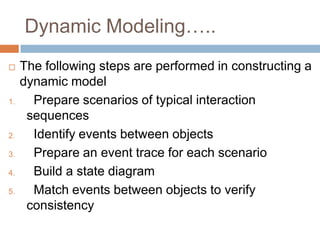
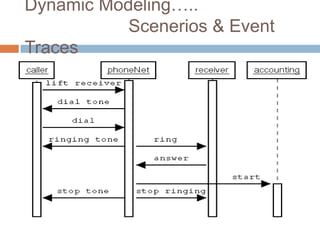
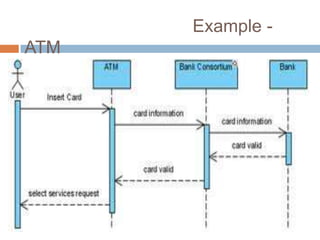
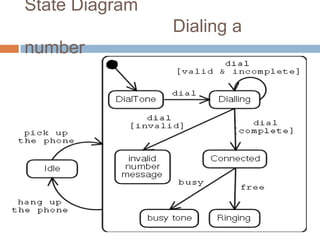
OMT uses three models - the object model, dynamic model, and functional model. The dynamic model represents the temporal, behavioral, and control aspects of a system using events, states, and state transitions. It shows how objects interact over time in response to events, and is represented through state diagrams that define the different states an object can be in and the events that trigger transitions between states.