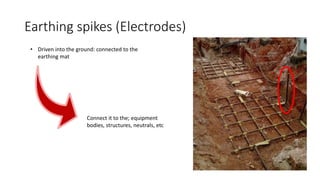
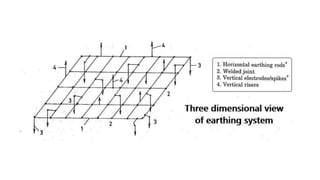

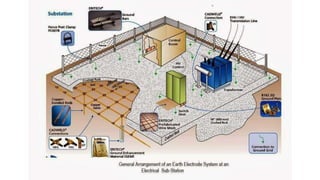
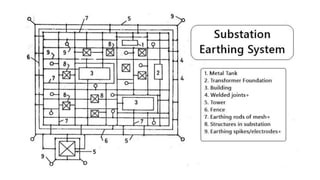

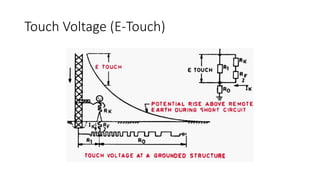
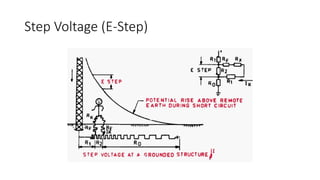
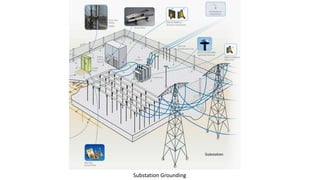

The substation earthing system comprises a grid of horizontal buried conductors connected to earthing spikes driven into the ground. This earthing mat provides several functions: ensuring personnel safety from electric shocks, providing a grounding path and discharge for over-voltages and faults. The earthing resistance is determined by how well the mat's conductors are connected and the soil resistivity - lower resistivity leads to lower resistance. Non-current carrying equipment and structures are connected to the earthing mat to limit fault voltages and currents for safety.













