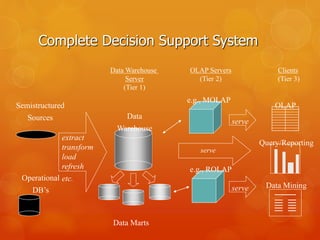
The document discusses data warehouses, defining them as integrated repositories that support management decision-making processes by providing organized, time-variant data. It outlines types of data warehouses, including enterprise data warehouses, operational data stores, and data marts, and highlights their applications, benefits, and challenges faced during implementation. In conclusion, an effective data warehousing strategy is crucial for generating accurate information guiding decision-making in response to evolving business environments.