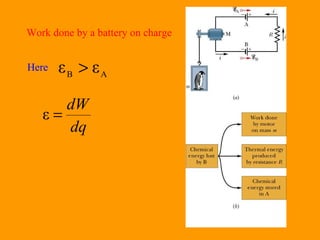
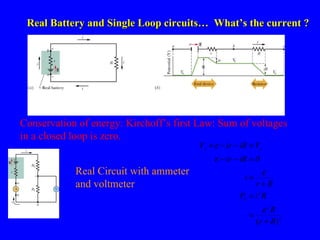
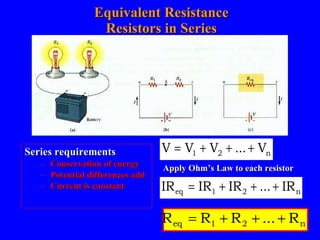
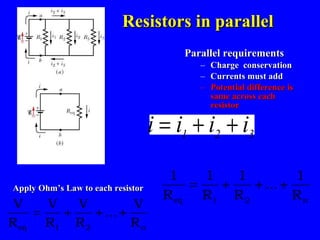
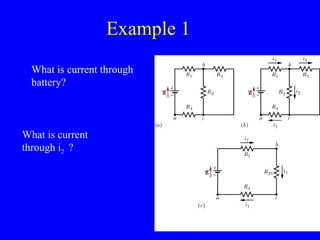
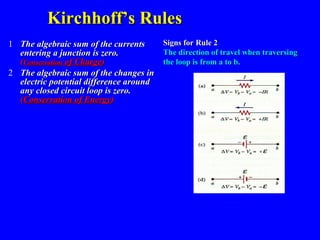
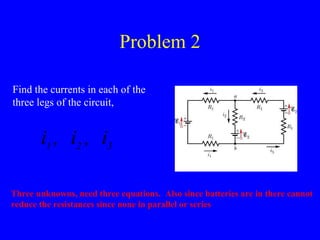
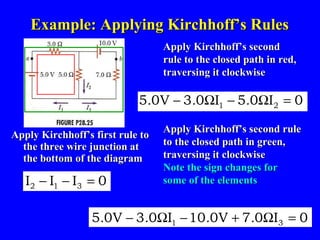
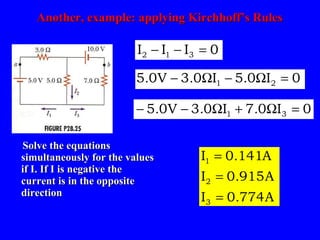
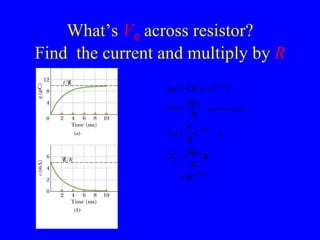
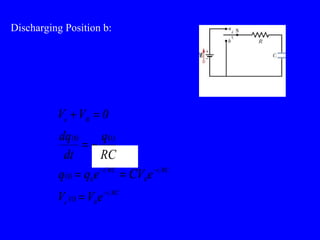
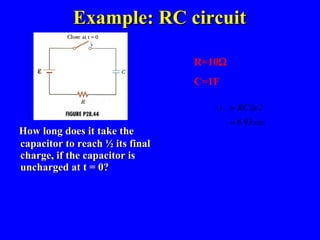
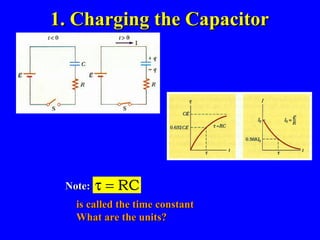
The document discusses Kirchhoff's rules for circuit analysis and RC circuits. Kirchhoff's rules state that the sum of currents entering a junction must be 0, and the sum of potential differences in any closed loop must be 0. RC circuits have time-dependent behavior when charging and discharging based on the time constant, which is the resistance times the capacitance. The document provides examples of applying Kirchhoff's rules to solve for currents in circuits and calculating the time it takes a capacitor to charge to half its final value in an RC circuit.