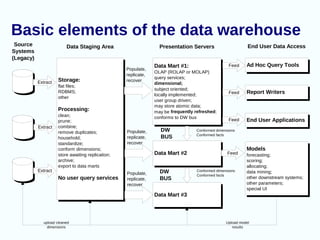
The document discusses data warehouses. It begins by defining a data warehouse as a subject oriented, integrated, time-variant, and non-volatile collection of data used to support management decision making. The goals of a data warehouse are to make an organization's information accessible, consistent, adaptive, resilient, and the foundation for decision making. The document then describes the basic elements and architecture of a data warehouse including data marts, OLAP, and how data is extracted, transformed, and loaded. It outlines benefits like increased productivity and competitive advantage as well as potential problems such as underestimating resources and high maintenance needs.