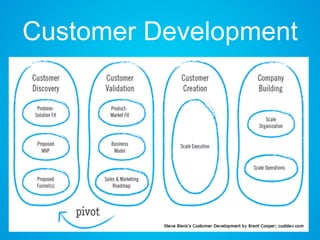
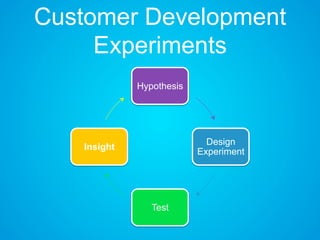
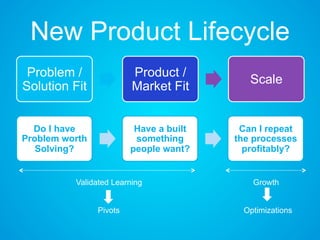
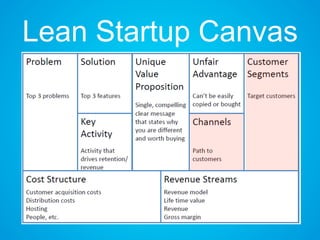
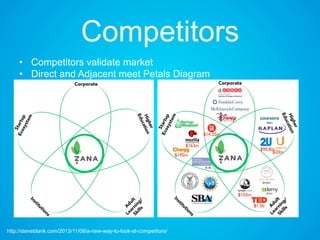
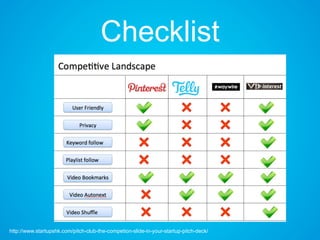
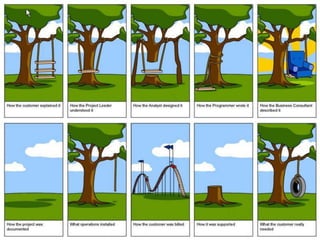
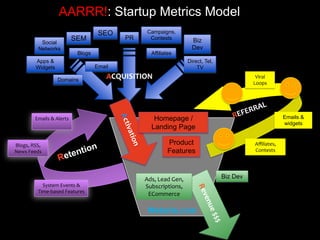
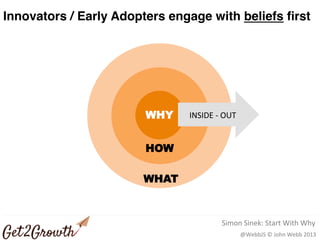
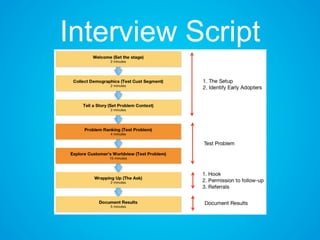
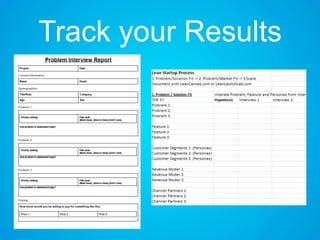
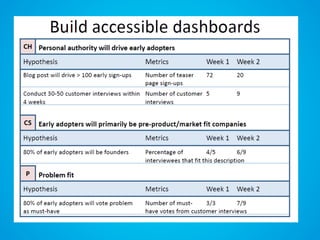
The document discusses the importance of research and customer development in validating business ideas and key assumptions. It emphasizes the roles of market choice, competition, and startup metrics in achieving success, alongside tactics for effective customer engagement and testing hypotheses. Key insights from prominent figures in the startup ecosystem, such as Marc Andreessen and Simon Sinek, are incorporated to illustrate foundational principles of the lean startup methodology.