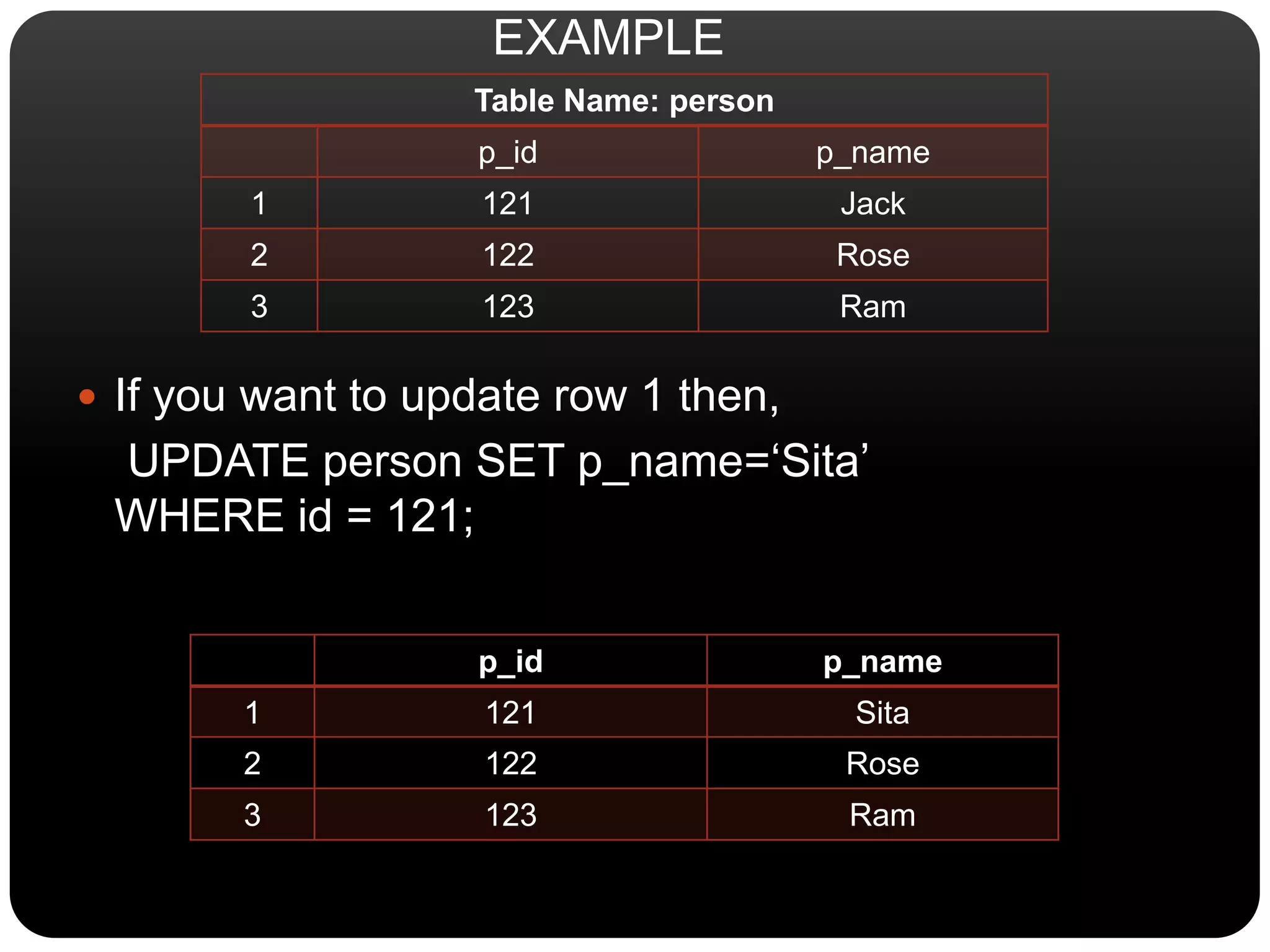
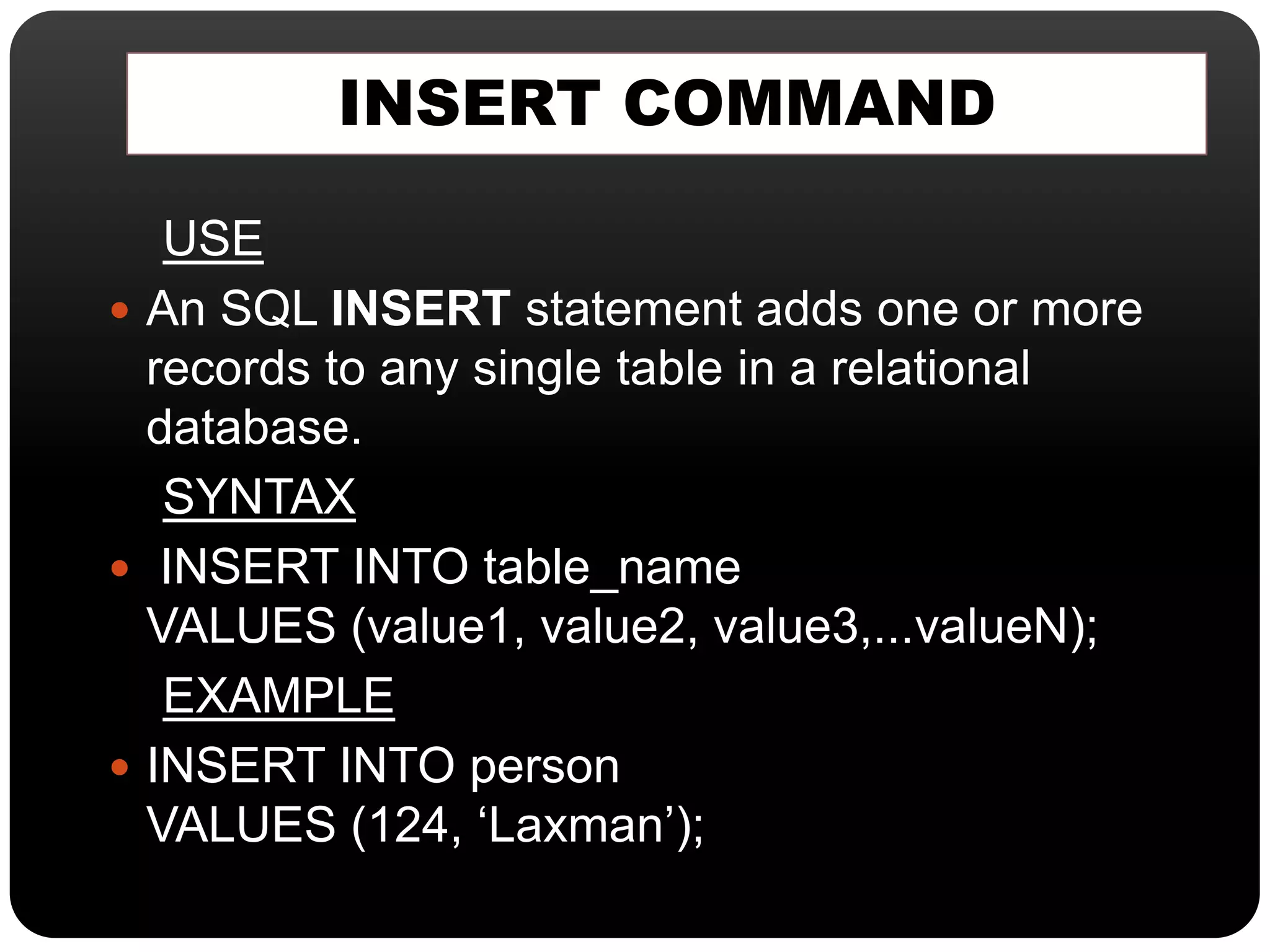
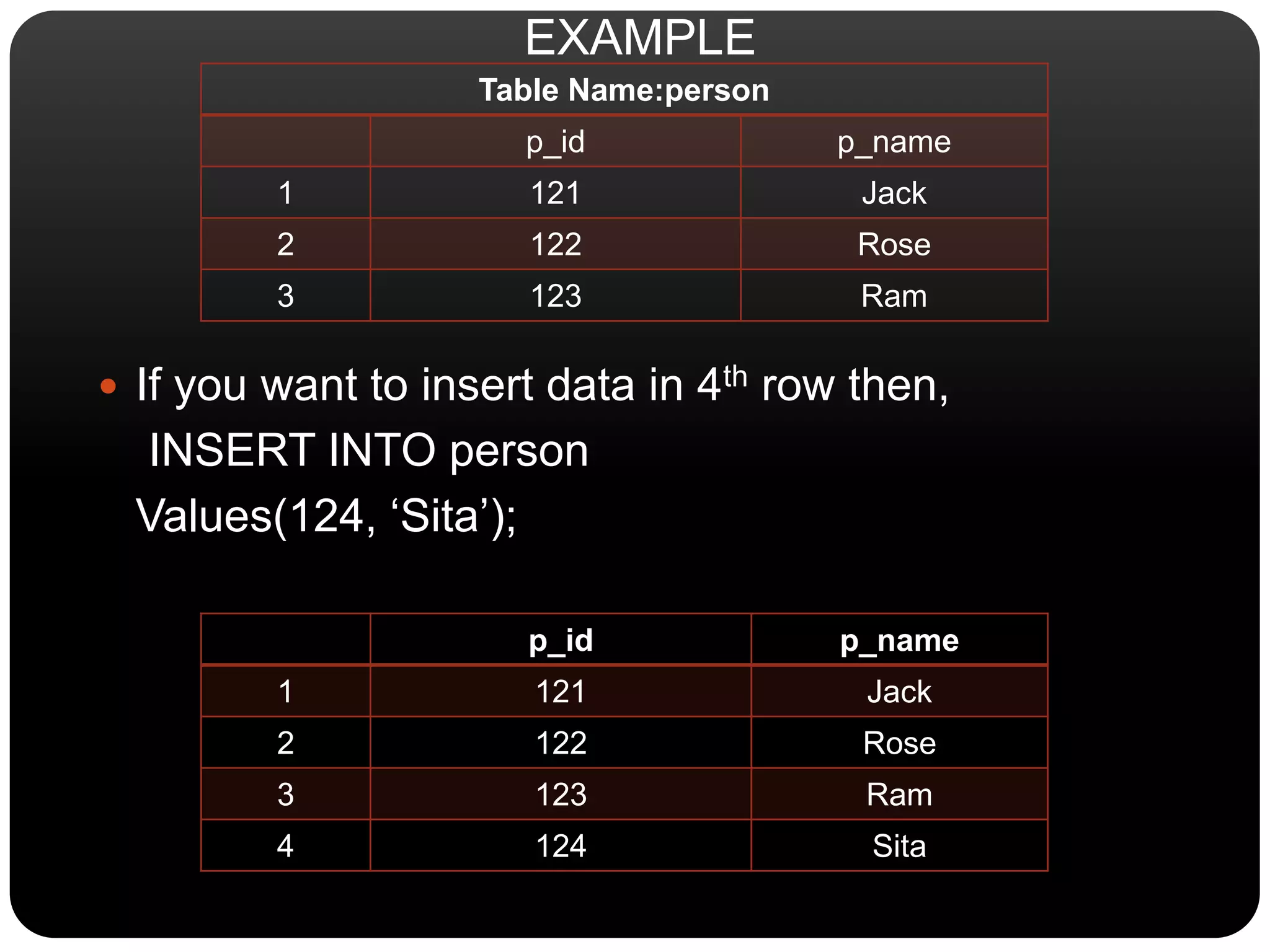
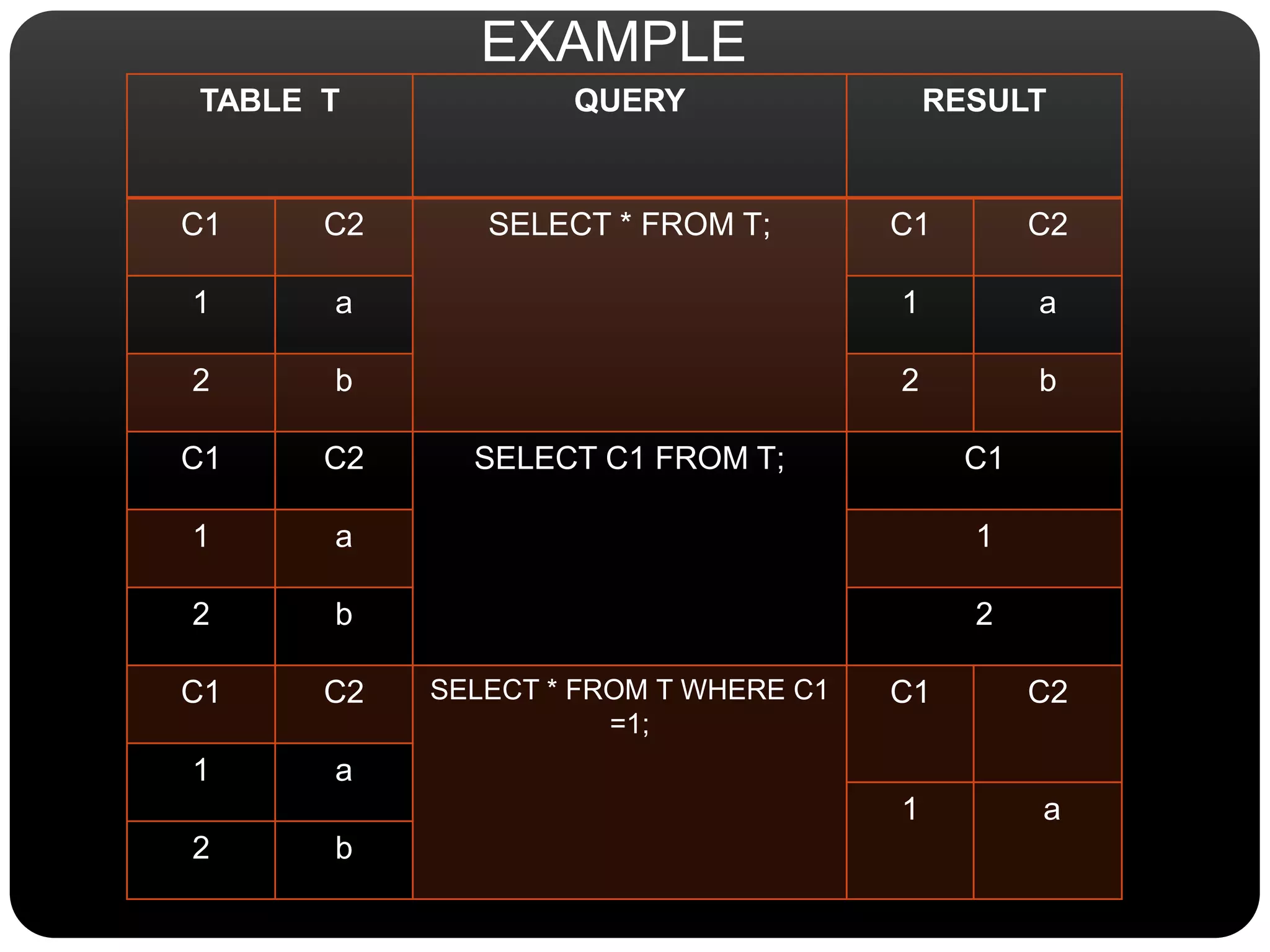
This document discusses SQL commands used for data manipulation. It describes four key SQL commands - SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. SELECT is used to view data from a table. INSERT adds new rows to a table. UPDATE modifies existing data in a table. DELETE removes rows from a table. Syntax and examples are provided for each command.





![SYNTAX
• DELETE * from table_name [WHERE CONDITION]
(if where condition is not used all rows in the table are
removed)
EXAMPLE
• DELETE from customer
WHERE CustomerName=‘Anil Khade’ AND
ContactName=‘Vikrant Kedare’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationaldatabasemanagementsystem-130818055920-phpapp01/75/Commands-of-DML-in-SQL-7-2048.jpg)

![UPDATE COMMAND
USE
An SQL UPDATE statement changes the data of
one or more records in a table.
Either all the rows can be updated, or a subset may
be chosen using a condition.
SYNTAX
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = valu
e [, column_name = value ...]
[WHERE condition]
EXAMPLE
UPDATE employee SET location ='Mysore'
WHERE id = 101;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationaldatabasemanagementsystem-130818055920-phpapp01/75/Commands-of-DML-in-SQL-9-2048.jpg)