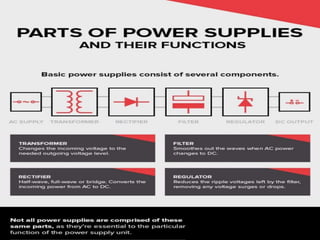
A power supply converts electric current from an energy source to the correct voltage and frequency required to power electrical devices like computers and electronics. It performs key functions like changing voltage levels to match the load's requirements in order to prevent overloading and damage. Power supplies are also needed to regulate output and filter fluctuations to provide steady power for sensitive devices. They come in different types depending on the input and output power needs.