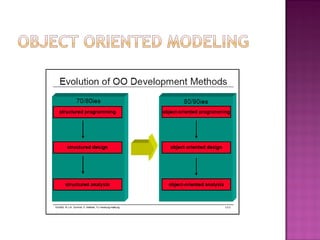
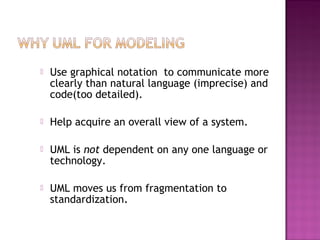
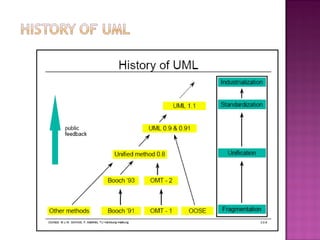
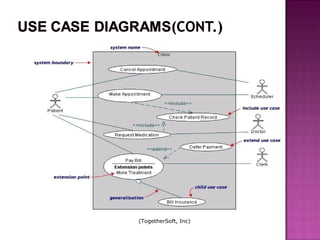
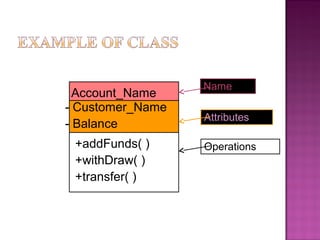
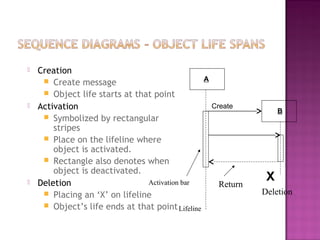
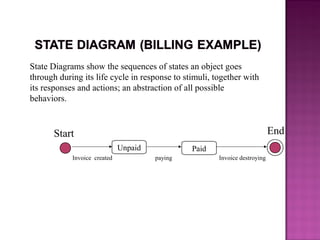
The document explains the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which is an industry-standard graphical language for modeling software systems used for requirements and specifications. It highlights the importance of UML in simplifying software design with various diagrams like use case, class, and sequence diagrams to communicate structure and behavior clearly. Additionally, it outlines key concepts such as visibility modifiers, relationships among classes, and the distinction between aggregation and composition in system modeling.