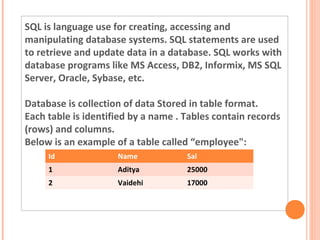
SQL is a language used to create, access, and manipulate databases. It allows users to define databases by creating tables with columns and rows, and then manipulate the data in those tables using commands like SELECT to query data, INSERT to add new rows, UPDATE to modify existing rows, and DELETE to remove rows. Common SQL commands fall into categories like DDL for data definition, DML for data manipulation, and TCL for transactions.








![SELECT STATMENT
Syntax
Select * or column1,column2..column n from table_name
[where condition];
Example
Select * from employee;
Select name from employee;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbysandeep-121127041250-phpapp02/85/Sqlbysandeep-11-320.jpg)
![INSERT STATMENT
Syntax
INSERT INTO table_name[(column1,column2,…)]
VALUES (value1, value2,....) ;
Example;
Insert into emp(id,name,salary)values(101,’Aditya’,100000);
Id Name Sal
1 Aditya 100000
2 Vaidehi 17000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbysandeep-121127041250-phpapp02/85/Sqlbysandeep-12-320.jpg)

![DELETE STATMENT
Syntax
DELETE FROM table_name
[WHERE column_name = some_value ]
Example:
delete from employee
where id=101;
Id Name Sal
102 Vaidehi 17000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbysandeep-121127041250-phpapp02/85/Sqlbysandeep-14-320.jpg)
