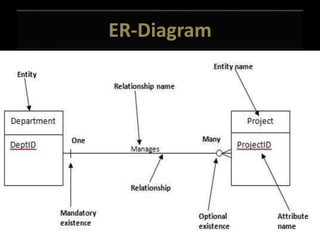
The document presents on database management systems. It defines a database as a collection of programs that stores and extracts information. It then gives examples of database applications and discusses the steps in database design such as requirements analysis and conceptual modeling. Several functions of database management systems are outlined including data storage, security, and transaction management. The roles and benefits of DBMS are also summarized.