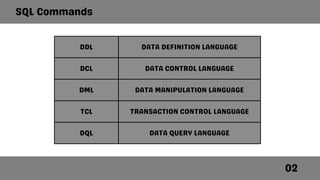
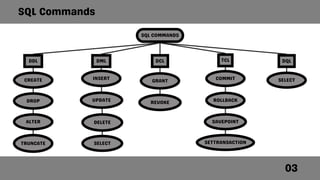
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a database language designed for managing data in relational database management systems and is the standard for database access and manipulation. It consists of various command categories including DDL (Data Definition Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language), and DQL (Data Query Language), each providing functionalities like creating, altering, and selecting data. Common commands include CREATE, ALTER, DROP, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, which allow users to define and manipulate database structures and records.









![12
DELETE
The DELETE statement is used to delete existing records in a
table.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE condition] ;
Example:
DELETE FROM Customers WHERE CustomerName='Yadu";
SQL Commands](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-240702051113-7b000a77/85/SQL-Basics-DDL-DML-DQL-Learn-The-BAsics-Of-SQL-pdf-12-320.jpg)
