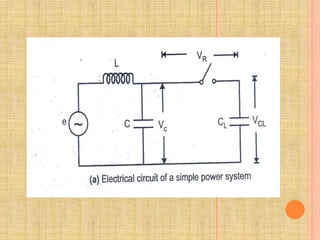
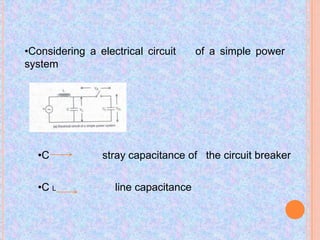
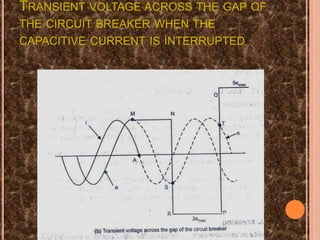
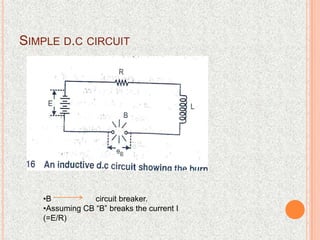
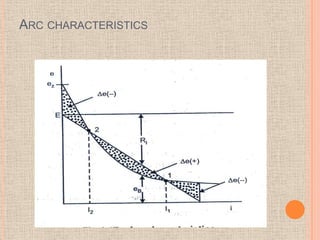
The document discusses interrupting capacitive current in DC circuits using circuit breakers. When a long transmission line or capacitor bank is switched off, high voltage transients can occur across the circuit breaker contacts due to the capacitive current. As the capacitive current is interrupted, the voltage across the breaker gap can oscillate between negative three times the maximum system voltage and positive five times the maximum system voltage. DC circuit breaking faces challenges in producing a current zero, preventing restrikes, and dissipating stored energy during the short breaking interval. Progressive arc lengthening, commutation principles, and spark gaps are discussed as techniques used in DC circuit breaker design to address these challenges.