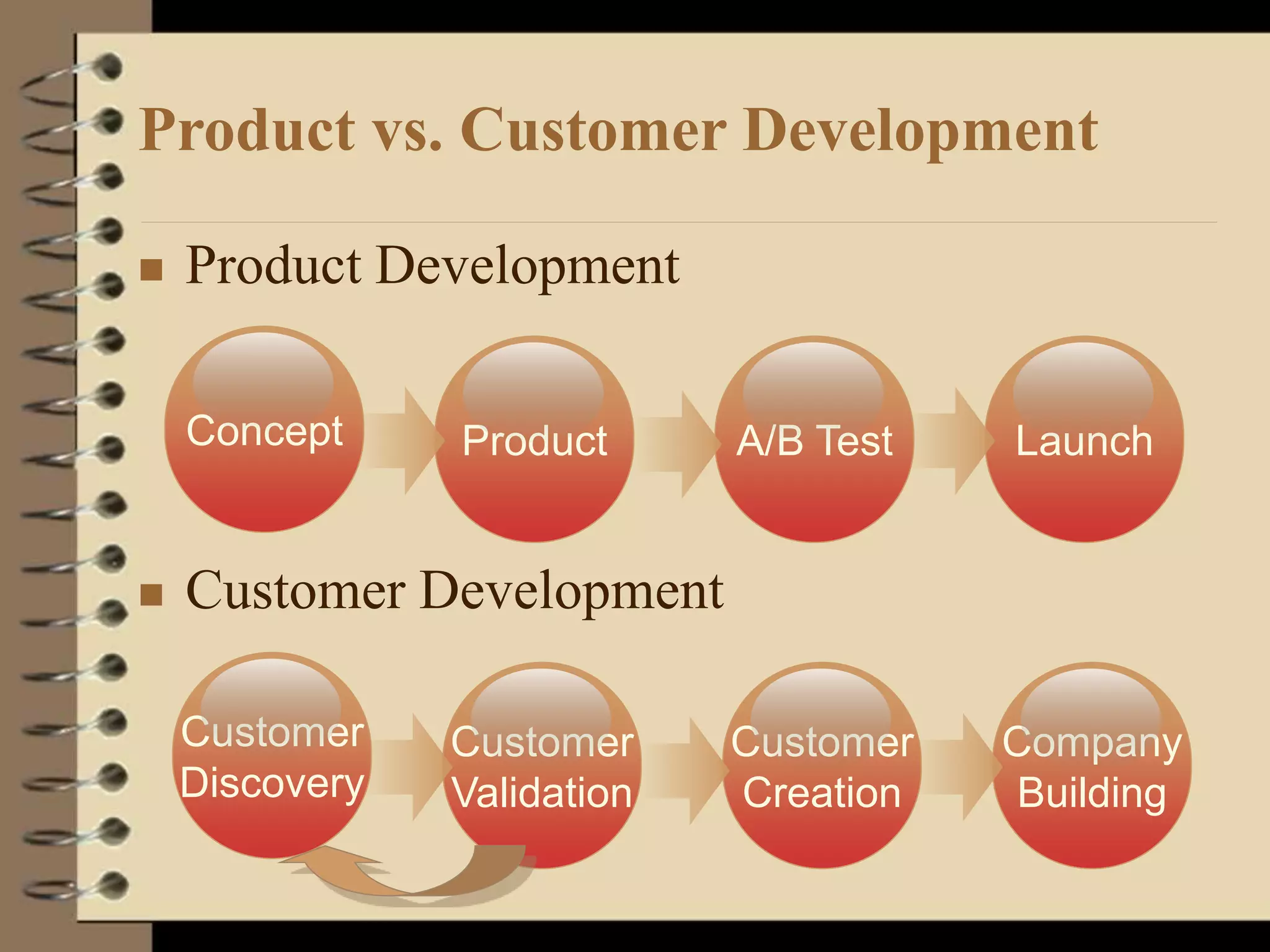
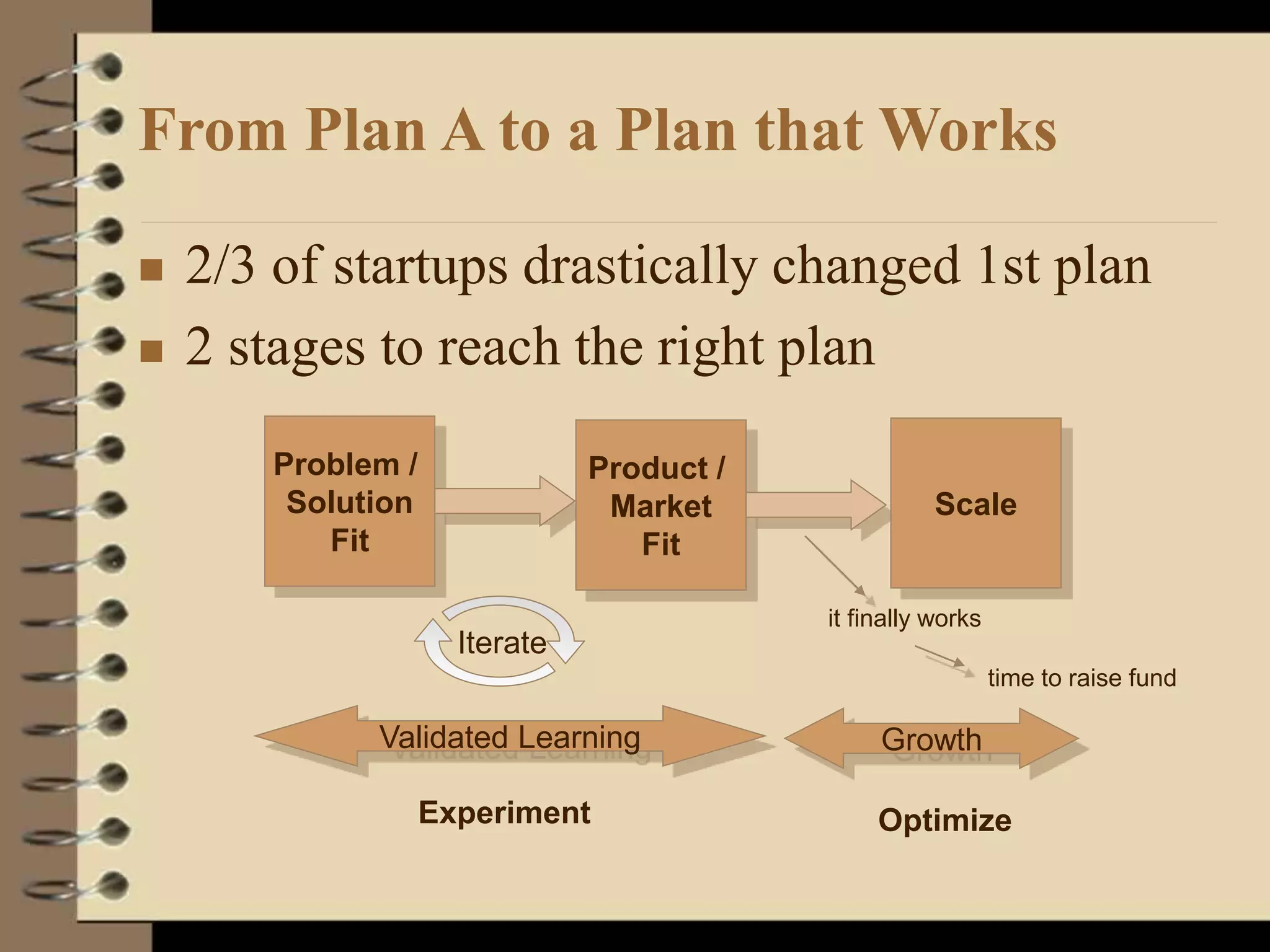
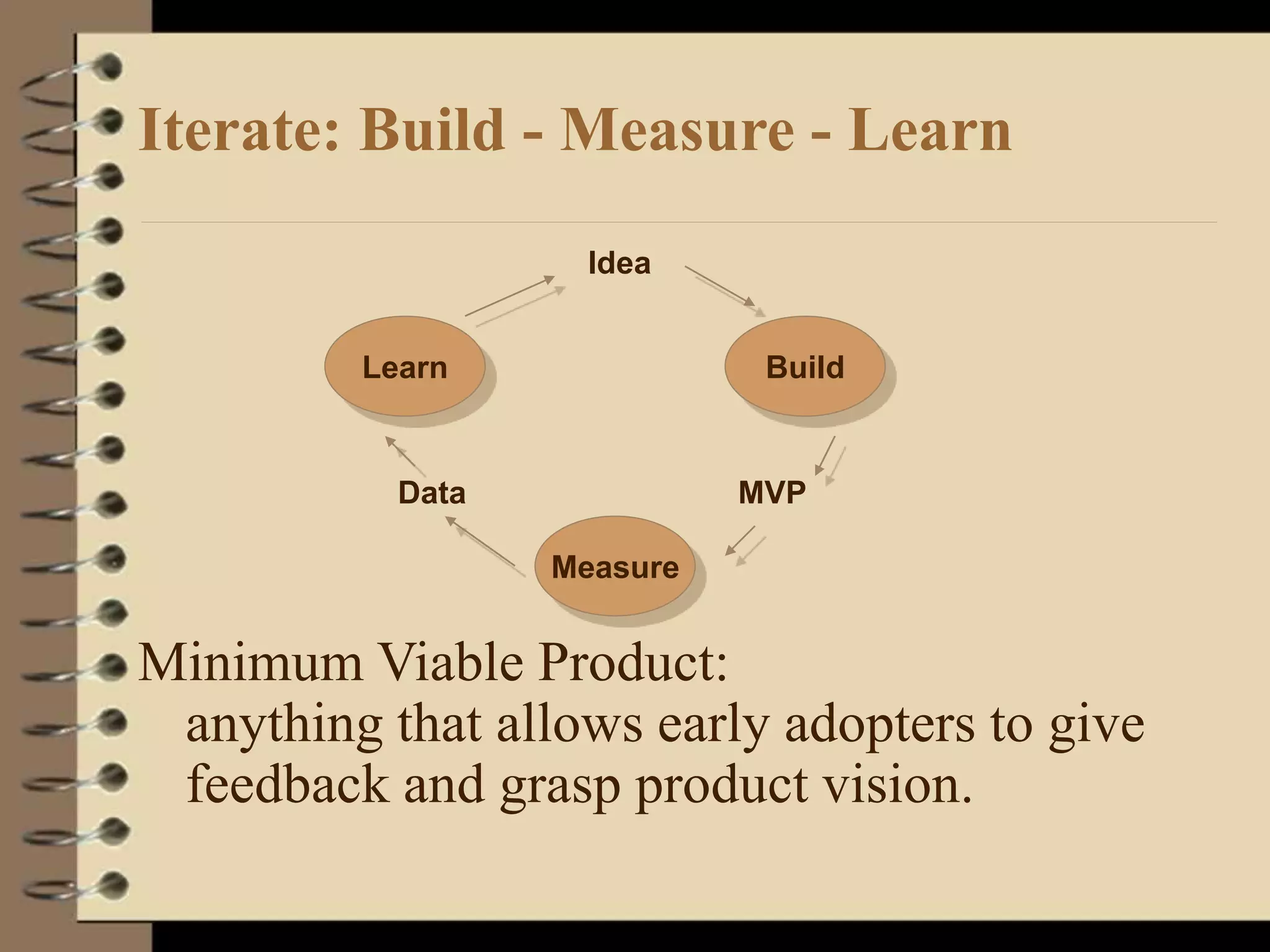
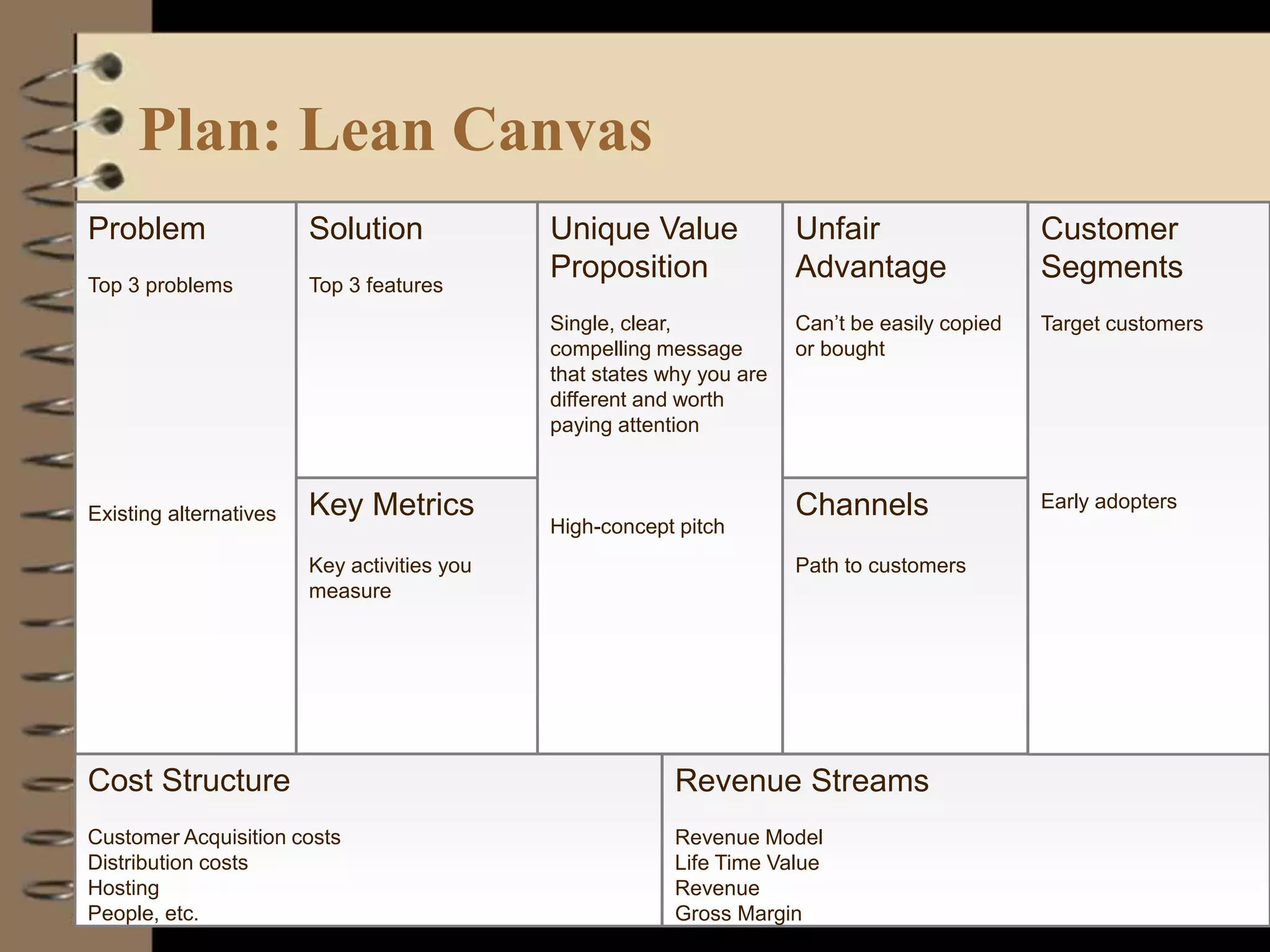
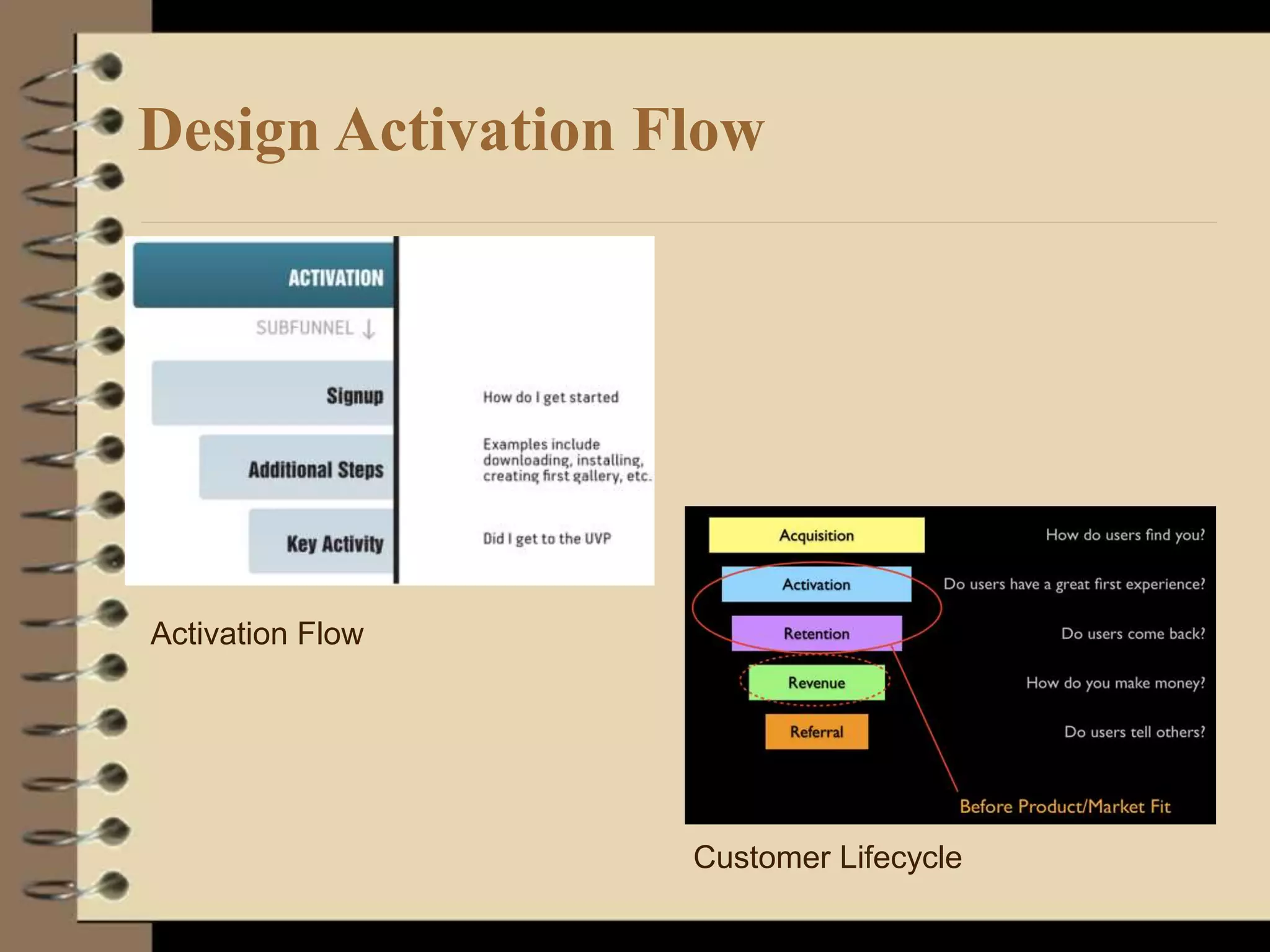
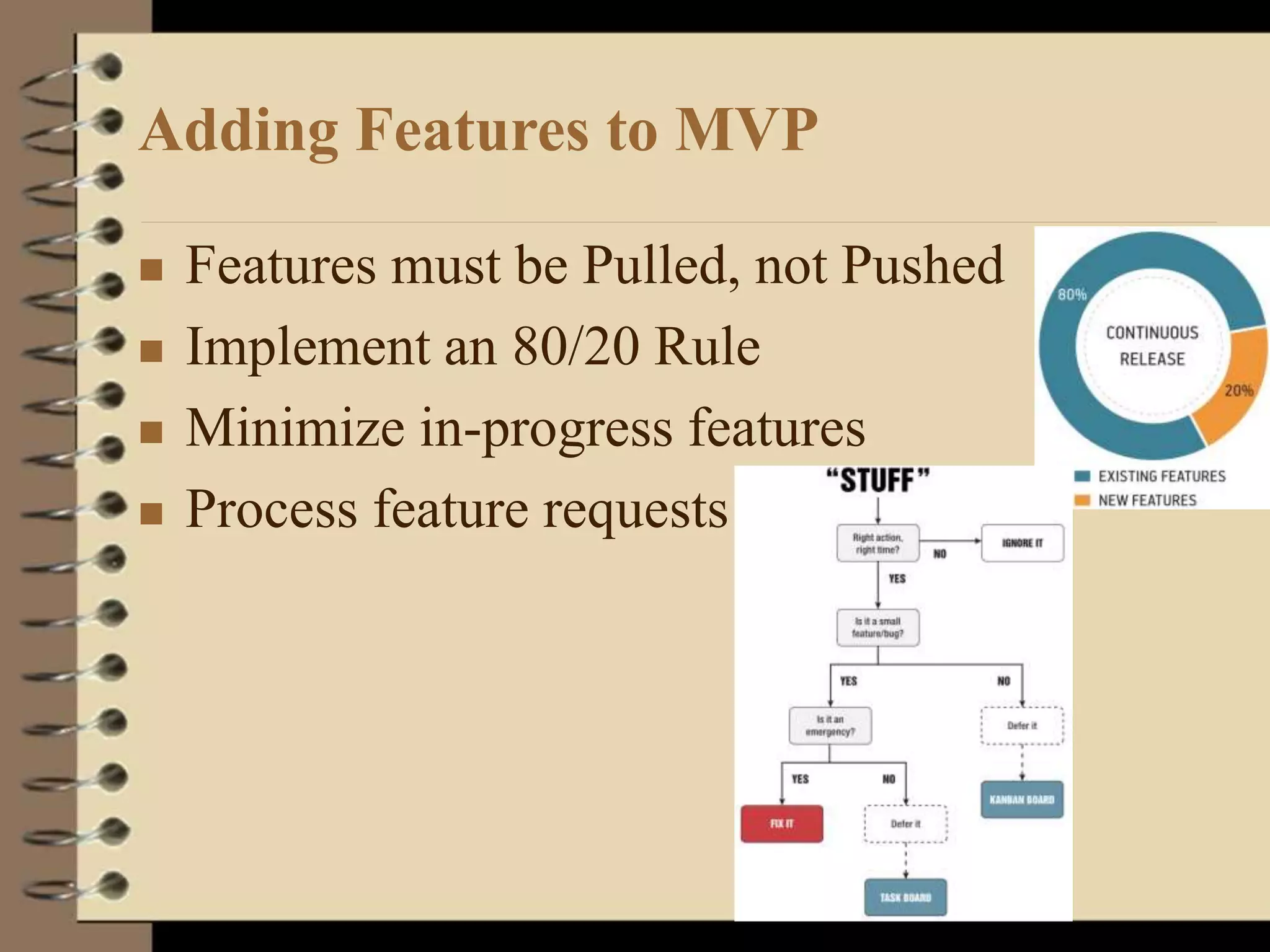
This document provides an introduction to running lean startups using agile and lean principles. It discusses how startups can fail if they don't get customer feedback through minimum viable products (MVPs). The key is to iteratively build, measure, and learn from customers to reduce risks. Startups should conduct customer interviews to understand problems and validate solutions before building MVPs. They should then measure metrics to determine which features to add or whether to pivot the product based on what customers say, not what founders think customers want. The overall goal is to accelerate sustainable growth through sticky, viral, or paid customer acquisition.