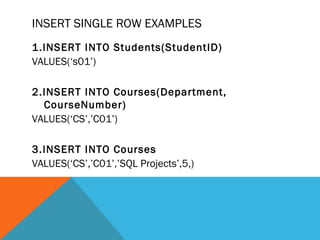
The document discusses the Data Manipulation Language (DML) in SQL. It describes the INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands. INSERT is used to add new rows, UPDATE changes existing rows by specifying conditions in a WHERE clause, and DELETE removes rows specified in a WHERE clause. Examples are provided for each command demonstrating how to insert single and multiple rows, update fields by condition, and delete rows based on conditions.



![DML COMMANDS
Insert- Insert is used to add a new row to a table
SYNTAX :
INSERT INTO tablename [(field list)] VALUES (value list)
Field list is optional
If field list is omitted, values expected for all columns (except IDENTITY)
INSERT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dmlslide-151216005536/85/database-slide-4-320.jpg)