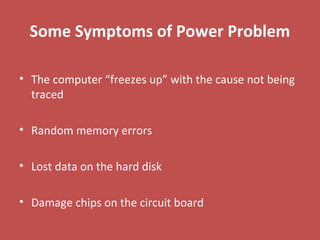
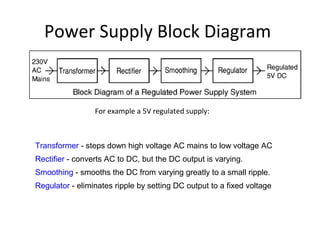
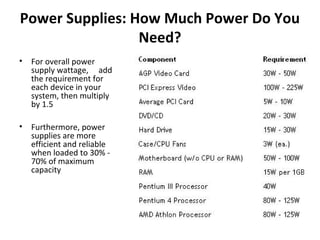
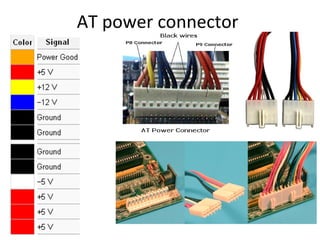
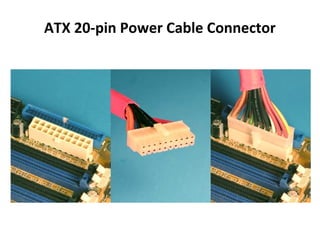
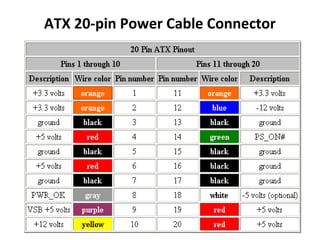
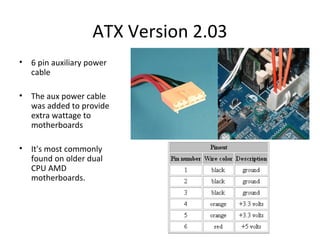
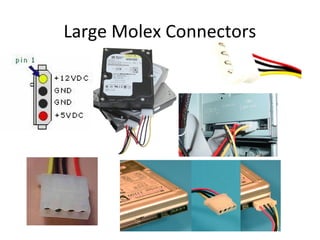
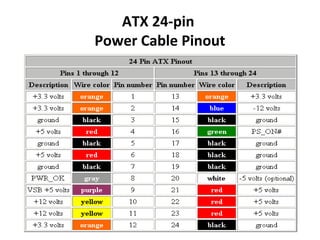
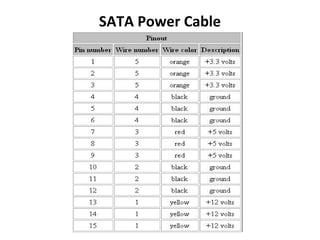
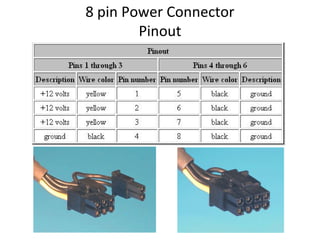
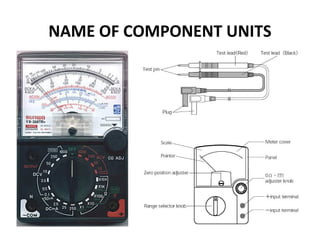
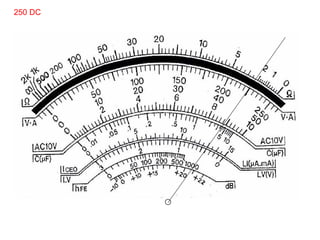
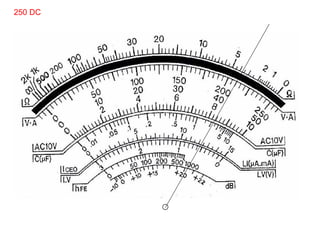
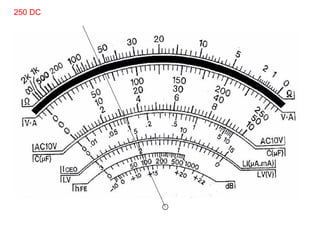
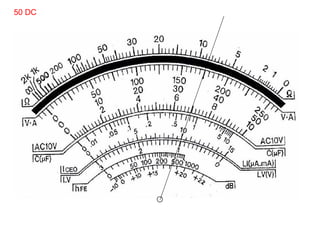
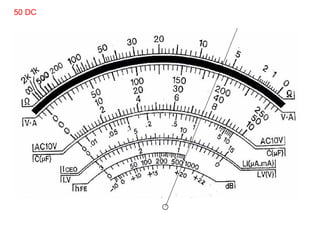
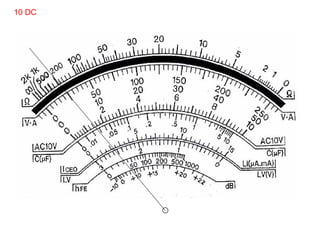
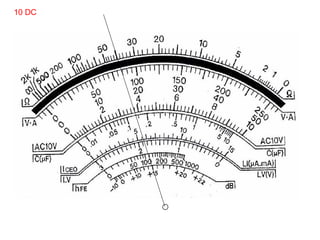
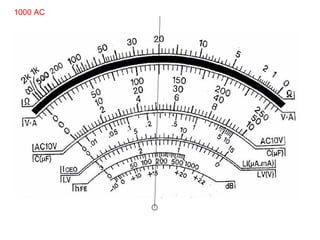
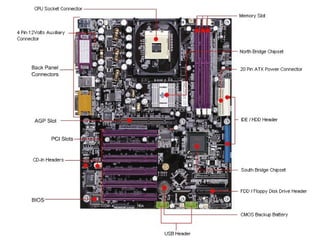
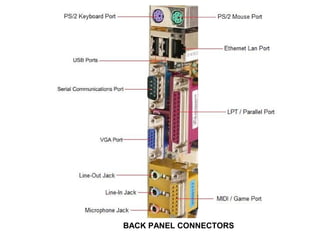
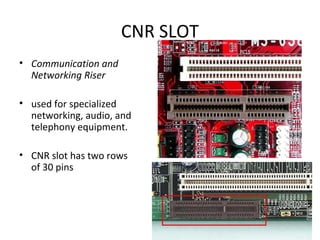
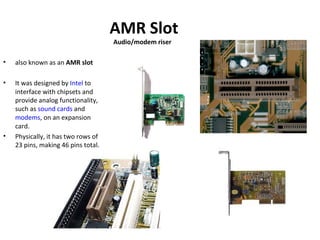
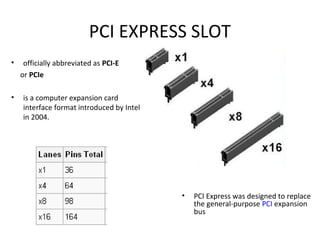
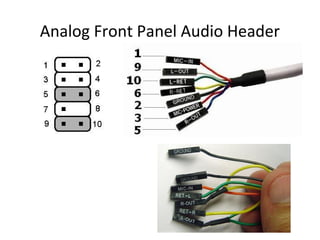
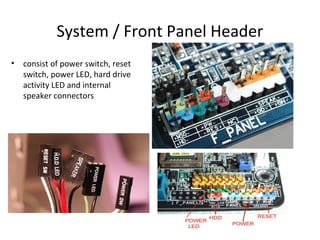
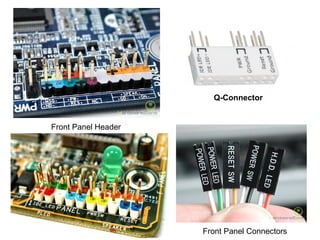
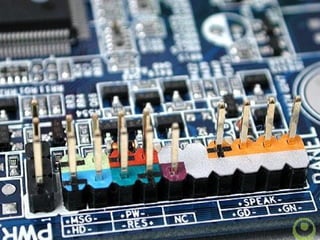
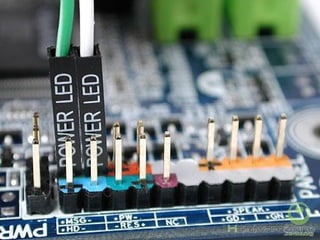
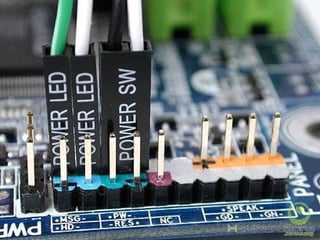
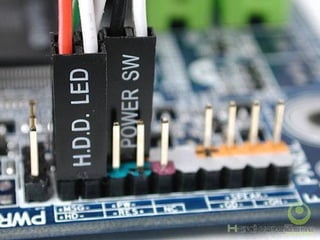
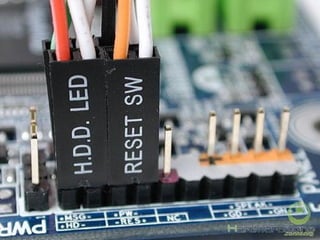
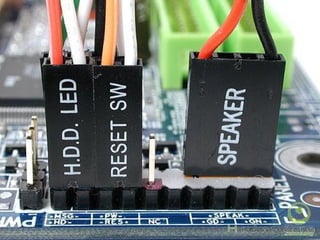
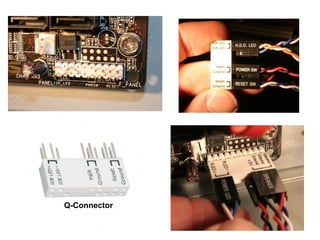
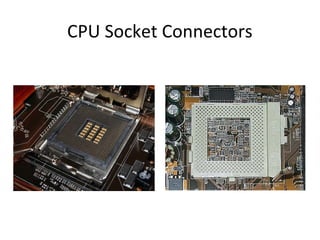
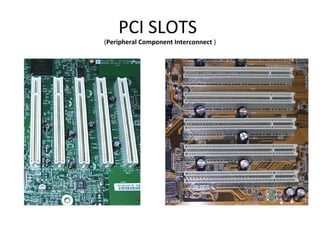
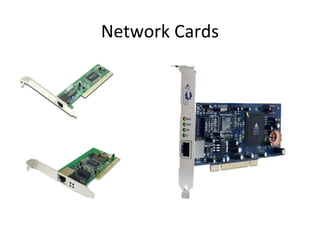
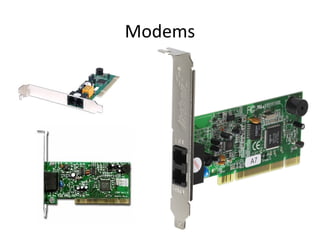
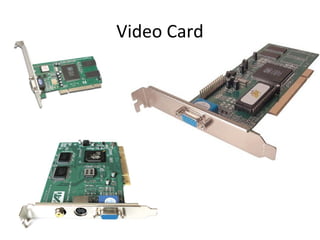
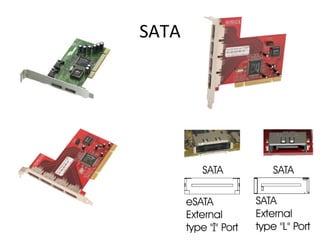
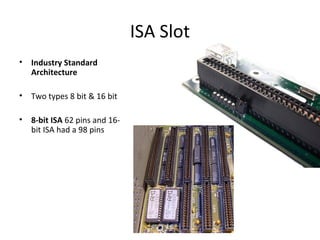
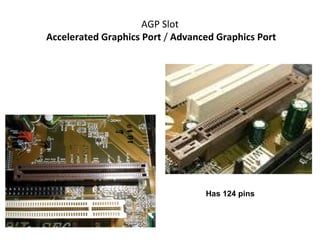
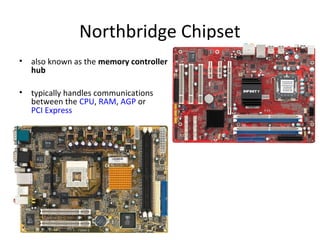
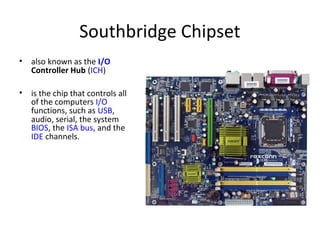
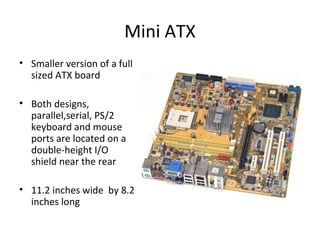
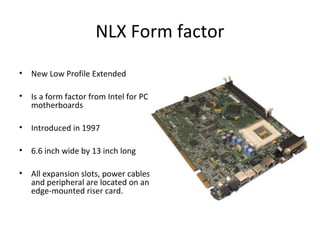
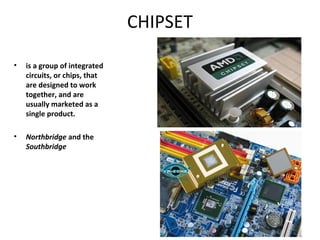
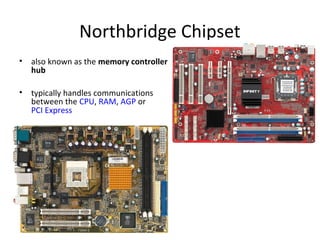
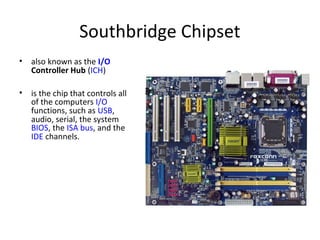
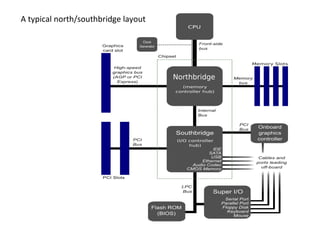
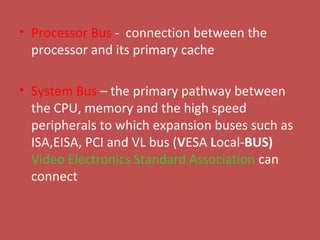
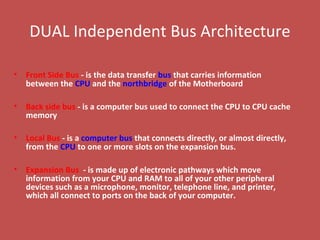
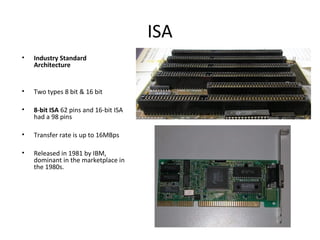
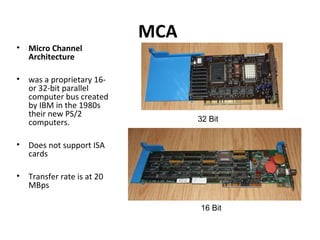
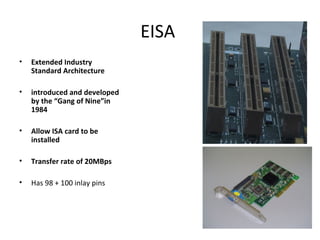
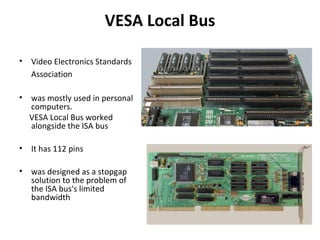
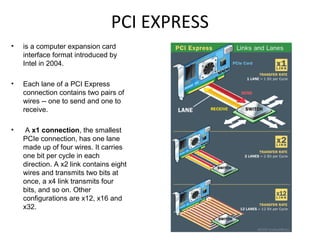
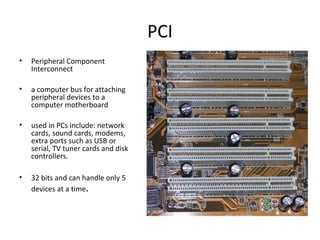
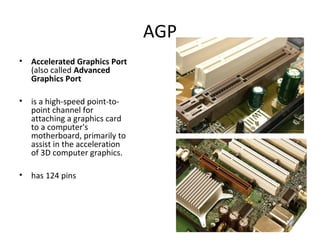
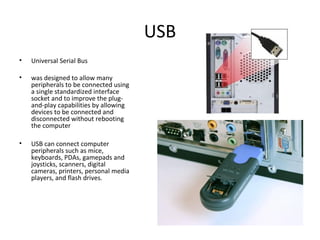
The document provides information about various components related to computer power and protection. It discusses automatic voltage regulators that monitor and regulate power supply, and uninterruptible power supplies that provide backup power during outages. It also covers symptoms of power problems, steps for power protection, power supply components and diagrams, and types of power connectors and supplies. Power needs are discussed in relation to system components.