This document defines and provides examples of various modeling techniques used in systems analysis and design:
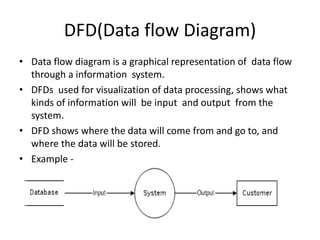
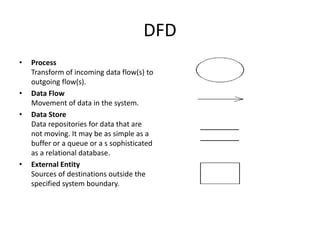
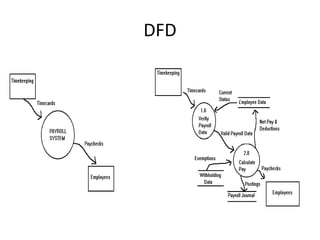
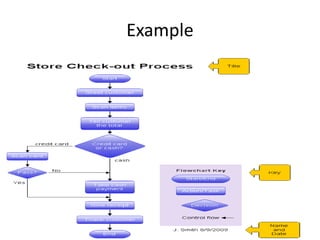
1) Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) visually represent the flow of data through a system and its processes, data stores, external entities, and levels of abstraction.
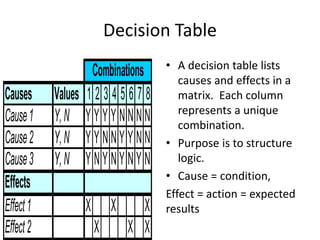
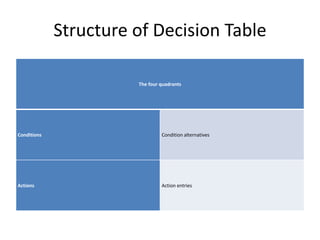
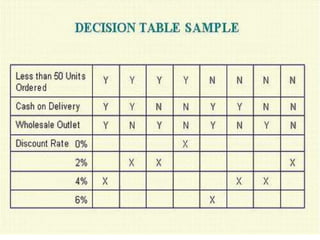
2) Decision tables organize the conditions and expected outcomes of decision logic in a matrix format.
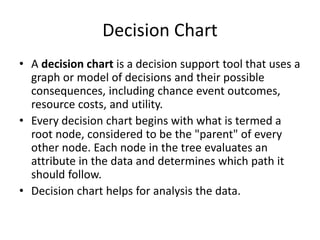
3) Decision charts use a tree structure to model decisions, consequences, probabilities, costs, and utilities.
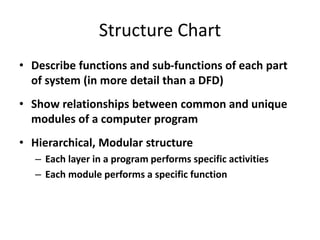
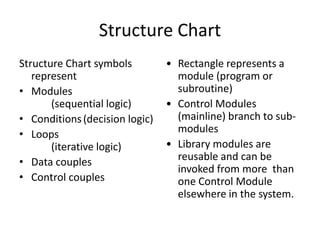
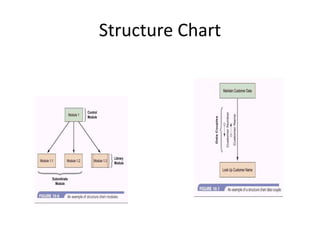
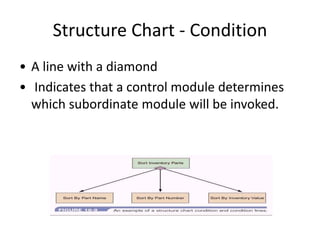
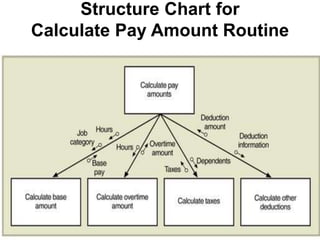
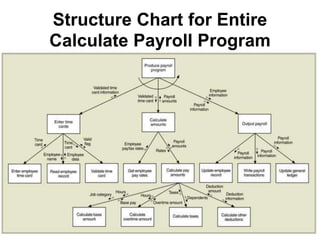
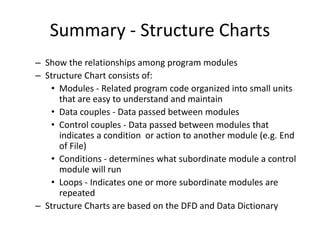
4) Structure charts describe the hierarchical modular structure and relationships between functions, subfunctions, modules, and control logic (conditions, loops, data coupling) within a system or computer program.