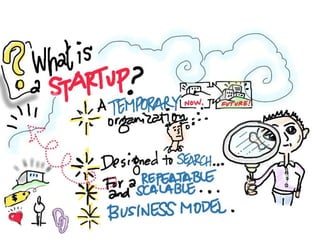
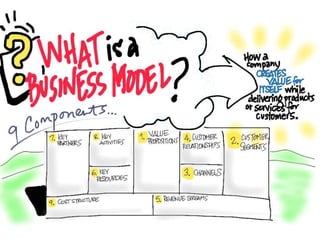
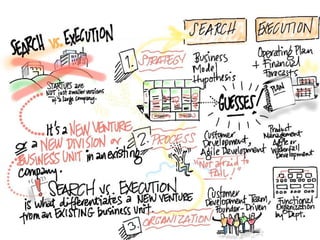
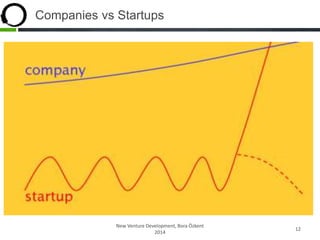
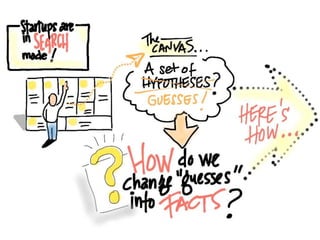
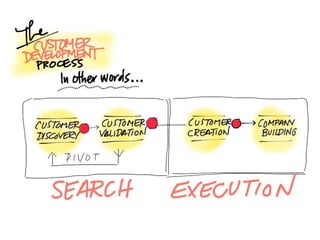
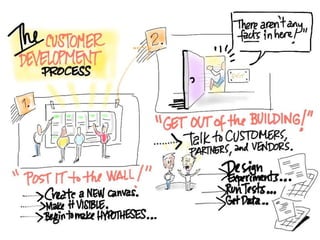
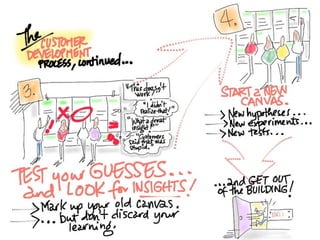
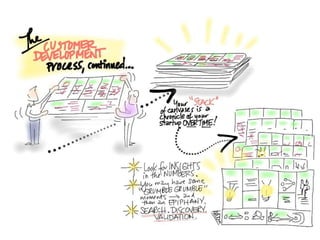
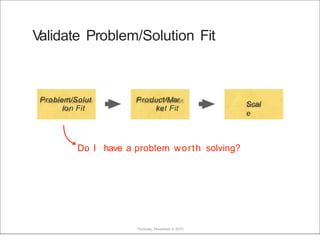
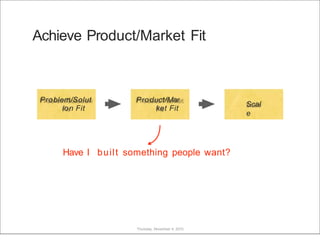
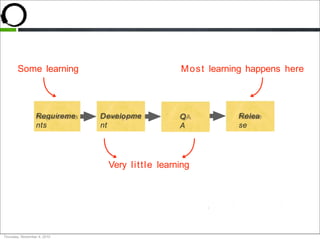
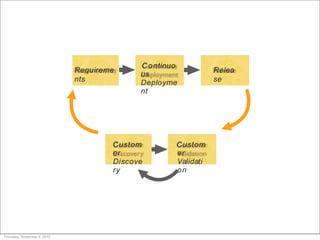
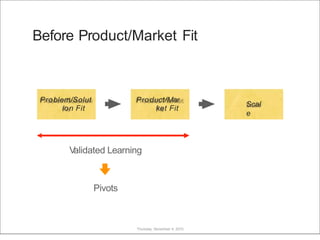
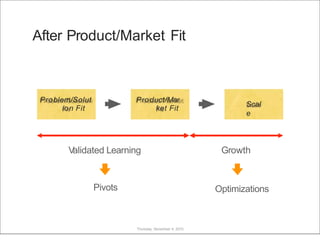
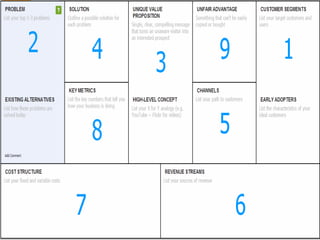
This document discusses what startups are and how they differ from large companies. It notes that startups have been responsible for 50% of innovation and 95% of radical innovation since WWII despite accounting for a small percentage of R&D spending. A startup is defined as an organization designed to deliver a product or service under extreme uncertainty through experimentation and hypothesis testing. Key aspects of startups discussed include their focus on achieving problem/solution fit and product/market fit through iterative customer validation, high failure rates, need for rapid decision making and learning, and emphasis on preserving cash. The document advocates for using the Lean Canvas model to structure startup learning through validating hypotheses with customers before scaling.